Volkswagen Polo Sedan (Volkswagen Polo Sedan) after entering the market for a variety of reasons has become a real bestseller. Famous brand, modern interior design and exterior, reliable and economical engines, as well as a good level of equipment and safety at an affordable price provided models wide demand.
Moreover, a budget car, similar to more solid models of the brand, also received a selection of transmissions. In addition to the traditional, the sedan can be installed in any configuration.
Read in this article
Polo Sedan ACPP

So, as you know, when choosing cars from the budget segment, many motorists seek to acquire the most reliable technique. At the same time, the pledge of the durable and trouble-free operation of all units is their simplicity in a constructive plan (proven and unpretentious fuel quality engine, manual transmission and minimum of complex technical equipment).
As for the automatic transmission, autolitants consider such a box of complex, dear and unreliable, that is, do not rush to change the mechanics on the machine. It is also believed that the car with an automatic box consumes more fuel and worse accelerates. Partially there is some truth in it, especially if we are talking about the old 4-speed automatic transmission of past generations.
Immediately we note, today the situation has changed somewhat. First of all, modern automatic checkpoints have 5 or more gears, and may also be more economical than mechanics. Also actively working electronics and a number of additional features and modes of automatic transmission allow such a box to compete with MCPP.
- Polo Sedan also did not exception, as Volkswagen offers this car with a modern automatic box. The sedan's polo is a reliable (especially compared to or or).
Transmissions simply not enough factory heat exchanger for cooling. The oil in the automatic transmission is very heated, especially in the heat when driving around the city. The result is a decrease in pressure, oil starvation, accelerated wear, turning of bimetallic sleeves of sliding oil pump and individual elements of the planetary row.
Also among the problems of this automatic transmission, the owners note the main pressure regulator in the hydraulicone. The malfunction of this kind leads to the fact that.
When and why you need to change the oil in an automatic transmission. Replacing transmission oil in Polo Sedan automatic transmission. Tips and recommendations.


On VW Polo Sedan cars, a sedan is installed either a five-speed manual transmission of modification 02T, or a six-speed automatic transmission of the model 09G.
Fig. 6. Manual transmission box Volkswagen Polo Sedan
1 - rear gearbox cover; 2 - leading gear V transmission; 3 - leading gear I gear; 4 - intermediate reverse gear; 5 - leading reverse gear; 6 - drive gear II transmission; 7 - leading gear III gear; 8 - mechanism for switching transmissions MCPP Volkswagen POLO; 9 - leading gear IV gear; 10 - clutch shutdown bearing; 11 - Carter clutch; 12 - primary (presenter) shaft; 13 - semi-axle gear flange for fastening the drive of the right front wheel; 14 - Differential box; 15 - driven gear of the main transfer; 16 - semi-axle gear flange for fastening the drive left front wheel; 17 - Carter gearbox; 18 - secondary (slave) shaft
A mechanical gearbox Gearbox 02T is a compact 5-step unit intended for use in VW Polo Sedan vehicles with an front axle drive. By design, this is a two-channel gearbox with an additional axis of the reverse gear.
At the input and on the outlet shafts, the osospheric gears of continuous engagement are installed. All moving gears rely on needle bearings. This achieves high smoothness of work.
The gear transmission gear of the MCPP Volkswagen Polo Sedan is a straight gear. The movable gears of the 1st and 2nd gears are installed on the output shaft, and the movable gears of the 3rd, 4th and 5th gears are located on the input shaft.
The input shaft relies on the cylindrical roller bearing in the clutch crankcase (movable fastening) and on the ball bearing (motionless mount) in the bearing block in the gearbox crankcase. To reduce the mass, the input shaft is drilled from the inside.
The input shaft has a fixed / movable mount. Like the input shaft, it is installed in the VW Polo Sedan Transmission Carter:
- relies on a cylindrical roller bearing (movable fastening) in the clutch crankcase.
- Rely on the ball bearing (motionless mount) in the bearing block along with the input shaft bearing.
To reduce the mass, the output shaft is drilled from the inside.
The gears of the 1st, 2nd gear and reverse transmission are fixedly fixed on the entrance shaft. The gears of the 3rd, 4th and 5th gears are movable and rotate on needle bearings.
Synchronizers of the 3rd, 4th and 5th gear gear Volkswagen polo sedan fixedly attached on the input shaft on the knaps.
