The following faults may occur in the brake system: ineffective braking (weak brake action); jamming the brake pads and the irregularity of them in its original position after the end of clicking on the brake pedal; uneven effect of the brakes of the right and left wheels of one axis; a leak brake fluid and air entering the hydraulic drive system; Exactness of the pneumatic drive system. The tightness of the joint of the hydraulic and pneumatic drive of the brakes is checked with an external inspection of the car. In the hydraulic drive of the place of tightness impairment, they are detected on the leakage of the brake fluid, in the pneumatic drive - on the hearing of the characteristic sound appearing during air leakage. To more accurately detect the location of the damage, the tested compound is coated with a soap emulsion and the appearance of soap bubbles determine the place of air leakage. The free move of the brake pedal in cars with hydraulic drive Regulated by changing the length of thrust connecting the brake pedal with the piston piston of the main brake cylinder. To this end, the GAZ-53-12 car establishes the pedal to the position at which it rests on the rubber buffer, release the lock nut and, rotating the coupling in one direction or the other, set the free move of the pedal 8 ... 14 mm. The gap between the primary piston and the pusher of the main brake cylinder must be in the limit of 1.5 ... 2.5 mm. If there is a pneumatic drive, this adjustment is reduced to a change in the length of the thrust connecting the brake pedal with the intermediate lever of the brake crane drive. The length of the thrust is changed by rotating the plug, screwed on the threaded end of the thrust. Brake chambers are checked for tightness when the compressed air is supplied. The soap emulsion is applied on the edge of the body flange near the tie bolts, the rod outlet holes from the chamber body and the pipeline fastening fitting to the camera. Filling with a compressed air chamber, follow the appearance of soap bubbles. As a rule, to eliminate air leakage, it is enough to pull out all the covering bolts to the camera body. If air leakage continues, then replaced the diaphragm. The pressure in the brake chambers is checked by a pressure gauge, which is connected to one of the chambers. Due to the operation of the compressor at idle the engine, the pressure in the pneumatic drive system increases to 0.7 MPa. The gaps between the pads and the brake drums in vehicles with a pneumatic drive are adjusted with the help of an adjustment worm located on the lever connecting the brake chamber rod with the slot fist shaft. The wheel is postponed and, turning the adjusting worm, the pads are brought to contact with the drum (the wheel is injected). After that, turning the worm in the opposite direction, weigh the pads from the drum before the start of the free rotation of the wheel. The diploma check the gap, which should be 0.2 ... 1.2 mm. After adjusting the gap, the stroke of the brake chamber stems is determined, which should be 20 ... 30 mm. Next check the free stroke of the brake pedal. Having finished brake mechanisms All wheels check the effect of brakes on the go. Braking wheels of one axis should begin at the same time and be uniform. After conducting several braking, check if the brake drums are heated. If the car is equipped with a pneumatic brake actuator, then the movement of the machine should be started when the pressure in the drive pneumatic system is below 0.5 MPa, and allow pressure reduction when moving below this value. At pressure below 0.5 MPa, the control lamp on the instrument panel lights up. With long-lasting descents, the engine cannot be turned off, so as not to spend the entire supply of air from the pneumatic cylinders. The handbrake must be adjusted in such a way as to eliminate the hide pads for the drum during the car movement. In the car ZIL-431410, the course of the manual brake lever is regulated by changing the length of the thrust connecting the brake drive lever with the adjusting lever. For this, the plug is exposed to which the thrust is connected to the lever. For proper adjustment The hand brake drive lever should be pulled out with an effort of one hand no more than four or five teeth of the rail fixing its position.
Diagnostics - determination of the technical condition of the car and its systems without disassembly and using specialized equipment. The main and primary task of car diagnostics is the identification of a possible malfunction in the car even before it declares itself.
Of course, diagnostic operations are manufactured in order to detect a malfunction and all possible methods Avoid costly auto repair, and thereby extending its resource, ensure reliable durable work and material and moral calm of the owner of the car, which is also important.
Of course, for each car owner, the main appearance will be the appearance of his iron friend, and, no matter how strange it sounds, but they meet that way! Always I want to see the car with clean and sparkling paint, as if just from the factory conveyor.
In second place, the reliability of the car is unquestionably - its ability to confidently and qualitatively carry out its primary transport work. Here, of course, a lot of attention is paid to the engine with its systems, as well as the diagnostics of the machine system, which is directly responsible for safety road.
One of these systems and perhaps the most important is the braking system of the car. It is intended to be able to reduce its speed, stop and retaining in a fixed state during parking. Let's figure it out in detail what you need to pay attention to the diagnosis. brake systems And what to check directly there.
- First of all, when diagnosing the brake system, the car conducts its visual inspection: the absence of leakage of the working brake fluid, its level and purity (determined by color and smell). IN modern cars With the anti-lock brake system, the working brake fluids of the DOT-5 standard are applied, remember it!
- Check the operation of the brake system directly in action by the method of running tests (drove on the car and feel how the brakes work) or on special stands, where the movement of the car is simulated. Also, I would like to note that in braking systems, it is forbidden to use nodes and details that do not match the brand of your car. It is important enough!
- Check the state of the brake pads and disks, determine their degree of wear and the remaining resource, diagnose the operation of the anti-lock brake system, the system of the car stability system, well, of course if such systems are available on the car!
- Carry out the parking brake system and, if necessary, it is adjusted, by tightening the cable of the so-called handbrake or laying the brake pads.
I would like to note that the braking system of the car is responsible directly for the safety of the road. It should work effectively and without any complaints, so in the diagnosis of the technical condition of this system it is necessary to pay great attention with each maintenance !!! Successful movement!
Uninterrupted operation of the brake system does not rise due to braking in front of the traffic light, large gaps, road coat and national signs of managing the machine.
The brake system, which includes including front brake mechanismconstantly experiencing serious loads. This increases the likelihood of an accident, because parts and internal mechanisms, such as rear brake mechanismfocus faster. Therefore, it becomes necessary to conduct such a procedure as diagnosis.
Diagnostics of the brake system: before and now. How held.
Most recently, many experts recommended such a thing as diagnostics of the brake system,every five thousand kilometers of the car. Now the indicator has become much smaller. After all, the brake system is necessarily checked by experts when passing inspection. Twice a year - the minimum number of times, according to experts, when such a diagnosis should be carried out.
The diagnosis of the brake system includes verification:
- Brake shoes
- Disc and drums
- Hub bear
- Brake fluid
- Brake hoses
- Caliper
- Workers cylinders
- Brake amplifier and main cylinder
Brake System Diagnostics: Methods and Methods
There are two basic methods that are conducted by checking the brake system in any car. This is a test on the stand and a road test.
Road Test
The road test itself is speaking any transport on transport. Even newcomers can feel when, when braking without pressure on the steering wheel, the car deviates to the side. There should be no screenshots and extra noises, failure brake pedals to the floor, improving the brake path and vibration. This all testifies to those present. brake system malfunctions.
Bench test
In the field, it is almost impossible to conduct high-quality diagnostics. It turns out only the minimum information about existing problems in the car. There are many factors that may affect the result of inspections carried out on road conditions. But when carrying out bench tests, it is possible to obtain more accurate information. All data obtained must be recorded on any media.
Using special programs on the computer, the information received information is processed. Thus, it can be understood in which really states are the brakes.
Stands for testing may relate to several types. Stands for static tests, platform and inertial, roller and power are the main types. The ovality of brake drums, the time of operation of the system, the total specific braking force is just some of the characteristics whose indicators can be found on the stand.

Effort on brake pedal, pressure in the brake system - there is an excellent opportunity to measure these indicators by contacting modern service centers. Sensors and appliances in service specialists fully allow relevant research. The human factor practically does not affect the tests that are conducted on the stand. This is definitely a big advantage of such checks.
The brakes in the car system will be reliably function only if a person is ready to spend time on what to perform checks in time, consistent with the recommendations from specialists. Of course, poster checks are more expensive, but it is never worth saving on your own security. The stand for static tests allows drivers to independently check their machines. But in any case, we repeat once again that the safety of drivers and passengers is better not to save. Only professional check will allow you to completely be confident in your car.
The repair of the brake system is necessary on all vehicles, however, it is necessary to diagnose the technical condition of the brake system every several thousand kilometers, this is necessary to reduce the likelihood of a car brake failure.
Share work on social networks
If this job does not come up at the bottom of the page there is a list of similar works. You can also use the Search button.
Page \\ * MergeFormat 28
P.
|
Introduction .................................................................................................... |
|
|
1.1. Principle of operation of the brake system .................................... |
|
|
1.2. Types of brake systems ...................................................... |
|
|
1.3. The main elements of the brake system of the car ................... |
|
|
2. Methods and equipment for diagnosing brake systems |
|
|
2.1. The main malfunctions of the brake system .............................. |
|
|
2.2. Requirements for brake systems ....................................... ... |
|
|
2.3. Methods and equipment for diagnosing brake systems ...... |
|
|
3.1. Choosing diagnostic equipment ................................. ... |
|
|
3.2. Technical characteristics of the selected equipment ............ ... |
|
|
Conclusion ……………………………………………………………. |
|
|
…………………... |
Introduction
The number of cars is becoming more and more, their number increases worldwide, every year. And with the number of cars, the number of accidents increases, due to which a larger number of people die and still remain disabled and cripples. Inappropriate technical condition and maintenance of cars, is one of the main causes of many accidents. Accidents arising from the failure of the various car systems carry the most serious consequences.
