Qualification - Technician
The profession of "car mechanic" was born with the development of road transport. The production and operation of cars increased the need for people to repair them in the event of a breakdown. With the invention of the conveyor belt by Henry Ford (1930s), the number of cars increased dramatically. This created the need for an increase in the number of people who know how to keep the car in good working order. The increasing complexity of the design of the car and the emergence of complex diagnostic equipment (50s of the XX century) leads to the separation of the specialties of the car mechanic: minder, auto electrician, painter, vulcanizer, etc. Today this the profession remains in demand, because the number of cars produced is growing steadily, and progress does not stand still. Noisy and dirty, they will gradually leave the city, and they will be replaced by highly efficient and environmentally friendly transport. Transport of the futureare solar-powered machines converted to use hydrogen. It does not matter that you are in heavy traffic, you have a "smart" car. Equipped navigation system, the car will pave the way in a fast stream, and the driver can relax. There are many predictions and fantasies about what the car of the future will be like. Many scientists are working on the latest technology in the automotive industry. Whatever it is, its main task - to serve a person will remain unchanged.
Transport of the futureare solar-powered machines converted to use hydrogen. It does not matter that you are in heavy traffic, you have a "smart" car. Equipped navigation system, the car will pave the way in a fast stream, and the driver can relax. There are many predictions and fantasies about what the car of the future will be like. Many scientists are working on the latest technology in the automotive industry. Whatever it is, its main task - to serve a person will remain unchanged.
That is why the specialty " Maintenance and repair of road transport ”is now in demand and highly paid.
Reliable work depends on the work of a car mechanic vehicle... The car mechanic monitors the technical condition of the car and, if necessary, carries out its timely repair. The safety of the movement of passengers in the car will depend on how the car mechanic tries. So responsibility is a necessary professional quality of a car repair mechanic.
Our graduates work in various transport companies, service stations. Many open their workshops and shops.
On the basis of the college there are training workshops, materially - technical base which allows you to practice during the training period, as well as to carry out college car repairs. In the same workshops, students carry out their graduation projects.
Students receive theoretical materials in specially equipped rooms equipped with various stands made by students of graduating groups as a thesis, as well as modern methods and programs for training specialists based on the latest achievements of science and technology.
The main task of training specialists for us is to bring them to the forefront of science and technology, while simultaneously developing analytical thinking and the ability to apply the knowledge gained in practice, which will allow them to be competitive and find employment in the most profitable for themselves in the future.
Every year the competition "Best in Profession" is held, where our students take an active part and win prizes.
On the day of the motorist, students of our college lay flowers at the monument to the soldiers - motorists of 1941-1945. On this day, there is an exhibition of rare cars that you will not find on an ordinary day.
During college, students can learn all the intricacies of the device, maintenance and repair. automotive engineering, learn how to professionally drive a car and a truck.
Also, students have the opportunity to study at a driving school at the FGBOU VPO SSTU named after Gagarin Yu.A. and get right.
 Personal qualities:
Personal qualities:

The car mechanic works both indoors (workshops, boxes, garages) and outdoors. It is possible to perform work in very uncomfortable positions. Large load on the musculoskeletal and visual apparatus.
A car repair mechanic can work both alone and in teams, interacting with specialists of other profiles. In this case, he needs the ability to work in a team, a developed sense of responsibility for the work of the team as a whole, as well as for the high-quality performance of all the work performed by different specialists.
:
- visual and hearing impairment;
- chronic diseases of the joints, deformity of the fingers;
- dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- allergic diseases;
- respiratory diseases;
- neuropsychiatric disorders.
Admission of applicants
| Name specialty |
Base | Term learning |
Form of study |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maintenance and repair road transport 23.02.03 Qualification - Technician |
based on 9 classes | 3 years 10 months | Full-time education |
| based on 11 classes | 2 years 10 months | Extramural studies | |
| Full-time education |
State educational standard in the specialty "Maintenance and repairroad transport» for the training of a specialist in this profile, it involves the study of manyprofessional and special disciplines:

To carry out competent maintenance and repair of road transport, a specialist must know not only its structure, but also understand the processes that occur during its operation. It is necessary to know and understand the physical and chemical processes occurring in the engine during its operation.
Successful mastering of the program will allow the student to understand that the specialty he has chosen is interesting and will be in demand by society, both today and in the foreseeable future. A car, like a living creature, requires daily care and maintenance, timely repairs and continuous diagnostics of its condition. Fulfillment of these requirements will allow you to operate the car for a long period and successfully perform the work.
 Upon completion of training, you will be able to work:
Upon completion of training, you will be able to work:
- bus and taxi fleets;
- trucking companies;
- convoys;
- transport shops;
- companies engaged in cargo transportation;
- car services;
- motor sports;
- service stations and instrumental control of cars;
- the automobile divisions of the Armed Forces and the Police.
INFORMATION FOR PARENTS