After the displacement of one of the gears, the corresponding "movable gear" also connects motionless with the inlet shaft. In place they are held with spring rings.
The gears of the 3rd, 4th and 5th gear and the synchronizer of the 1st / 2nd transmission are fixedly fixed on the output shaft in the direction of rotation using fine knaps.
In place they are held with spring retaining rings. The movable gears of inclusion of the 1st and 2nd gears rotate on the output shaft on needle bearings.
A new feature of the design of the gearbox Volkswagen Polo Sedan is a modular structure. A typical example of the module is a support plate of bearings with two ball bearings.
Ball bearings are not installed in the gearbox crankcase, but a separate reference plate.
Input and output shafts assembly with gears are installed in the bearing support plate outside the transmission crankcase, so this node is easy to install in the gearbox crankcase.
Two ball bearing for "fixed mounting" of the input and output shafts are part of the node of the bearing plate plate and are installed in it with a tension.
Ball bearings are held by a curly plate. The figure plate is welded to the support plate of bearings.
Ball bearings have radial seals on both sides, preventing from entering the bearings of abrasive particles from the transmission oil.
Bearing support plate flange in the form of glasses with a tight landing is installed in Carter PPC VW Polo Sedan Sedan and attached to the Carter with six bolts.
Two-digit synchronizers of the 1st and 2nd gears Before the gear on the input shaft will be engaged with a synchronizer and with a synchronizer rope with gears on the output shaft, it is necessary that the gears rotate "synchronously" (have been synchronized).
Synchronization of rotation is carried out when transferring transmissions by friction of the cone on the gear and on the synchronizer.
An increase in the area of \u200b\u200bthe frictional surface of the cone is about two times improves synchronization by about 50%, while the force required to switch gear decreases approximately half.
This achieves improved smoothness when switching from the 3rd to 2nd transmission and from the 2nd to the 1st transmission.
Two -Conous synchronizers of each of these gearboxes 02T Volkswagen Polo Sedan consist of the following details:
- Cone synchronizer.
- Ring synchronizer (internal).
- Conical ring.
- Ring of the synchronizer (outdoor).
The differential forms a sedan single node with the MCPP Volkswagen Polo. It is installed on two modernized conical roller bearings in a mechanical gearbox crankcase and in a clutch crankcase.
Differential Carter is compacted outside, in flange shafts, two seals of different diameters. The main transmission gear is row to the videoer of the differential and enters the gear of the output shaft.
The engine torque is transmitted to the gearbox through the input shaft. The torque is transmitted by a pair of gears on the output shaft and from it to the gear of the main transmission with differential. Thus, the torque and turnover depend on the selected gears of the input shaft.

Fig. 7. Drive Manual Gear Management Volkswagen Polo
1 - counterweight lever gear shift; 2 - gear lever; 3 - gear selection lever; 4 - gear shift cable; 5 - gear selection cable; 6 - thermo screen; 7 - Kulis gear lever; 8 - ball support; 9 - Gearbox control lever
Outdoor gearbox switching gearbox Volkswagen polo sedan
To isolate the shift lever from vibration and oscillations created by the power drive, the gearbox is equipped with a switching mechanism with a cable drive.
The connection between the gear shift lever (in the car) and the gearbox is carried out using two cables.
Two cables transmit movement lever movements to select and enable transmissions to the transmission mechanism transmission mechanism MCPP VW Polo Sedan.
The mechanism (lever of the selection and lever of inclusion) converts the movement of two cables forward and backward, as well as to the rotational movement of the gear shift shaft.
On the lid of the switching mechanism there is an angular lever. It allows you to fix the switching shaft in a given position when the repair work is performed. This part greatly simplifies the operation of adjusting the cable switching mechanism.
Internal transmission mechanism MCPP Volkswagen Polo Sedan
Moving the switching mechanism is transmitted to the gearbox from above. The switching shaft moves in the shift mechanism cover.
When the transfer is selected, it is shifted in the axial direction, and when the transmission is turned on, it turns. In certain positions, the gear shift shaft is fixed by two spring-loaded balls.
The plugs of inclusion of the 1st / 2nd and 3rd / 4th gears are installed on radial-resistant ball bearings, thanks to this design, the switching mechanism of the PPC Volkswagen polo works easily. The plug of inclusion of the 5th transmission is set on sliding bearings.