Relevance of the topic The course work lies in the fact that the most important system responsible for the safety of the car is the brake system. Car design is constantly being improved, but the presence of a brake system remains unchanged, which contributes to stopping the car if necessary, which retains the lives of pedestrians, drivers and passengers, as well as other road participants. The repair of the brake system is necessary on all vehicles, however, it is necessary to diagnose the technical condition of the brake system every several thousand kilometers, this is necessary to reduce the likelihood of a car brake failure.
The goal of the course work - Improving the efficiency of diagnosing the car braking system, by developing recommendations on the selection of diagnostic equipment of brake systems and.
To do this, it is necessary to solve the followingtasks :
- perform an analysis of the brake system of cars;
- explore the methods of diagnosing the brake system;
- examine the equipment used in the diagnosis of brake systems.
Object research is the technology of diagnosing a braking systeme We are cars.
Subject of study represents the means and methods of diagnosisabout streaming the brake system of the car.
Research methodsUsed in this work are methods of generalization, comparisons, analysis and analogies.
Structure of coursework consists of introduction, three chapters, sbut kesty and list of 10 sources used.
1. Brake system device
1.1. Principle of car brake system
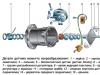
Easy to understand in the example hydraulic system. When pressed on the brake pedal, the pressure force on the brake pedal is transmitted to the main brake cylinder (Fig. 1.1).
This node converts an effort that is applied to the brake pedal, into the pressure in the hydraulic brake system, to slow down and stop the car.
Fig. 1.1. The main cylinder device
Today, to increase the reliability of the brake system, two-section main cylinders are installed on all cars, which share the brake system into two contours. The two-section cylinder braking can ensure the performance of the brake system, even if one of the contours is deployed.
If there is a vacuum amplifier in the car, then the main brake cylinder is attached over the cylinder itself or is there in another place where the brake fluid is locatedwhich connects to the sections of the main brake cylinder through flexible tubes. The tank is necessary to control and replenish the brake fluid in the system, if necessary. On the walls of the tank is available to view the level of fluid. And also, a sensor is mounted in the tank, which follows the level of the brake fluid.
Fig. 1.2. Scheme of the main brake cylinder:
1 - rod of vacuum brake amplifier; 2 - retaining ring; 3 - byproof opening of the first circuit; 4 - compensatory opening of the first circuit; 5 - the first tank section; 6 - the second tank; 7 - bypasic opening of the second contour; 8 - compensation opening of the second contour; 9 - Return spring of the second piston; 10 - the main cylinder case; 11 - cuff; 12 - second piston; 13 - cuff; 14 - Return spring of the first piston; 15 - cuff; 16 - external cuff; 17 - boot; 18 - first piston.
In the housing of the main brake cylinder there are 2 pistons with two return springs and with sealing rubber cuffs. Piston, with the help of brake fluid, create pressure in the working circuits of the system. Then, return springs return the piston to its original position.
Some cars are equipped with a sensor, on the main brake cylinder, which controls the pressure drop in the contours. If not a tightness occurs, it warns the driver in a timely manner.
About the work of the main brake cylinder:
1. When pressing the brake pedal, the rod of the vacuum amplifier leads to movement 1st piston (Fig. 1.3.)
Fig. 1.3. The work of the main brake cylinder
2. The compensation opening is closed, moving through the cylinder by the piston and the pressure is created, which acts on the 1st outline and moves the 2nd piston of the next circuit. Also moving forward the 2nd piston in its circuit closes the compensation hole and also creates pressure in the 2nd circuit system.
3. The pressure generated in the contours provides the operation of working brake cylinders. And the emptiness that was formed when the pistons movement is immediately filled with a brake fluid through special bypass holes, thereby preventing entering the system, unnecessary air.
4. At the end of braking, pistons due to the action of return springs, returned to its original position. At the same time, compensation holes receive messages with a tank and due to this pressure levels with atmospheric. And at this time, the wheels of the car are stamped.
The piston in the main brake cylinder, in turn, which begins to move and thereby increases the pressure in the system of hydraulic tubes leading to all the wheels of the car. Brake fluid under high pressure, on all wheels of the car, having an effect on the piston of the wheel braking mechanism.
And which, already in turn, moves the brake pads and those pressed against the brake disc or brake drum of the car. The rotation of the wheels is slow down and the car stops due to the friction force.
After we release the brake pedal, the return spring returns the brake pedal to its original position. The effort that acts on the piston in the main drum also weakens, then its piston, also returns to his place, forcing the brake pads with friction linings on them, thereby freeing the drum wheels or discs.
There is also a vacuum brake amplifier used in brake systems of cars. Its use, significantly facilitates all the operation of the brake system of the car.
1.2. Types of brake systems
Brake system is needed for slowing down vehicle And the full stop of the car, as well as its retention on the spot.
To do this, the car uses some brake system, as is the parking, working, auxiliary system and spare.
Working brake system Used constantly, at any speed, to slow down and stop the car. The working brake system is activated by pressing the brake pedal. She is self effective system Of all others.
Spare brake system Used when the main fault. It happens in the form of an autonomous system or its function performs part of a working working brake system.
Parking brake system Need to hold the car in one place. The parking system I use to avoid spontaneous movement of the car.
Auxiliary brake system Applied on a car with an increased mass. The auxiliary system is used to brake on the slopes and descents. It does not rarely, it happens that on cars the role of the auxiliary system is played by the engine, where the exhaust pipe overlaps the flap.
The brake system is the most important integral part of the car, serving to ensure active security Drivers and pedestrians. On many cars used various devices and systems that increase the efficiency of the braking system - this is an anti-lock system (ABS ), amplifier emergency braking (Bas. ), brake amplifier.
1.3. The main elements of the car brake system
The brake system of the car consists of a brake drive and brake mechanism.
Fig.1.3. Brake hydraulic diagram:
1 - Contour Pipeline "Left Front-Right Rear Brake"; 2-signal device; 3 - Contour Pipeline "Right Front - Left Rear Brake"; 4 - the main cylinder tank; 5 is the main cylinder of hydraulic brakes; 6 - vacuum amplifier; 7 - brake pedal; 8 - rear brake pressure regulator; 9 - parking brake cable; 10 - brake mechanism rear wheel; 11 - the adjusting tip of the parking brake; 12 - parking brake drive lever; 13 - Brake mechanism of the front wheel.
Brake mechanism The rotations of the vehicle wheels are blocked and, as a result, the brake force appears, which causes the car stop. Brake mechanisms are on the front and rear wheels car.
Simply put, all brake mechanisms can be called well. And already in turn, they can be separated by friction - drum and disc. The braking mechanism of the main system is mounted in the wheel, and the mechanism of the parking system is located behind a handout or transmission.
Brake mechanisms usually consist of two parts, from fixed and rotating. The fixed part is the brake pads, and the rotating part of the drum mechanism is the brake drum.
Drum brake mechanisms(Fig. 1.4.) Most often stand on the rear wheels of the car. During operation due to wear, the gap between the shoe and the drum increases and mechanical regulators use to eliminate it.
Fig. 1.4. Drum Brake Rear Wheel Mechanism:
1 - cup; 2 - clamping spring; 3 - drive lever; 4 - brake shoe; 5 - upper blast spring; 6 - spacer plank; 7 - adjusting wedge; 8 - wheel brake cylinder; 9 - brake shield; 10 - bolt; 11 - rod; 12 - eccentric; 13 - Purpose Spring; 14 - lower chamber spring; 15 - clamping spring space plank.
On cars can use various combinations of brake mechanisms:
- two drum rear, two disk front;
- four drums;
- four disk.
In the brake disk mechanism(Fig. 1.5.) - The disk rotates, and inside the caliper is installed, two fixed blocks. In the caliper, workers cylinders are installed, when braking, they press brake pads to the disk, and the caliper itself is securely fixed on the bracket. To increase the heat removal from the working area, ventilated discs are often used.
Fig. 1.5. Disc brake diagram:
1 - wheel heap; 2 - guide finger; 3 - viewing hole; 4 - caliper; 5 - valve; 6 - work cylinder; 7 - brake hose; 8 - brake shoe; 9 - ventilation hole; 10 - brake disc; 11 - wheel hub; 12 - Miscoring cap.
2. Methods and equipment for the diagnosis of brake systems
2.1. Basic brake system malfunctions
The brake system requires itself close attention, because It is forbidden to operate a car, with a faulty brake system. This chapter discusses the main malfunctions of the brake system, their causes and ways to eliminate them.
Enlarged brake pedal work. It occurs due to lack, or leakage of brake fluid from working cylinders. It should be replaced by working cylinders, rinse the pads, discs, drums and add brake fluid if necessary. And also this contributes to the hit in the brake system, in this case, it is simply necessary to remove it by pumping the system.
Insufficient braking efficiency. Insufficient brake efficiency occurs during grinding or wear of the brake pads, it is also possible to join the pistons in working cylinders, overheating brake mechanisms, depressurization of one of the contours, the use of low-quality pads, violation in operationABS, etc.
Incomplete disbuilt wheels of the car.This problem occurs when the brake pedal does not have a free move, you just need to adjust the position of the pedal. The problem may also be in the most important cylinder, due to the encounter of the pistons. There may be increased protrusion of a vacuum amplifier rod, or rubber seals, just swelling, due to gasoline or oil, then in this case it is necessary to replace all rubber parts, as well as rinse and pump the entire hydraulic system.
Turning one of the wheels when the pedal is released.Most likely weakened the brass spring of the rear wheel pads, or due to corrosion, or simply contaminants - the piston in the wheel cylinder, then it is necessary to replace the working cylinder. It is also possible to disturb the position of the caliper relative to the front wheel brake disc, when weakening the fastening bolts. There may still be a violation in the workABS , swelling of the sealing rings of the wheel cylinder, incorrect adjustment of the parking system, etc.
Driva, or deviation from straight movement when braking.If the car, moving along a flat and dry road, during braking began to be rejected in any direction, then this can be promoting the piston of the main cylinder, clogging the tubes due to clogging, pollution or combustion of brake mechanisms, different pressure in wheels, and may not be It works one of the brake system circuits.
Increased effort on brake pedals when braking. If it is necessary to attach a lot of effort to stop the car, then the vacuum amplifier is most likely faulty, but also the hose is also damaged, which connects the engine inlet tube with a vacuum amplifier. And it is also possible to host the piston of the main cylinder, wear the pads and new blocks can still be installed, which simply have not worked.
Increased noise when braking. When the brake pads are worn, a squeaking sound occurs when braking, due to the friction of the wear indicator, sliding the disk. Also, the pads or the disk can be salted or contaminated.
2.2. Requirements for car brake systems
The brake system of the car, except for the general requirements for the design, has increased special requirements, because It ensures the safety of car traffic on the road. Therefore, the brake system in accordance with these requirements should provide:
- minimum brake path;
- car stability during braking;
- stability of brake parameters with frequent braking;
- quick triggering of the brake system;
- proportionality of effort on the brake pedal and on the wheel wheels;
- ease of control.
The brake systems of the car, there are requirements that are regulated by the UNECE Rules No. 13 applied in Russia:
Minimum brake path. Brake system on cars should be highly efficient. The number of accidents and accidents will be less if the maximum value of the deceleration is high and approximately equal to various cars and the type of car moving in the intensive stream.
And also brake routes of cars must be simultaneously close to each other, with a difference of about 15%. If the minimum brake path is reduced, not only high traffic safety will be ensured, but also an increase in the average velocity of the car.
The necessary conditions for the minimum brake path is the smallest time required to trigger the vehicle braking, as well as the braking of all wheels at the same time and the ability to bring brake forces to the maximum clutch value and ensure the desired distribution of the brake forces between the wheels of the vehicle in accordance with the load.
Brake stability. This requirement increases the efficiency of car braking on the road with small clutch coefficients (icy, slippery, etc.) and thereby increases the level of security of all participants in the roads.
In compliance with the proportionality between the brake forces and loads on the rear and front wheels, the braking of the car is ensured with a maximum slowdown under any road conditions.
Stable braking. This requirement is associated with the heating of the braking mechanism during braking and possible impairment of their actions when heated. So, when heating between the brake drum (disk) and friction pads of the pads, the friction coefficient decreases. In addition, when heating brake linings, their wear is significantly increased.
The stability of the brake parameters at frequent braking of the vehicle is achieved with the coefficient of friction of the brake linings, equal to about 0.3-0.35, practically independent of the speed of sliding, heating and water from entering the water.
From the time of operation of the brake system of the car, the braking path will depend on that significantly affects the safety of motion. Mainly, the type of brake drive depends on the triggering system. Car with hydraulic drive will be 0.2-0.5, in vehicles with a pneumatic drive 0.6-0.8 and in road trains with a pneumatic drive 1-2. When performing these requirements, a significant increase in car safety is ensured in various road conditions.
The effort on the brake pedal during the braking of the car should be 500 - 700 H (the minimum value for passenger cars) during the course of the pedal is 80 - 180 mm.
2.3. Methods for diagnosing brake systems
To diagnose brake systems of cars, two main diagnostic methods are used - road and stand.
- Road diagnostic method is designed to determine the length of the braking pass; steady slowdown; car stability in time of braking; brake system operation time; The slope of the road on which the car must still stand;
- The stand test method is necessary for calculating the overall specific brake force; The coefficient of non-uniformity (relative unevenness) of the brake forces of the axis wheels.
To date, there are many different stands and appliances for measuring brake qualities by various methods and methods:
- inertial platforms;
- static power;
- power roller stands;
- inertial rolleries;
- devices measuring the deceleration of the car during road testing.
Inertial platform stand. The principle of operation of this stand is based on the measurement of inertia forces (from rotationally and progressively moving masses) arising during the car braking and applied in the pairing places of the vehicle with dynamometer platforms.
Static power stands. These stands are roller and platform devices that are designed to turn the "breakdown" of the inverted wheel and the measurement of force applied at the same time. Statistical power stands have, pneumatic, hydraulic or mechanical drives. The brake force is measured when hanging the wheel or when it is supported on smooth running drums. This method has a lack of diagnosing brakes - is the inaccuracy of the results, as a result of which the conditions of the present dynamic braking process are not repeated.
Inertial roller stands. They have rollers that have a drive from the electric motor or from the car engine. In the second example, due to the rear (leading) wheels of the car, the rollers of the stand rotate, and from them with mechanical transmission - And the front (slave) wheels.
After the car is installed on an inertial stand, the linear velocity of the wheels is adjusted to 50-70 km / h and sharply slow down, at the same time separating all the bench carriages by turning off the electromagnetic couplings. At the same time, in the places of contact of the wheels with rollers (ribbons) of the stand arise inertia forces, opposing the brake forces. After some time, the rotation of the bench drums and wheels of the car stop. The ways passed by each car wheel during this time (or the angular slowdown of the drum) will be equivalent to brake paths and brake forces.
The braking path is determined by the frequency of rotation of the rollers of the stand, fixed by the meter, or by the duration of their rotation, measured by the stopwatch, and the slowdown is an angular desperometer.
Power roller stands Using the clutch forces of the wheel with a roller make it possible to measure braking force in the process of its rotation at a speed of 2.10 km / h. Rotation of wheels is carried out by the rollers of the stand from the electric motor. Brake forces are determined by the reactive moment that occurs on the stator motor gearbox of the stand when braking wheels.
Roller brake stands allow to obtain quite accurate results of checking brake systems. With each repetition of the test, they are able to create conditions (first of all the speed of rotation of the wheels), are absolutely identical with the previous ones, which is provided with an accurate job of the initial braking speed by external drive. In addition, when testing on power roller brake stands, a measurement of the so-called "ovality" is provided - an assessment of the non-uniformity of the brake forces in one turnover of the wheel, i.e. The entire braking surface is investigated.
When testing on roller brake stands, when the force is transmitted from the outside (from the brake bench), the physical pattern of braking is not violated. The brake system should absorb the incoming energy even though the car does not have kinetic energy.
There is another important condition - safety tests. The safest tests are on power roller brake stands, since the kinetic energy of the test car on the stand is zero. In case of failure of the brake system during road testing or on the platform brake stands, the probability of an emergency is very high.
It should be noted that by the combination of its properties, it is the power roller stands that are the most optimal decision both for diagnostic lines of maintenance stations and for diagnostic stations conducted by GOSTHAS.
Modern power roller stands for checking brake systems can define the following parameters:
- According to the general parameters of the vehicle and the state of the brake system - the resistance to the rotation of the non-rotated wheels; non-uniformity of the brake force in one turnover of the wheel; Mass coming on the wheel; Mass coming on the axis.
- On working and parking brake systems - the greatest brake force; brake system operation time; non-uniformity coefficient (relative unevenness) brake forces of axis wheels; Specific brake force; Effort on the control body.
Control data (Fig. 2.3.) Displays the display in the form of digital or graphic information. The diagnostic results can print and stored in the computer's memory in the database of diagnosed cars.
Fig. 2.3. Brake system monitoring data:
1 - indication of the inspected axis; Software front axle brake; ST - parking brake system; Zo - working brake rear axis
The results of checking the brake systems can also be displayed on the dashboard (Fig. 2.4.)
The dynamics of the braking process (Fig. 2.5.) Can be observed in graphical interpretation. The schedule shows the brake forces (vertically) relative to the effort on the brake pedal (horizontally). It reflects the dependence of the brake forces from the injection force on the brake pedal for both the left wheel (the upper curve) and the right (lower curve).
Fig. 2.4. Brake Stand Dashboard
Fig. 2.5. Graphic display of the dynamics of the braking process
With the help of graphic information, you can also observe the difference in the brake forces of the left and right wheels (Fig. 2.6.). The graph shows the ratio of the brake forces of the left and right wheels. The braking curve should not go beyond the boundaries of the regulatory corridor, which depend on the specific regulatory requirements. Observing the character of changing the schedule, the diagnostic operator can make a conclusion about the state of the brake system.
Fig. 2.6. The values \u200b\u200bof the brake forces of the left and right wheels
- Recommendations for the choice of brake diagnostics equipment
3.1. Selection of diagnostic equipment
SPACE brake stands have a certificate of quality management system according to UNI EN ISO 9001-2000 confirms the use of advanced technologies, the use of modern coatings, high-quality materials and components, which makes it possible to export equipment in more than forty countries.
Diagnosing the car braking system is carried out by rollers, which are divided into 3 types. Brake stands have a different design and engine power, but the main main feature is the maximum value of the brake force (Table 3.1).
Table 3.1.
Roller aggregates for brake stands
|
Model |
Max. Brake force |
|
PFB 035. |
5000 kg |
|
PFB 040. |
6000 kg |
|
PFB 050. |
7500 kg |
|
PFB 715. |
7500 kg (dual speed) |
And also another important characteristic is the coefficient of friction between the wheel of the car and the rollers of the stand. In our case, we take a value equal to 0.7. To select the brake stand, we define the braking force.