When the transfer is turned on and, therefore, the switching plug is shifted under the action of the shifting of the gear. The segments of the switching on the transmission are located in the limits of the synchronizers of the corresponding pair of gears.
The movement of the gear (right-left) gear lever is converted to the movement of the gear selection cable forward and back with the selector lever. The selector lever turns on the axis.
Using the external mechanism of the VW Polo Sedan gearbox, the movement of the gear selection cable and back is converted to the movement of the shift shaft up and down.
The gear selection cable is attached to the transmitting lever. The transmitting lever is mounted on a hinge on the gearbox crankcase, it is connected through the slider with the switching shaft.
In the gearbox for vertical return-transit movements of the shaft, the appropriate shifting finger is sent to the drive of a specific switching plug of the selected transmission (1st / 2nd transmission; 3rd / 4th transmission; 5th / 6th transmission either reverse).
Machining mechanism for switching on the reverse gearbox VW POLO
To protect against accidental switching on the reverse transmission, a push type retainer is used. The reversing transmission switching mechanism is built into the gear shift mechanism housing.
Before selecting and enable the reverse transmission, the driver should unlock the locking mechanism.
When you try to enable the reverse transmission, just as the front run transmission, the switching lever stop lever rests on the retainer (part of the switching mechanism case).
When pressing the lever and overcoming the force of the spring, the lever is moving down through a spherical guide switching lever, while the locking protrusion is lowered below the retainer.
During the subsequent movement of the selector to switch the reverse transmission, the retainer does not prevent the movement and turn on the reverse transmission becomes possible.
Spring pushes the gear lever back to the position turned on and holds it in the reverse transmission position.
Adjusting the cable switching mechanism MCPP VW Polo Sedan
The procedure for adjusting the transmission gear mechanism is simplified due to the presence of an angular lever on the cover of the switching mechanism and the retaining pin of the gear lever.
The adjustment procedure always begins with switching the transmission of the Volkswagen Polo sedan gear:
Disconnect the cables. The locking mechanism on the shift cable and the selection cable is shifted forward until it stops, then blocked by turning to the left. Now you can adjust the length of the cable.
Block the switch shaft. A corner lever is installed on the gear shift mechanism cover, which allows you to block the gear shift shaft.
To do this, shift the switch down to the position between the 1st and 2nd gears. By pressing it down, click on the corner lever towards the switching shaft, then turn it. The angular lever will lock and block the switching shaft in this position.
Locking gear lever. Gearbox lever GPP Volkswagen Polo sedan should be transferred to the position of neutral transmission between the 1st and 2nd gears.
On the gear lever there is a locking hole. Through this hole into the hole under the gearbox housing, the lock pin is inserted.
Fixation of cables in place. Now the locking mechanism on the selector cable and on the switching cable can be returned again. The spring displays the locking mechanism to a specified position and holds it in place. After that, we should again weaken the corner lever and remove the lock pin.
The gear shift lever should now be in the neutral transmission position between the 3rd and 4th gears.
Volkswagen Polo Sedan - a popularly beloved car, produced since 1975. For a long time the existence of the brand, 5 generations of the vehicle came to the markets.
Manual Transmission
The Volkswagen Polo Sedan car is installed on a five or six-speed mechanical gearboxes. The transmission is performed on a two-shoulded scheme with synchronized transmissions. In the manual transmission, the main transmission with differential is combined with a common crankcase.
Types of repair of mechanical transmission
The narration should be started with the fact that the repair of the GPAP polo sedan is partial or capital. With local recovery, the box is removed, disassembled, washed, defects. Defecting - the process of determining the cause of the breakage. After a defective, the master 100% will correctly indicate a specific malfunction. Overhaul also implies a complete removal of the unit. Mechanisms:
- completely dealt;
- are washed;
- defecting is carried out, but completely.
Faulty mechanisms are determined, spare parts that were worn and do not function.
Causes of breakage and solving the problem
- With spontaneous shift switching, the ships of switching shifts were most likely made or a breakdown of the retainer springs occurred. The closure of the synchronizer clutch on the hub can also be increased. It will help only the professional repair of the MCPP Volkswagen Polo 1,4, conducted in the service.