Brake effort is the power of the car's wheel interaction with the outside of the roller (imitation of the movement of the car along the road). It is expressed in Dan.
1 Newton \u003d 0,101972 kg.
1 Dan \u003d 10 Newton \u003d 1.01 kg.
For the convenience of calculations, we take 1 dan \u003d 1 kg with 1% minor error.
μ \u003d f / m
Friction coefficient μ - Power ratioF to mass m.
This expression means the relationship between the mass of the car and the power required to move along the road.
If we have a lotM. interacting with the surface and 0.5 kg of powerF. For its movement, then the friction coefficient μ will be 0.5.
Upon this averaged value, the roller brake stand is chosen, for example, PFB 035 \u003d 500 DEN.
Motor power (and roller actuator) allows accurate measurements of force F Over 510.2 kg. To the tangent surface of the roller. After measuring this magnitude, the motor reduces the speed, and further measurements are not performed. For determining maximum massWe use the previous formula:
W \u003d f / μ
We get 500 kg / 0.7 \u003d 714 kg (a mass acting on one roller). Hence it follows that weight Limit On the axis is 1428 kg.
For the maximum theoretical mass value on the axis, we can choose the PFB 035 model. This choice is not accurate, because the friction coefficient is highly dependent on the characteristics of the tire (the poor tire has lower friction) and other conditions. For example, the maximum braking force does not measure the braking time of the previously damaged tire, in order to avoid its further wear. It also allows you to slightly increase the maximum axis weight. It should be noted that the weight of the axis is not just half full weight The car, as the unloaded car has a greater weight on the axis, but if you load the car, respectively, the axis load increases.
3.2. Specifications of selected equipment
The principle of operation of the Space line (Italy) is a consistent collection and software processing of measurement results and visual control of the technical condition of the PBX with the help of measuring instruments of equipment included in the package of tool control. Car testing procedure is controlled from the console remote control either from the keyboard, processed and remembered by the processor, visualization of testing using the monitor, all images 3D graphics, print results on the printer, interface for connecting:
- stand of the station;
- suspension tester;
- gas analyzer;
- chymometer;
- tachometer.
List of measured parameters:
Rolling resistance;
Disks ovality or brake drum relative;
Maximum brake force on the wheel;
The difference between the brake efforts between the right and left wheels of one bridge;
The efficiency of braking working and parking brakes;
Effort on the foot brake pedal and on the hand brake lever
On the brake stand you can experience both cars with a drive for all 4WD wheels. The test procedure for full 4WD drive cars is divided into two separate phases for each bridge. In the first phase, the left roller aggregate begins to rotate along the movement, and the right - in the opposite direction. At the same time B. dispensing box The transfer to the second axis is discharged, and, therefore, the moment of rotation is not transmitted to the wheels that are not standing on the rollers. The results will be shown after testing both axes. At the end of the measurements of the brake efforts on each bridge, you can see the brake effort schedule.
Fig. 3.2. Testing procedure is full of drive cars.
After all the data and the car came down in the computer's memory, a page with final test results of the entire brake system appears on the monitor screen (Fig. 3.2.).
Technical characteristics of standsPFB 035, PFB 040 and PFB 050 are shown in Table 3.2
Table 3.2.
Specifications
|
Specifications |
PFB 035. |
PFB 040. |
PFB 050. |
|
Load on the axis when testing / during transit, kg |
2500/4000 |
2500/4000 |
2500/4000 |
|
Maximum brake forceN. |
5000 |
6000 |
7500 |
|
Accuracy,% |
|||
|
Speed \u200b\u200bwhen testing |
|||
|
Power engines, kW |
2x4.7 |
2x5.5. |
|
|
Diameter of drums, mm |
|||
|
Clutch coefficient |
More than 0.7. |
More than 0.7. |
More than 0.7. |
|
Nutrition, V. |
380 / 3F. |
380 / 3F. |
380 / 3F. |
Comparison of price profitability, repair and duration of performance are shown in Figure 3.3
Fig. 3.3. Comparative stand chart (in percentage ratio).
Conclusion
The modern car works in a wide variety of road and climatic conditions. Long operation Inevitably leads to the deterioration of its technical condition. The performance of the car or its aggregates is determined by their ability to perform the specified functions without violating the established parameters. The performance of the car depends primarily on its reliability, which is understood by the ability of the car to safely transport goods or passengers when complying with certain operational parameters.
When writing work, special literature was studied, including articles and textbooks, theoretical aspects are described and the key concepts of research are disclosed.
During the writing course, the brake system was studied. Methods and methods for restoring the performance of the brakes were considered. And in conclusion on the basis of the material studied, recommendations were developed to select the SPASE diagnostic equipment, of the three roller stands PFB 035, PFB 040 and PFB 050. During the study of the technical characteristics, the price category, the cost of repair and service life was taken solving the choice of the first PFB 035 unit, as it is a more optimal option for the price category, and technical characteristics Not much inferior to the rest of the stands, as well as on the cost of repair and service life, which is given in Figure 3.3, is more profitable.
List of sources used
1. GOST R 51709-2001. Motor vehicles. Safety requirements for technical condition and verification methods. - M.: Starotinform, 2010. - 42 p.
2. Derevko V.A. Brake systems of passenger cars - M.: Petit, 2001. - 248 p.
3. Diagnosing cars. Workshop: studies. Manual // Ed. A.N. Kartashevich. - Minsk: new knowledge; M.: Infra-M, 2011. - 208 p.
4. Roller brake stands for passenger cars:Space. [electronic resource].URL: http: // www. Alpoka. RU / CATALOGUE / STR 1__13__ ITEMID __73. HTML.
5. Diagnosis and control of motor vehicles [Electronic resource]. URL: http://ktc256.ts6.ru/index.html.
6. Maintenance and repair of cars: Mechanization and environmental safety of production processes // V.I. Sarbaev, S.S. Selivanov, V.N. Konoplev - Rostov: Phoenix, 2004. - 448 p.
7. Maintenance and repair of cars: a textbook for the stud. // V. M. Vlasov, S. V. Zhankaziev, S. M. Kruglov et al. - M.: Publishing Center Academy, 2003. - 480 p.
8. Technological processes Diagnosing, maintenance and repair of cars: studies. Manual // V.P. Ovchinnikov, R.V. Needin, M.Yu. Bazhenov - Vladimir: Publishing House Vladim. State University, 2007. - 284 p.
9. Technological processes of maintenance, repair and diagnostics of cars: studies. Manual for studies Higher. studies. institutions // V.G. PERSIONS, V.V. Mishoustin. - Novocherkassk: Yurgu (NPI), 2013. - 226 p.
10. Harazov A.M. Diagnostic Support for Maintenance and Car Repair: Ref. Manual - M.: Higher. Shk., 1990. - 208 p.
Other similar works that may interest you. Ishm\u003e |
|||
| 20713. | Development of recommendations for choosing equipment for diagnosing car brake system | 412.16 Kb. | |
| Car design is constantly being improved, but the presence of a brake system remains unchanged, which contributes to stopping the car if necessary, which retains the lives of pedestrians, drivers and passengers, as well as other road participants. Repairing the brake system is necessary on all cars, | |||
| 11115. | Improving the brake quality of the car in operation | 1.52 MB. | |
| Developers and constructors of brakes of foreign and domestic firms are becoming increasingly preferred by developing disc brakes with stable characteristics in a wide range of temperatures, pressures and speeds. But such brakes can not fully ensure the effective operation of the brake system, anti-lock systems (ABS) become more reliable. | |||
| 7978. | Strategic management. Basic approaches to the choice of strategy | 27.13 Kb. | |
| In the face of a tough competition and a rapidly changing situation, the organization should not only focus on the inner state of affairs, but also to develop a long-term behavior strategy that would allow them to have a change in the changes occurring in their environment. In the past, many organizations could successfully have to pay attention mainly to the daily work on domestic problems associated with improving the efficiency of resource use in current activities. Currently, the task of rational ... | |||
| 11416. | Development of technology for producing friction materials for restoration of brake pads of railway cars | 1.34 MB. | |
| Present thesis Made within the framework of the above program in collaboration with the specialists of the TTC "KM", PCTU them. DI. Mendeleev, Institute of Machine Studies (Moscow) and the Academy of Transport (Almaty). It should be noted that the data presented in this paper are the first in the Republic of Kazakhstan and should be considered as the results of search and problem NIR | |||
| 16759. | Restructuring of corporate borrowers for the choice of creditors: the solution of macro problems on the micro level | 14.73 Kb. | |
| A significant deterioration in the economic situation in the country and the world led to the fact that the majority of Russian enterprises, including large, collided with numerous financial problems and permanent increase in debt. The total amount of defaults is that total for the year since September 2008. The reason lies in the fact that all the money was assieved in banks: to support the financial market and industries ... | |||
| 6511. | Principles bought systems armp cable l_nіynyh tract of systems of transmission | 123.51 Kb. | |
| A set of automatic regularist Rensant is recognized for regularwist Rіvnіv Protem Pіdsilyuvachіv Mag_stralі in the default intelligence і for Stub_lіlіzatsky's zagasannya channels storker. | |||
| 8434. | Visa of regional systems (arm-systems) accountant that їh budova | 46.29 KB. | |
| The form of the regional system of the Armsisters of the accountant TA ~ Budova 1. Structural Budova Regional Systems. Waterova oblaimy OS systems on the basis of the Basic ARM is characterized by a baggage aspect of Mozlivih Vіantіv їch wobble. Vi_Layyuchi Klasifіkatsіinі Measure AWP ENTAGE SAI SPECIAL PILLIBY їKH BOOTIVIA І Vddovdnimnnya Yak structural-flowsіonal Miscea Zaiman Skin AWP Roses_l Funki-Diagnostic Tasks Serm Avdosobi Organizatsії Ровазовання соваски за закиніва зранна і іізний півніва комнина і Інші Рівніваргонна і Інші | |||
| 5511. | Recommendations for reducing costs at the Profile LLC | 97 Kb. | |
| The expenses of the enterprise, organizations relate to the main economic indicators of the enterprise activities and are a decrease in economic benefits as a result of the disposal of assets (cash, other property) and (or) the emergence of obligations | |||
| 5115. | Calculation of energy consumption and main recommendations for energy saving | 121.88 KB. | |
| There is no heatchard in the apartment, therefore measures to save heat will not lead to a decrease in utility bills. Installation of an individual instrument of accounting for an apartment is impossible for technical reasons. The apartment has double-glazed windows and glazed balcony. This reduces heat loss and helps to establish the optimal level of comfort in the apartment. | |||
| 10438. | Methodical recommendations for mathematics textbooks for 10 - 11 classes | 75.1 Kb. | |
| The authors offer approximate thematic planning for the base level at the rate of 15 hours per week - geometry and 25 hours per week algebra. Geometry 10 11 is allowed by the Ministry of Education Russian Federation as methodical recommendations On the use of textbooks for 10-11 classes in organizing the study of the subject on the basic and profile levels ... | |||
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Posted by http://www.allbest.ru/
1. Brake system malfunctions
2. General diagnosis of brake systems
3. Types of stands and methods of testing brake systems
4. Fundamental device Power roller stands for diagnosing brake systems
5. Principle of operation of power roller stands
6. Car brake system efficiency meters road method
7. Elemental diagnostics and adjustment work on the brake system
8. Replacement of brake fluid
9. Features of maintenance of the brake system with a pneumatic receipt
Bibliography
1. Brake system malfunctions
According to statistics, road traffic accidents caused by the brake system malfunctions are 40 ... 45% of the total number of accidents occurring for technical reasons. We present the main malfunctions of the brake system that appear during the operation of the car under the action of wear, aging and other factors.
Insufficient braking efficiency can be caused by a decrease in the friction coefficient between brake pads and drums due to wear or grinding friction linings, increasing the gap between them.
Non-chronic braking of all wheels can lead to a car drift, the reasons for this: unequal gaps between friction linings and brake drums, lubrication of lining, wear of wheel brake cylinders or pistons (hydraulic drive), stretching the brake diaphragms (pneumatic actuator), uneven wear of brake or friction linings.
The peeing the brake mechanisms occurs when the brake pads of the brake pads are cut, strongly contaminated the brake drums or brake drive rollers, breaking the brake linings rivets and jamming them between the shoe and the drum (disk). In car with hydraulic drive, the jamming occurs when the pistons are jammed in the brake cylinders or when the compensation opening of the main brake cylinder is clogged.
The driving of the brake pedal when braking in vehicles with hydraulic equipment occurs due to air in the brake system.
Braking cars for the allowed pedal comes due to a loose landing inlet valve Control of the brake crane, the absence of a gap between the pusher and the piston (hydraulic drive).
Weak pressure in the system and air leakage (pneumatic) are due to slippage of the belt of the compressor, air leaks in compounds and pipelines of the highway, laundrances of the adjustment of the valves to the clips of the compressor.
2. General diagnosis of brake systems
General diagnosis of brake systems in ATO, auto-service organizations (OA) or control during the passage of state technical inspection Includes:
Measuring control of the efficiency of braking vehicle (TC) working and parking brake systems, as well as the stability of the vehicle when braking the working brake system;
Organoleptic and, if necessary, measuring control of the tightness of the pneumatic or pneumatic part of the pneumohydraulic brake actuator and the elements of the brake mechanisms of the wheels.
The braking efficiency of the vehicle is measured using a roller brake stand to test the brake systems or the road method, if due to its dimensional or structural characteristics of the vehicle can not undergo control of these indicators on the stand.
3. Types of stands and metreatment Testing Brake Systems
There are several types of stands using various methods and methods of measuring brake qualities: static power, inertial platform and 12 roller, power roller, as well as instruments for measuring the deceleration of the car during road testing.
Static power stands They are roller or platform devices designed to turn the "breakdown" of the inverted wheel and the measurement of force applied at the same time. Such stands may have a hydraulic, pneumatic or mechanical drive. The measurement of the brake force is possible when the wheel is elected or when it is supported on smooth running drums. The disadvantage of the static method of diagnosing the brakes is the inaccuracy of the results, as a result of which the conditions for the real dynamic braking process are not reproduced.
Principle of operation of an inertial platform stand It is based on measuring inertia forces (from progressively and rotationally moving masses) arising when braking the car and attached in the contact places of wheels with dynamometer platforms. Such stands are sometimes used on ATP for input control of brake systems or express diagnostics of vehicles.
Inertial roller stands Consist of rollers that have a drive from the electric motor or from the engine of the car, when the driving wheels of the vehicle drive the rollers of the stand, and from them using a mechanical transmission - and front (slave) wheels.
After installing the vehicle on the stand, the circumferential speed of the wheels is adjusted to 50 ... 70 km / h and sharply slow down, at the same time separating all carriages of the stand by turning off the electromagnetic couplings. At the same time, in the places of contact of the wheels with rollers (ribbons) of the stand arise inertia forces, opposing the brake forces. After a while, the rotation of the bench drums and wheels of the car stops. The ways passed by each car wheel during this time (or the angular slowdown of the drum) will be equivalent to brake paths and brake forces.
The braking path is determined by the frequency of rotation of the rollers of the stand, fixed by the counter, or by the duration of their rotation, measured by the stopwatch, and slow down - the angular desperometer.
The method implemented by an inertial roller bench creates the conditions of car braking, as close as possible to real. However, due to the high cost of the stand, insufficient safety, labor intensity and high costs of the time required for diagnosing, the stands of this type are irrational when diagnosing ATP.
Power roller stands In which the clutch forces are used with a roller, allow measurement of brake forces during its rotation at a speed of 2 ... 10 km / h. Such speed is selected because at a speed of 13 tests, more than 10 km / h significantly increases the amount of information about the performance of the brake system. The brake force of each wheel is measured by braking it. Rotation of wheels is carried out by the rollers of the stand from the electric motor. Brake powers are determined by the reactive moment that occurs on the stator of the motor gearbox when braking the wheels.
Power roller stands allow to obtain quite accurate results of checking brake systems. With each re-test, they are able to create conditions (first of all the speed of rotation of the wheels), are absolutely identical with the previous ones, which is provided with an accurate job of the initial braking rate by external drive. In addition, when testing on power roller stands, the so-called ovality is measured - the estimate of the non-uniformity of the brake forces in one turnover of the wheel, i.e. The entire braking surface is investigated.
When testing on power roller stands, when the force is transmitted from the outside, i.e. From the brake stand, the physical pattern of braking is not broken. The brake system should absorb the incoming energy, even though the car does not move (its kinetic energy is zero).
There is another important test condition - safety. The most secure - tests on strength roller stands, since the kinetic energy of the test car on the stand is zero. It should be noted that by the aggregate of its properties, it is the power roller stands that are the most optimal solution for both ATP and diagnostic stations conducted by GOSTHAS.
Modern power roller stands To check brake systems, a number of parameters can be determined:
General parameters of the vehicle and the state of the brake system: resistance to the rotation of non-optical wheels; non-uniformity of the brake force in one turnover of the wheel; Mass coming on the wheel; Mass coming on the axis; the power of resistance to the rotation of the non-rotated wheels;
The parameters of the working brake system: the greatest brake force; brake system operation time; non-uniformity coefficient (relative unevenness) brake forces of axis wheels; Specific brake force; effort on the management body;
Parking brake parameters: the greatest brake force; Specific brake force; Effort on the control body.
Information on the results of the control is displayed on the display in digital or graphic form or on the instrument rack (in the case of the application of the arrow output of the information). The diagnostic results may also be displayed on the print and stored in the computer's memory as a database of diagnosed cars.
4. Principal device of power roller stands for dibrake Systems Agnostation
The main components of such stands are usually: two interconnected set of rollers placed in a supporting and perceiving device, respectively, for the left and right sides of the car; power cabinet; rack; remote control; Silic meter pressure on the brake pedal. The vehicle is installed on the test bench so that the wheels of the inspected axis are located on the rollers.
(Persistently perceiving device (Figure 1) is intended for placing the support rollers and the forced rotation of the wheels of the diagnosed axis of the car, as well as for the formation (using the brake force sensors and the mass) of the electrical signals, proportional to the braking force and part of the mass of the vehicle coming to each Wheel diagnosed axis.
Figure 1. The scheme of the reference device: 1, 5, 7, 10 - rollers; 2.9 - gear motors; 3.8 - strain gauges; 4, 11 - tracking rollers; 6 - frame; 12 - Mass sensors.
The reference-perceive device consists of a box 6 of a box cross section, in which two pairs of support rollers (5, 7 and 1, 10) are located on spherical self-aligning bearings (5, 7 and 1, 10) interconnected by a drive chain.