- Switching gear is difficult and hearsed in a crush? The reason becomes the incomplete clutch shutdown, the malfunction of the gear shift drive cables, a significant attenuation of the synchronizer springs, a bodied oil that does not meet the requirements established. The way to solve the problem is the repair of the clutch shutdown drive, removal from the air hydraulic system. It will also be necessary to pour the oil of the desired brand to try to eliminate the problem, conducting the repair of the MCPP Volkswagen Polo sedan with its own efforts.
- Does it take scrape and felt vibration in the gearbox? Possible causes of non-correct functioning are weakening fastening or damage to the engine supports or manual transmission. There may also be worn or damaged by the gears, the idling engine is impaired. Solving the problem is pulling up fastenings or replace support. If it is impossible to independently diagnose the system of the system in 100% of cases, a professional inspection of the car and the subsequent repair of the MCPP Volkswagen Polo sedan 1.6 in the service is required.
Quality Warranty - Professional Masters Help
Urgent repair of MCPP Volkswagen Polo? Contact our service where a large spare parts warehouse has more than 5,000 items. During the restoration work, the wizard uses only the equipment that meets the requirements of the manufacturer's plant. Specialists of the service have a high level of qualifications and a rich experience in repairing mechanical transmissions.
Do not try to solve the problem yourself, because quality repair is a privilege of professional masters.
The Volkswagen Polo sedan can be equipped with one of two gearboxes: either a six-speed automatic 09G, or a five-speed mechanical 02T.
09G Automatic Transmission
Constructed along the traditional planetary scheme with braking frictions and through the torque converter is connected to the engine crankshaft. The electronic control system control system constantly monitors the vehicle speed and engine load, eliminates the driver's errors. At a low speed of movement, the control system in order to avoid engine overload does not allow to turn on higher transmission. It is not possible to turn on the downward transmission at too much speed to prevent the maximum permissible speed of rotation of the crankshaft engine. When a reduction in the speed of the car transmission is automatically, without the participation of the driver, switch to lower frequencies. At the time of the full stop of the car automatically turns on the first gear.
The automatic transmission consists of a torque converter, a pump, a planetary gearbox, multi-disc clutch, multi-disc brakes and valve block.
Hydrotransformer Plays the role of clutch. At the beginning of the car movement, it smoothly connects the engine and the gearbox mechanism, and also increases the torque. The housing of the hydrotransformer is connected to the engine crankshaft via the drive disk and constantly rotates when the engine is running. The inner cavity of the hydrotransformer is filled with the working fluid. The engine rotates the torque converter, which results in a pumping wheel, creating flows of working fluid in the direction of the turbine wheel. The latter begins to rotate due to the streams of the working fluid generated by the pumping wheel. With a high difference in the rotational speeds of turbine and pumping wheels, the reactor changes the direction of fluid flow, increasing the torque. As the difference in speeds decreases, it becomes unnecessary and therefore installed on the overtook coupling.
Hydraulic system Control automatic transmission includes a pump, pressure regulator, an acute range selection valve, auxiliary valves (solenoids), couplings and brakes. The pump installed in the front of the gearbox crankcase creates pressure and supplies the working fluid to all systems in the gearbox.
Planetary reductor Ravinium systems - gear transmission with external and internal gearboxes, which provides various ways to connect its elements to produce various gear ratios.
Planetary rows Corresponds to the gear unit in a manual transmission and help change the transfer ratio in an automatic transmission when switching transmissions.
Ribbon brakes temporarily block the elements of the corresponding planetary row on the automatic transmission body.
Control drive Automatic gearbox Cable, designed by the same principle as the drive control of the manual box, but differs from it by the number and design of parts. The salace of the automatic transmission selector is installed in the same place on the floor tunnel as the mechanical box control lever, and connected to the control unit on the gearbox cable.
Differentialconical, four-palitite. The hermetic compound of the internal hinges of the front wheels with the differential gears is provided with decompositions.
Manual gear 02T
Made on a two-walled scheme with synchronized transmissions. The gearbox and the main transmission with differential have a common crankcase. Carter clutch is connected to the front of the gearbox crankcase. On the back of the gearbox crankcase installed steel stamped cover.
On the primary shaft, the leading gears I and II gear and reverse gear, made in one integer with the primary shaft, and the leading gears III, IV and V transmissions are freely rotated on needle bearings.