Rollers 1 and 5 are connected via deaf clutches with coaxial gearboxes 2 and 9. Each pair of rollers has an autonomous drive from an electric motor connected to it 4 ... 13 kW. Electrical engine The gearbox leads rollers in motion and maintains a constant speed of rotation. Drive engines for rollers sets can be activated using remote control, thanks to which the measurement commands can be supplied from the car, or using an integrated automatic two-position switch.
As a rule, there are planetary gearboxes in the brake stands having high gear ratios (32 ... 34), which makes it possible to obtain a small speed of rotation of the rollers. The AC motor leads in motion the leading roller by means of a toothed transmission. The rear ends of the gearboxes are installed in spherical bearings, while the motor gearboxes are balanced suspended. Corps motor gearboxes Tensometric sensors 3 and 8 are associated.
Between the supporting rollers are installed freely rotating spring-loaded tracks 4 and 11, having two sensors: a sensor for the presence of a car on the support rollers, which, when lowering the tracking roller, gives the corresponding signal; Wheel rotation tracking sensor, outstanding the corresponding signals when the wheels are rotated for the diagnosed TC
Currently, some manufacturers, such as Cartec, are not installed in their stands of the tracking rollers. Such benches are equipped with sensors that provide contactless determination of the presence of the car on the rollers of the stand. Sensors determine the presence of a car on the stand and with the correct position of the vehicle on the rollers of the stand (in the longitudinal and transverse directions) give a signal to start drive engines.
On the frame 6 at the bottom under the supporting rollers there are four mass sensors 12, having the stops at the ends to set and fix the support device in the foundation pit (or on the frame).
The frame of the support-perceive device is placed on rubber lining to pay off vibration. The surfaces of the rollers of power stands are made by corrugated with steel welcox, providing a constant 16 clutch coefficient as the rollers wear, or are covered with basalt, concrete and other materials providing good tire clips. For a better clutch of rollers with wheels, both rollers are made by lead, and the distance between them is to make it impossible to make a car from the braking stand. Carry out a car from the stand after checking the brakes of the drive axis is provided by the reactive torque of gearboxes or lifts located between the rollers. Sometimes for this purpose, one of the rollers (from the departure side) provide a device that allows you to rotate only one way.
Brake stands are equipped with special devices that prevent start of roller aggregates in the case when one or both wheels are blocked. Thus, the car and tires are protected from damage by the rollers. Run is also blocked in the case of pressing the brake pedal ahead of time, too high resistance to the rotation of the rollers of one or both wheels, clamping the brake pads, etc.
5. Principle of operation of power roller stands
At the entrance of the car on the brake stand, the mass of the axis is measured if there is a weighing device; With its absence, the mass of the axis can be administered from another stand, for example, a stand for checking the shock absorbers. When the car is installed on the test bench, then the tracking rollers 4 pressed and transmit a stand signal on bringing the stand into action; Both tracking rollers should be pressed to turn on the stand. In the future, the tracking rollers are used to determine the tire slipping relative to running rollers and give a signal to disable drive motor gearboxes when slipping.
The principle of the stands of the stands is based on the transformation of strain-spector sensors of the reactive moments of the brake forces arising from the braking of the vehicle wheels, as well as the gravity of the axis of the car acting on the roller aggregates into the analog electrical signals. The braked wheel is driven by rollers. During braking, depending on the magnitude of the brake force on a balancingly suspended motor gearbox, a jet occurs. The motor of the gearbox is rotated at an angle proportional to the braking force. The reactive moment that occurs during the rotation of the gear motor is perceived by the strain gauge sensors 3 and 8 (see Figure 1), one end of which is fixed on the paws of motor gearboxes 2 and 9, and the second on the frame 6.
The speed of rotation of the brake bend rollers is compared at the speed of rotation of the tracking rollers. The difference of speeds of rotation of the tracking rollers and the brake stand rollers determines the magnitude of the slippage. With such a slippage of the stands automatically turn off the drive of the braking rollers 17 stand, which protects the tires from damage. Usually, when checking, it is hampered until at least one of the tracking rollers will notice the exceeding the normative values \u200b\u200bof the slippage and will not turn off the drive engines. When one wheel is reached by one wheel of the installed slipping boundary, both support rollers are disconnected. The maximum measured value is written as the maximum brake force.
Checking the brake pedal effort allows you to determine not only normalized values, but also the performance of the vacuum amplifier of the brake system, and compare the operating modes of wheel braking mechanisms.
Signals from strain resistor sensors come to the computer, where they are automatically processed by a special program. According to the results of measurements of the brake forces and the mass of the car, the axial and total specific brake forces and non-uniformity of the brake forces are calculated. Measurement results and calculated values \u200b\u200bare presented in graphic and digital form on the monitor, then the print device prints the measurement protocol.
Consider the technological sequence of measurement of parameters on the power roller brake stands on the example of a passenger car. 1. The car is installed on the stand to diagnose brake systems (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Car position on the brake stand: 1 - diagnosed car; 2 - dashboard; 3 - booth rollers; 4 - Measurement sensor Pressing brake pedal.
Before checking the technical condition of the TC brake systems on the brake stand, it is necessary:
Check the air pressure in TC tires and, if necessary, bring it to normal;
Check the TC bus in the absence of damage and degradation of the tread, which can lead to the destruction of the tire when braking on the stand;
Inspect the wheels of the vehicle and make sure the reliability of their attachment, as well as the absence of foreign objects between the dual wheels;
Assess the degree of heating the elements of the brake mechanisms of the test axis by the organoleptic method (the temperature of the elements of the brake mechanisms should not be higher than 100 ° C). The optimal for the inspection can be considered conditions under which the heating of brake drums (disks) allows you to keep a person's unprotected hand in direct contact with this item for a long time (it follows such an assessment, observing precautions to avoid burns);
Install on the brake pedal, the device (Pressing force sensor) to control the parameters of the brake systems when the specified force actuate is reached;
Carrying out wet wheels to remove moisture from brake mechanisms, it is carried out by repeatedly pressing the brake pedal.
2. Includes booth electric motors and measure brake force (without pressing the brake pedal) caused by the resistance to the rolling of the wheels. This magnitude is proportional to the vertical load on the wheel and for passenger cars is usually 49 ... 196 N.
If the resistance force of the wheel is greater than 294 ... 392 N, this means that the wheel is inhibited, so it should be found out the possible reason for this (the small gap between the brake pads and the drum (disk), jamming the pistons in the working cylinders, the abnormal tightening of the wheel hub bearings etc.).
3. Smoothly press on the brake pedal with an effort no more than 392 N and remove the testimony (the permissible difference of brake forces for the wheels of one axis should not exceed 50%).
4. Smoothly press the brake pedal so as to create 490 ... 784 N on each wheel, and maintain it constant for 30 ... 40 s. Brake Diagnostics Malfunction Roller
If the difference in the testimony of the brake forces is very big, it means that moisture got into the brake mechanisms. This can usually be observed when checking cars entered on the stand after washing. In the event that the difference between the two testimony is preserved and after heating the brakes, this is explained by one of the following reasons: the surface of the brake pads underwent crystallization and severe grinding and has a low coefficient of friction, which can be confirmed when performing the entire test cycle, if the brake force is small increases despite the presence of significant efforts on the brake pedal; The pistons of work cylinders are fully bred in the initial position, this is confirmed by the fact that 19 Increasing the efforts on brake pedals do not cause the brake force on the wheel.
To clarify the possible malfunction, it is necessary to inspect the brake mechanism of the wheel. If in the process of testing the brake forces of one or two wheels rhythmically fluctuate (the amplitude of oscillations of 196 ... 392 H) with a constant force of pressing the brake pedal (147 ... 196 H), this indicates the issues of ellipseality or intimacy of the drums and Wheels, deformation of disks, incorrect tire profile. It is conventionally assumed that ellipsence or inconception is approximately 0.1 mm for every 98 H oscillations of the brake force.
5. When the brake pedal is released, the measuring arrows (numbers) are returned to minimal values \u200b\u200bcreated by rolling resistance. The speed and uniformity of the return arrows (digits) estimate simultaneousness and quality of wheels.
6. Increase the force of pressing the brake pedal to 49 H, the brake force is recorded until the wheel blocking is reached. During these tests, the uniformity of the brakes is evaluated.
If there is a minor increase in the brake forces of both wheels (for example, with an effort on the pedal 98 H, the brake force on wheels is 833 N, and with an increase in force to 196 H, it increases to 1176 N instead of 1568 ... 1666 N), then it means that the type of friction linings applied on the car or is unsuitable due to excessively high hardness or their surface crystallized or grilled during operation.
If there is a rapid increase in the brake forces (for example, with an effort on the pedal 98 H, the brake force on wheels is 833 N, and with an increase in force to 196 H, it increases to almost 1960 N), then the brakes have a tendency to self-blocking. This is especially dangerous when braking on a wet road. Increased tendency to self-blocking can be caused by the use of friction linings from too soft materials.
In drum brakes, a similar phenomenon may occur if the pads are incorrectly adjusted. In addition, cars having a brake amplifier, the tendency to block the wheels can be caused by incorrect operation of the amplifier.
Brake forces that are created on wheels at the time of their blocking are crucial to evaluate the performance of brakes. However, it should be borne in mind that the magnitude of the brake force at which the wheels are blocked is determined by factors, many of which do not depend on the technical condition of the vehicle braking system, for example, 20 weighing per wheel, tires, wear and tread pattern .
7. Similar to checking the brakes of the front wheels, checking the brakes of the rear wheels.
8. Summing up the brake forces on each wheel, determine the specific brake force, which should be at least 50% of the total vehicle. In this case, the specific brake force is checked separately for the front and rear axles.
To check the manual (parking) brakes, it is necessary to gradually move the parking brake lever before blocking the wheels. This operation should be carried out especially carefully, since at the time of blocking the wheels, the car that is not retained by the non-optical front wheels can move from the bench to the jerk back, so during tests at a distance of 2 m from the car there should be no people.
By moving the manual brake lever, count the number of snore mechanism clicks in order to check the correctness of the drive adjustment. Simultaneously check the efficiency of braking and the uniformity of the drive. Technically serviceable hand brake Must provide brake forces on both wheels, the sum of which should not be less than 16% of the total mass of the car.
In the same sequence, measurements of the parameters of the brake systems with a pneumatic receipt are made. In the pneumatic system, the pressure sensor is installed. To do this, it is necessary to remove the plug from the valve of the control output of the supply circuit of the pneumatic brake system and screw the pressure sensor in its place.
The dynamics of the braking process can be observed in graphical interpretation. In Figure 3, and the dependence of the brake force changes (vertically) from the thread of the brake pedal (horizontally) for the left (upper curve) and for the right wheel (lower curve) are shown.
Figure 3, B shows a change in the difference in the brake forces (vertically) when braking the left and right wheels. It can be seen that the braking curve goes beyond the boundaries of the stability corridor, and this is unacceptable and testifies to unstable braking.
Watching a change in the schedule, the diagnostic operator can make a conclusion about a particular brake system malfunction, for example, by the difference in braking forces, or by the character of the change of the waveform.
Figure 3. Graphic display of the dynamics of the braking process: a - change of brake forces depending on the effort of pressing the brake pedal; b - the difference in the difference of the brake forces of the left and right wheels; 1 - width of the stability corridor.
6. Brake System Efficiency Measuresvehicle road method
The effectiveness of the brake system of the car can be checked with the help of special meters - desperometers or desktop. Such meters are used in the absence of brake stands and in field conditions or if it is impossible to check the vehicle (for example, motorcycles) on the stand.
When using a TC deslerometer in a circular state, they accelerate and dramatically slow down to a one-time foot brake pedal. The principle of the desserometer is to fix the path of moving the moving inertial mass of the device relative to its body, fixed by car. This movement occurs under the action of inertia strength during the braking of the car proportional to its slowdown. Translationally moving load, pendulum, liquid, or acceleration sensor, and a meter - a switch, a scale, a signal lamp, a self-inspector, a composter, etc. To ensure stability, the dessemerometer is equipped with a damper (liquid, air, spring), and for Ease of measurements - a mechanism that locks the maximum slowdown.
The most widely distributed meter of the efficiency of the braking systems of the "Effect" (Figure 4).
Figure 4. General form Measuring instrument of efficiency of brake systems "Effect" (Russia): 1 - socket for connecting a printer (computer); 2 - power cable connector; 3 - Effort sensor cable connector; 4 - dashboard; 5 - suction cup; 6 - "Cancel" button; 7 - "Select" button; 8 - clamp; 9 - indicator; 10 - clamp pen; 11 - Power button "On"; 12 - "Enter" button; 13 - Effort sensor; 14 - printer cable connector; 15 - connector for connecting to the cigarette lighter socket; 16 - printer power button; 17 - printer.
The device determines the installed slowdown, the peak value of the force of pressing the pedal, the length of the braking path, the response time of the brake system, the initial braking speed and the linear deviation of the vehicle, and also produces recalculation of the brake path rate to the real initial braking rate.
To check the braking system efficiency, the device is attached on the glass of the right or left door of the car. The arrow of the arrow of the device must coincide with the direction of movement of the car being checked. A force sensor is installed on the brake pedal. The sensor cable is connected to the instrument block depending on the source used (car on-board network or rechargeable batteryincluded in the instrument). The device has the ability to print information using a special cable.
7. Elementary diagnostics and adjustmentbrake system work
Organoleptic control. Organoleptic control includes controlling the technical condition of the brake drive elements and the brake mechanisms of the wheels.
When monitoring the technical condition of the brake elements, the following checks are carried out:
Inspection for damage;
Estimate of the performance of a pneumatic brake drive;
Inspection of the correct functioning.
The elements of the TC brake drive are considered faulty in the case of:
The presence of a pipeline contact not provided for by the vehicle with elements of TCs and other defects;
The inability to hold the lever locking device (handle) of the parking brake system;
Non-working state of a pneumatic or pneumatic-hydraulic brake driving pressure gauge;
Disorders of the tightness of the hydraulic brake actuator (the presence of leakage of the brake fluid);
Unreliable fastening;
Response system of signaling and controlling the operation of brake systems in less than four cycles of complete actuation of the working brake system;
Swelling of the brake drive hoses under pressure, damage to the outer layer of hoses, reaching the layer of their reinforcement;
Non-working state of the system of signaling and controlling the operation of brake systems;
The presence of hotels or lateral displacement of the brake pedal;
An inoperable state of the function of automatic emergency braking of the trailer;
The lack of a TC or installation provided by the construction without coordination with the manufacturer either by another authorized organization of additional brake drive elements.
When monitoring the technical condition of the elements of the brake mechanisms of the wheels, the following checks :
Inspection for damage (cracks, residual deformation and other defects);
Assessment of fastening reliability;
Inspection of ease of movement.
The elements of the brake mechanisms of the TC wheels are considered faulty in the case of:
The presence of contaminants impede checks;
The presence of residual deformation, cracks and other defects;
Jamming elements of the brake mechanism; - unreliable attachment;
The lack of a vesicle-provided vehicle or installation without coordination with the manufacturer or another authorized organization of additional elements of brake mechanisms.
With the elementary diagnosis of the car brake system, it is determined by: the free course of the brake pedal; gaps between friction linings and brake drums of wheels; pressure in the brake system; time of operation of the brake mechanisms; The size of the outlet of the rods from the brake chambers; The distance from the end of the pressure regulator lever to the body spar; The performance of the vacuum amplifier.
Free move of the pedal of the brake hydraulic wheels are determined using a special or conventional line. The end of the line is rest in the floor, and the middle part is installed opposite the pedal. Press your hand to the pedal to a noticeable increase in resistance from the pedal when it moves. On the scale of the line records the free move of the pedal.
Control of the free stroke of the brake drive pedal It is recommended to hold on a new car through 2 ... 3 thousand km, and in the future every 20 thousand km. In most brands of passenger cars, with a good braking system, the magnitude of the free move the drive pedal is within 3 ... 6 mm. If free running does not match the norm, the adjustment is made by changing the length of the pusher.
For trucks And buses can be checked and regulated by the full and free course of the brake pedal.
The performance of the vacuum amplifier The brake system is checked in the following sequence. Press the wheel brake drive pedal to about the middle of its full move when disabled Engine, Engine is started and if the brake drive pedal moves downwards, then the vacuum amplifier is good.
When diagnosing the pressure regulator, the car is installed on a lift or inspection ditch. Carefully clean the knit controller and remove the protective case. Sharply click on the brake drive pedal. With a working pressure regulator, the protruding part of the piston will move relative to the housing.
To maintain the brake system in a working condition, periodically before departure, it is necessary to control the level of brake fluid in the tanks, perform adjustment operations.
At that every 10 thousand km, the mileage controls the level of the brake fluid in the tank (tanks), which, when the lid is installed, should reach the lower edge of the filling neck. Value should be liquid only the brand that was used before; Mixing liquids of different brands is unacceptable. If the tank is equipped with a fluid control sensor, then it is necessary to check the sensor operation: by pressing the pusher on the tank cover, observe the turning on the control lamp on the instrument panel. At the time of verification, the engine ignition system must be enabled.
Reducing the level of brake fluid in the tank indicates its possible leakage. Having found a leak, you should carefully examine the entire system and, if necessary, make a suspender of connections or replacing cylinder cylinder cylinders.
An increase in the free stroke of the pedal, its failure and the appearance from the second or third pitching of the feeling of elasticity from the sidden pedal indicate the presence of air in the brake system.
To remove air produce pumping the brake system as well as for the clutch drive. The order of pumping the brake system for each car is individual, but in the absence of specific recommendations, it may be as follows. For automobiles with front and rear contours, first pump the contour of the front wheels, and then the rear, starting in each contour from the wheel, the most remote from the main brake cylinder. For vehicles with diagonal contours, consistently pump out: left rear, right front, right rear and left front wheels.
8. Replacing the brake fluid
After 2 years of operation or every 45 thousand km, the mileage replaces the brake fluid. If the brake system is used with heavy load, for example, when driving through a hilly area or with high humidity, the brake fluid must be changed once a year. Gigroscopic brake fluid, i.e. It is capable of absorbing water molecules from the air. Absorption occurs through the brake hoses and the tank surface made according to rubber and plastics, which are permeable to air molecules. Increased water content in the brake fluid leads to a significant decrease in its boiling temperature, as well as corrosion of the elements of the brake system. As a result, damage to the brake system occurs, and its functioning is significantly worsening and in the hot season may result in education aerial traffic Due to the evaporation of water.
In order to replace the brake fluid into the hydraulic drive system, the air does not fall, the following rules must be followed:
Adhere to the same procedure of action as when pumping the clutch, but use a hose with a glass tube at the end, which is lowered into a vessel with brake fluid;
Pressing the brake pedal, pump up the old brake fluid until the new brake fluid does not appear in the tube; After that, there are two full stroke of the brake pedal and holding it down, the fitting is cleaned; When pumping, they monitor the level of fluid in the tank and the liquid is rapped in a timely manner to the maximum level; repeat this operation on each working cylinder in the same order as when pumping;
Fill the tank to the maximum level and check the operation of the brakes when the car is moving.