The secondary shaft is combined with the lead gear of the main transmission, in addition to the shaft, freely rotating on the bearings of the sliding gears I and II gears are installed on the shaft. The driven gears III-V gear and reverse transmission are installed on the slots.
Front transfer transmissions are included with the axial movement of the couplings of two synchronizers and III-IV gears installed on the secondary shaft and primary shafts, respectively, as well as the clutches of the transmission synchronizer, installed on the primary shaft. The reverse gear is turned on in the engagement of the intermediate reversing gear with the driven gear, which is a crown made in one integer with the inclusion coupling I and II gear installed on the slots of the secondary shaft. The gear shift mechanism is located inside the gearbox crankcase. Outside there are two levers of the mechanism: the switching lever and the gear selection lever.
The mechanical transmission control drive consists of a gear shift lever with a ball support installed on the body base, two shift and gear cables, as well as a mechanism located in the gearbox crankcase. To ensure a clear switching on the gear gear shift lever, the switching mechanism is made in one integer with a massive counterweight. From heating by thermal radiation of the exhaust gas release system, the cables are protected by thermo-screen installed on the basis of the body. Cables for choosing and switching gear are constructively different from each other and not interchangeable.
main gear Consists of a pair of cylindrical gears, selected by noise. The torque is transmitted from the head gear of the main transmission to the differential further on the drives of the front wheels.
Differentialthe mechanical transmission in the design is completely similar to the differential automatic transmission.
Mechanical transmission VW Polo Sedan: 1 - flange of the drive of the right wheel; 2 - Carter clutch; 3 - primary shaft; 4 - gearbox switching mechanism; 5 - retainer for adjusting the transmission control drive; 6 - Carter gearbox; 7 - reverse light switch; 8 - rear lid; 9 - Sapun; 10 - left-wheel drive flange; 11 - plug hole.
Drives front wheels
The drives of the front wheels include external and internal hinges of equal angular velocities (Sls) connected by the shafts of the drives. The outer hinge provides the possibility of only the angular movements of the connected shafts. Internal hinge additionally to the corner provides axial shifts of shafts when turning the front wheels and the operation of the suspension.
Birfield Outer hinge consists of a housing, separator, closure and six balls. To accommodate balls in the hinge body and in the cable, grooves are made. In the longitudinal plane, the grooves are made along the radius. This provides the desired angle of rotation of the exterior hinge. The slot tip of the exterior hinge body is set in the hub of the front wheel and is attached to her nut. Outdoor hinge rope is installed on the shaft slots and fixed on the shaft by a locking ring.
Internal car drive hinge with a mechanical gearbox type of lebro, like a birfield type hinge, consists of a housing, separator, clip and six balls. In the hinge body and in the cable, grooves are made to accommodate balls. The difference of this hinge from the birfield type hinge is that the grooves of the hinge housing are made straight, and not by radius, which allows the details of the hinge to move in the longitudinal direction. The housing of the inner hinge is attached with six bolts to the flange with the outer slots, fixed in the semi-axle gearbox of the transmission with a spring retaining ring installed in the flange shank proto. The hint of the inner hinge is installed on the shaft slots and is fixed on the shaft of the locking ring.
In external joints of the Birfield type and lebro, the balls of one sorting group are installed. All the details of the hinge are selectively selected to each other, so it is impossible to repair the hinge of the replacement of individual parts, moreover, only a hinge is supplied to the spare parts, as well as a small Remkomplekt, which includes a locking ring, cover, casing clamps and in some cases lubricant .
The internal car drive hinge with a manual transmission type TRIPEZ consists of a housing and three rollers on needle bearings, attached to the trunky hub. In the hinge case, grooves are made for rollers. The three-type hub is fixed on the shaft by a locking ring of the rollers allow the hub to move in the grooves of the hinge housing in the axial direction, so that the drive can lend or shorten to compensate for the mutual movement of the suspension and the power unit. The tip of the internal hinge case with the outer slots is fixed in the semi-axis gearbox gearbox with a spring retaining ring, installed in the shaft of the internal type hinge of the tripod supplied into spare parts in the form of two repair kits: a large, including all the details of the hinge, and a small, similar to remarklete of the outer hinge .