For pumping hydraulic brake systems, special installations can be used.
The principle of operation of the installation (Figure 5) lies in the fact that with the help of an elastic inner membrane, it first separates the brake fluid from the air, thereby preventing their mixing and formation of a hazardous emulsion, and then under pressure in 20 MPa, it removes the old brake fluid, replacing it with a new one And removing the air from the system.
Figure 5. Appearance Installations for replacing the brake fluid.
Installation with a large set of adapters included in basic complete setcan replace the brake fluid as in passenger carsand in light trucks.
9. Maintenance features Tor.motor System with Pneumatic Driver
For the pneumatic acting brake systems of the construction of past years (ZIL, MAZ, KRAZ, KAMAZ), adjustment of the gap is produced by changing the position of the 28 expansion fist, which is achieved by rotating the worm of the adjustment lever. The need to adjust the gap is determined by the length of the brake chamber rod, which should not exceed 35 mm for the front and 40 mm for the rear brakes. The difference during brake chamber rods on one axis should not exceed 5 mm.
To check the rod run, you must click on the brake pedal until it stops, feeding compressed air into the brake chamber, and measure the stroke. If the stroke of the brake chamber is exceeding the normative values, then you need to adjust, turning the hexagon head of the adjusting lever shaper counterclockwise (Figure 6) counterclockwise (Figure 6).
Figure 6. Adjustment lever scheme: 1 - housing; 2 - pusher; 3 - movable half-guns; 4 - spring; 5 - plug; 6 - Worm worm; 7 - Sealing ring.
In modern cars and buses to maintain a constant gap between the friction pads of the pad and the disc brake mechanism, equipped with a device for automatically compensating for brake pads. However, the degree of wear of the brake linings and the brake disc should be periodically checked. The frequency of inspections depends on the intensity of the operation of the vehicle, but it should be carried out at least once every three months (if limiting wear sensors are not provided).
The total thickness of the new brake pad C (Figure 7) should be 30 mm, and its thickness of the base D is 9 mm. If the thickness of the friction overlay is at least in one place less than 2 mm, then the brake block is subject to replacement. An insignificant painting of friction material on the edges of the lining is allowed.
Figure 7. Permissible dimensions of the disc and block of vehicles with a pneumatic drive of the brake system: A - the thickness of the brake disc; C - the total thickness of the new brake pad; D - the thickness of the base of the brake pad; E - the thickness of the brake lining; E is the minimum thickness of the brake pad, including the thickness of the base.
The thickness of the brake disk A is measured in the thinner; For a new disk it is 45 mm. The minimum thickness of the brake disc, at which it is subject to replacement is 37 mm. The minimum thickness of the brake pad, including the thickness of the base F, 11 mm; Upon reaching this magnitude, the brake block is replaced.
Pier brake discs It seems appropriate only in exceptional cases - to increase the working surface of the friction lining in the process of work, for example, if there are numerous scratches on the working surface of the brake disc. The minimum disk thickness after the duct should be at least 39 mm.
When replacing the brake pads and, if necessary, a check of the mechanism of automatic clearance adjustment can be checked (Figure 8, a).
To do this, remove the wheel, shifted the movable bracket by its guides towards inner TC, press the inner brake plug 5 from the stops.
Figure 8. Check (A) and adjustment (b) mechanism of automatic adjustment of disc brake mechanisms of vehicles with a pneumatic drive of the brake system: 1 - movable bracket; 2 - tongue-plug; 3 - adapter; 4 - regulator; 5 - brake shoe; 6 - probe; 7 - key.
The clearance is measured between the base of the brake pad and the stops (it must be within 0.6 ... 1.1 mm). The gap is greater or less specified may indicate a malfunction of the mechanism of automatic clearance adjustment, and its performance should be checked. To do this, from the regulator, a special tongue-plug is removed from the regulator 2. The key is put on the adapter 3 and, rotating the adapter counterclockwise, turn the regulator 4 for two or three clicks (towards zazon increases). Press the TC brake pedal 5-10 times (at a pressure of about 0.2 MPa). In this case, if the automatic adjustment mechanism is running, the wrench must turn slightly clockwise. With each next click on the pedal, the angle to which the key rotates will decrease.
If the key does not rotate at all, it turns only when the brake pedal is first pressed or rotated at each press on the pedal, but then returns back, the mechanism of automatic clearance adjustment is faulty and the mobile brake brake brake is replaced.
The pressure regulator in the compressor is adjusted to the beginning of the air supply by the compressor by rotating the cap of the pressure regulator, and the disconnection of the compressor from the system is made using gaskets (with an increase in the thickness of the gasket, the shutdown pressure decreases, and with a decrease - increases). Regulator's response pressure value: 0.6 MPa - switching on; 0.70 ... 0.74 MPa - shutdown.
The safety valve is adjusted with a screw fixed screw, pressure 0.90 ... 0.95 MPa
When servicing a pneumatic drive of the car brakes, first of all, it is necessary to monitor the tightness of the system as a whole and its individual elements. Special attention They turn to the tightness of the connections of pipelines and flexible hoses and at the site of the attachment of hoses, since it is here that compressed air leaks occur most often. The places of severe air leakage can be determined by ear, and the places of weak leakage - with a soap emulsion.
Air leakage from pipelines connections are eliminated by a suspender with a certain point or replacement of individual connections. If the leakage is not eliminated after tightening, then you need to replace rubber sealing rings.
The tightness check should be carried out at rated pressure in the pneumatic reception of 60 MPa, the compressed air consumers included and the non-working compressor. The drop in the pressure from the nominal in air balloons should not exceed 0.03 MPa for 30 minutes with the free position of the drive controls and for 15 minutes with the included.
Care and maintenance of cameras with spring energy accumulators is a periodic inspection, cleaning from dirt, checking the tightness and operation of brake chambers, tightening fastening nuts to the bracket.
Checking spring-pneumatic brake chambers for tightness is carried out in the presence of compressed air in the drive circuit of the emergency or parking brake and in the rear trolley brake drive circuit.
The pneumatic brake actuator has a pressure regulator, combined with a compressed air adsorption dryer. For drying air used adsorbents (special granulated substances). The normal functioning of the desiccant is ensured when 50% of the time it works in air injection mode, and the remaining 50% of the time is regeneration, the process of purging the adsorbent with dry air from the regeneration receiver. Therefore, for the effective operation of the desiccant, it is necessary to monitor the tightness of the pneumatic actuator, not allowing leaks exceeding the established limits. The replacement of the filter element (cartridge) of the compressed air dryer is made as needed when the presence of condensate is found in the pneumatic system receivers. Depending on the operating conditions and the technical condition of the air acceptor devices, the replacement frequency can be from one to two years.
Bibliography
Lecture №5 "Diagnostation and that brake system" is presented in the 2nd part of the lectures on the discipline "Technical operation of cars" and developed for students of specialties 1-37 01 06 Technical operation of cars (in directions) and 1-37 01 07 Full-time car service and correspondence forms of training.
Posted on Allbest.ru.
Similar documents
Device of the brake system with hydraulic drive: Purpose, types, principle of operation. Providing brake system performance: maintenance, repair; possible malfunctions; Organization of diagnostic and adjustment work.
attestation work, added 05/07/2011
The main types of car brake systems and their characteristics. Purpose and device of the brake system of the VAZ-2110 car. Possible malfunctions The brake system, their causes and elimination methods. Safety and environmental protection.
course work, added 01/20/2016
Appointment general device Brake systems of the car. Requirements brake mechanism and drive, their types. Security measures relative to brake fluid. Materials used in brake systems. Principle of operation of the hydraulic working system.
examination, added 08.05.2015
The components of the brake system of tractors. Description of the brake mechanisms with a pneumatic drive. general characteristics Brake pneumatic system of MTZ-80 tractors and MTZ-82. Adjusting the brake crane. Malfunctions of brake systems, ways to eliminate.
coursework, added 20.10.2009
Device and principle of operation of the car brake system VAZ 2109. Regulatory documents regulating the value of the parameters of the effectiveness of these mechanisms. Procedure for diagnosing brake systems, rules for using stand and processing results.
coursework, added 02.06.2013
The device and the principle of operation of the brake system of the car. Principle of operation and main constructive features Working brake systems. Brake efficiency and stability motor vehicle. Conduct the working brake system.
course work, added 13.10.2014
Replacing both brake pads. Girling and Bendix brake system elements. Brake recommendations for car drivers with new brake pads. Troubleshooting brake caliper and brake cylinder pistons, health check.
abstract, added 05/26/2009
Calculation of the ideal and maximum braking moments. Building a diagram of the distribution of specific brake forces. Checking the brake quality of the car for compliance with international regulatory documents. Project calculation of drum brake mechanisms.
course work, added 04/05/2013
Calculation of the parameters of the brake system of the car. The distribution coefficients of the brake forces along the axes. The total area of \u200b\u200bthe brake linings of the wheel brake. Specific permissible friction of friction material. The total corner of the brake pads.
examination, added 14.04.2009
The role of metrological measurements in the automotive industry. Tests of brackets, wheel brake cylinders and brake force regulators, main brake cylinders without vacuum amplifiers, hydraulic amplifiers. Test equipment schemes.