For lubrication of hinges, a special lubricant is used with the Molybdenum disulfide (domestic analog of SCRM-4). The cavities of all hinges are protected from road dirt and water to rubber corrugated covers, fixed on hinges and shaft shafts by clamps: respectively, large and small.
The drives of the drives differ in length, therefore the drives of the right and left wheels are non-violent.

Drives of right "a" and left "in" wheels Volkswagen Polo Sedan (MCPP): 1- Corps of the internal hinge; 2 - holder of the dirt cover of an internal hinge; 3 - dirt cover of an internal hinge; 4 - clamp fastening of the dirt cover of the internal hinge; 5 - Right wheel drive shaft; 6 - small clamp fastening of the dirt cover of external hinge; 7 - Fiberglass Outdoor Hinge Case; 8 - a large clamp of the fastening of the dirt cover of the outer hinge; 9 - exterior hinge body; 10 - protective washer; 11 - Left wheel drive shaft.
Clutch
Dry one-piece grip with a central diaphragm spring is installed on the Volkswagen Polo sedan cars with a manual transmission.
Pressure disk Mounted in a steel stamped casing attached by six bolts to the engine flywheel.
Slave disk Located on the slots of the primary shaft of the gearbox and clamped the diaphragm spring between the flywheel and the pressure disk.
Clutch shutdown bearing On the guide sleeve is attached by two bolts to the clutchcap and moves along the sleeve with a fork based on the ball support, screwed into the clutch crankcase. The ball support is powered by a clutch shutdown hydraulic cylinder. The bearing is fixed on the fork with two spring locks. The plug is fixed on the ball support also a spring retainer.
Hydraulic clutch off:
- the main cylinder installed in the engine compartment of the working cylinder;
- pipeline enclosing the tube and hoses;
- the clutch pedal connected to the pinner of the main cylinder by the retainer.
The main cylinder is connected by a hose with a tank, common to both major cylinders and installed on the main brake cylinder. The working cylinder is attached by bolts to the gearbox carder and affects its rod on the plug. A brake fluid is used in the clutch shutdown hydraulic drive. Adjusting the clutch shutdown drive is not provided.

Clutch elements VW Polo Sedan: 1 - Carter clutch; 2 - clutch shutdown lever; 3 - clutch shutdown bearing; 4 - push clutch cover assembly ("Basket"); 5 - clutch casing; 6 - slave disk; 7 - flywheel.
On Volkswagen Polo cars, a sedan is installed either a five-speed manual transmission mod. 021 or a six-speed automatic transmission pattern mod. 09g.
The mechanical transmission is made according to a two-time scheme with synchronized transmissions. The gearbox and the main transmission with differential have a common crankcase. Clutch Carter 11 is connected to the front of the gearbox crankcase. On the back of the crankcase
Manual gearbox: 1 - rear gearbox cover; 2 - leading gear V transmission; 3 - leading gear I gear; 4 - intermediate reverse gear; 5 - leading reverse gear; b - leading gear II transmission; 7 - leading gear III gear; 8 - gear shift mechanism; 9 - leading gear IV gear; 10 - clutch shutdown bearing; 11 - Carter clutch; 12 - primary (presenter) shaft; 13 - semi-axle gear flange for fastening the drive of the right front wheel; 14 - Differential box; 15 - driven gear of the main transfer; 16 - semi-axle gear flange for fastening the drive left front wheel; 17 - Carter gearbox; 18 - secondary (slave) shaft
gearbox installed steel stamped cover 1.
On the primary shaft 12 there are leading gears I and II gears and transmission of the reverse, made in one integer with the primary shaft, and the leading gears III,
IV and V transmissions are freely rotated on needle bearings.
The secondary shaft 18 is made together with the leading gear of the main transmission, in addition to the shaft, freely rotating on the bearings of the sliding gears I and II gears are installed on the shaft. Leaded gears III,
IV and V gear and reverse transmission are installed on the slots.
The front-end transmissions are included with the axial movement of the couplings of the two synchronizers Hi and III-IV gears installed on the secondary valves of the primary shafts, respectively, as well as the clutches of the transmission synchronizer, installed on the primary shaft. Reverse transmission turns on to the engagement of the intermediate gear 4 of the reverse with the slave
Gear is a secondary shaft. The gear shift mechanism is located inside the gearbox crankcase.
Outside there are two levers of the mechanism: the switching lever and the gear selection lever.

Manual control control drive: 1 - counterweight gear lever; 2 - gear lever; 3 - gear selection lever; 4 - gear shift cable; 5 - gear selection cable; b - thermo screen; 7 - Kulis gear lever; 8 - ball support; 9 - Gearbox control lever
The mechanical transmission control drive consists of 7 ychaga 9 shifting gear with ballproof 8 installed on the body base, two switching cables 4 and select 5 gears, as well as a mechanism located in the gearbox crankcase. To ensure a clear inclusion of the gear shift arm 2, the switching mechanism is made in one integer with a massive counterweight 1. From heating with thermal radiation of the exhaust gas release system, the cables are protected by thermo-screen 6 installed on the base of the body. The selection and gear shift cables are constructively different from each other and non-refamous.
The main transmission is made in the form of a pair of cylindrical gears, selected by noise. The torque is transmitted from the drive gear of the main transmission to the differential and then on the drives of the front wheels.
Differential conical, four-telled. The tightness of the junction of the vortices of them hinges of the front wheels with the gears of differential is provided by the glands.
The automatic box is transmitted by the traditional planetary scheme with frictional braking and connected to the engine crankshaft through the torque converter. The electronic control system of the automatic transmission constantly monitors the speed of the car and the engine load, eliminates the driver's errors, not allowing it to turn on a higher transmission at a low speed speed to avoid engine overload, or downward transmission at too much speed, which eliminates the possibility of exceeding the maximum permissible frequency Rotation of the crankshaft engine. When a reduction in the speed of the car, the transmission automatically switches to lower without the driver's participation. At the time of the complete stop of the car automatically turns on I gear.
Details of the automatic transmission control algorithm described in the "car device"
The automatic transmission consists of a torque converter, a pump, a planetary gearbox, multi-disc clutch, multi-disc brakes and valve block.
The hydrotransformer plays the clutch role and serves to smoothly connect the engine and the gearbox mechanism and increase the torque at the beginning of the car movement. The housing of the hydrotransformer is connected to the engine crankshaft via the drive disk and constantly rotates when the engine is running. The inner cavity of the torque converter is filled with the working fluid for automatic transmissions. The engine rotates the torque converter and activates the pumping wheel, which creates flows of working fluid in the direction of the turbine wheel. The latter begins to rotate due to the streams of the working fluid generated by the pumping wheel. With a high difference in the rotational speeds of turbine and pumping wheels, the reactor changes the direction of fluid flow, increasing the torque. As the difference in speeds decreases, it becomes unnecessary and therefore installed on the overtook coupling.
The hydraulic control system of the automatic transmission includes a pump, pressure regulator, an acute range selection spool valve. Auxiliary valves (solenoids), couplings and brakes. The pump installed in the front of the gearbox crankcase creates pressure and supplies the working fluid to all systems in the gearbox.
The planetary rows correspond to the gear unit in the manual transmission and serve to change the transfer ratio in the automatic transmission when switching gear.
The planetary gearbox of the Ravinium system is a gear transmission with external and internal gears, which provides various ways to connect its elements to produce various gear ratios.
Ribbon brakes serve to temporarily block the elements of the corresponding planetary row on the automatic transmission body.
Drive automatic transmission control drive is designed by the same principle as the drive control of the manual box, but differs from it by the number and design of parts. Kulis 4 (Fig. 6.8) The automatic transmission selector is installed in the same place on the floor tunnel 3 as the mechanical box control lever, and is connected to the control unit on the gearbox 7 cable 1.
Differential automatic transmission in the design is completely similar to the mechanical transmission differential.

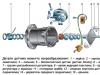
Automatic gearbox: 1 - Carter of the main transmission gearbox; 2 - heat exchanger of the working fluid; 3 - bracket left support suspension of the power unit; 4 - selector position sensor; 5 - casing of the hydrotransformer; B - hydrotransformer

Automatic transmission control drive: 1 - transmission control cable; 2 - handle lever gear control selector; 3 - tunnel floor; 4 - Kulis of the gearbox control; 5 - Cover of the gearbox control selector; b - cable holders; 7 - gearbox
To repair the gearbox, especially automatic, a large set of special tools and the corresponding artist preparation is required, so in this section only the removal and installation of the gearbox, replacing its seals, repairing the drive. If necessary, repair the gearbox in a specialized service.