The area of professional activity of graduates in the specialty "Maintenance and repair of road transport": organization and performance of maintenance and repair works of motor vehicles, organization of activities of primary labor collectives.
Advantages of the specialty:

Profession restrictions: disgust for "dirty" work, the need to constantly master new technologies, high physical stress, high responsibility for the end result.
A road vehicle maintenance and repair technician prepares for the following activities:
- Maintenance and repair of vehicles.
- Organize and carry out maintenance and repair work for vehicles.
- Realize technical control during storage, operation, maintenance and repair of vehicles.
- To develop technological processes for the repair of units and parts.
- Organization of the activities of the team of performers.
- Plan and organize maintenance and repair work for vehicles.
- Control and evaluate the quality of the work of the contractors.
- Organize safe work during the maintenance and repair of vehicles.
FEDERAL AGENCY FOR CONSTRUCTION AND Housing and Utilities.
Far Eastern State Interregional Industrial and Economic College.
Specialty: 1705.
"Maintenance and repair of motor vehicles".
Course work
on the subject:
Industry economics
Option number 9
Checked: Completed:
teacher: student of group TOPA - 51
/ S.V. Lapteva ../ / V.A. Kopeikin /
"" 2005 "" 2005
Khabarovsk.
Introduction.
1.1. Description of the enterprise.
2. Settlement part.
2.1. Calculation of the wage fund.
2.1.2. Calculation of the wage fund for auxiliary workers.
2.1.3. Calculation of the wage fund for foremen and employees.
2.2. Calculation of the unified social tax.
2.3. Calculation of costs for materials and spare parts.
2.5. Cost calculation and calculation for 1000 km of run.
Conclusion on the project.
 1. Settlement - explanatory note.
1. Settlement - explanatory note.
1.1 Introduction.
Automobile transport is of great importance, as it serves all sectors of the national economy. Passenger traffic by buses and cars on intracity, suburban and international routes is increasing annually. In our country, the range of transportation of goods and passengers is continuously increasing due to an increase in the performance of cars, an improvement highways and building new ones. The production of trucks and road trains of increased carrying capacity is significantly increasing - the most important reserve for increasing the efficiency of using road transport, since its productivity increases and the cost of transportation, and hence the cost of goods, decreases.
To successfully solve the tasks set by road transport, it is necessary to constantly maintain cars in good technical condition, create a maintenance organization that would provide for the timely and high-quality performance of all car care operations. At the same time, it is necessary to use the correct techniques for performing each operation and widely use the means of mechanization. Qualified performance of maintenance works ensures trouble-free operation of units, assemblies and systems of vehicles, increases their reliability and maximum turnaround times, increases productivity, reduces fuel consumption, reduces transportation costs, and improves traffic safety.
Improving the quality of services by accelerating the pace of scientific and technological progress based on the reconstruction of existing enterprises and the widespread introduction of new technology and advanced technology rational forms and methods of organizing production and labor, provision of spare parts, effective management of production activities and quality control of work. Development and improvement of cars repair production require the correct organization of car repair, which in turn depends on a number of factors, the most important of which is the rational location of repair enterprises, their specialization and production capacity. The efficiency of the use of vehicles depends on the perfection of the organization of the transport process and the properties of vehicles to keep within certain limits the values of the parameters characterizing their ability to perform the required functions. During the operation of the car, its functional properties gradually deteriorate due to wear, corrosion, damage to parts, fatigue of the material from which they are made, etc. Various malfunctions appear in the car that reduce the efficiency of its use.
To prevent the appearance of defects and their timely elimination, the car is subjected to maintenance (MOT) and repair. MOT is a complex of operations or an operation to maintain the health or serviceability of a car when used as directed during parking, storage or transportation.
Repair is a complex of operations to restore performance and restore the resource of a car or its component parts.
1.2. Characteristics of the design object.
HPATP-1 is a municipal enterprise, and is subsidized. It is located in the city of Khabarovsk at the address: Prospect 60-letiya Oktyabrya 17. To calculate the cost of work at the electric starter repair site, a group of indicators of initial data for design is taken. From the design assignment, the following is accepted:
· Type of rolling stock LiAZ-5226;
· Аи - the average listed (inventory) number of cars 153 units;
· Lcc - average daily mileage of the car 153 km;
·  Natural and climatic conditions of operation (moderately cold - 0.9);
Natural and climatic conditions of operation (moderately cold - 0.9);
· Drg - the number of working days in a year 365;
· Тн - the duration of the rolling stock operation on the line 12.3 hours.
Li - coefficient of production of cars per line 0.8
·  Tob.pr. - labor intensity of the projected section (electrical workshop for the repair of starters) - 9046.2 people / hour.
Tob.pr. - labor intensity of the projected section (electrical workshop for the repair of starters) - 9046.2 people / hour.
S - area of the site (zone) - 36m2
· Correction of standards are taken from the Regulations.
K1 - coefficients for adjusting standards depending on the category of operating conditions - (0.8) table. 2.8 & 2.7;
· K2 - coefficient of standard correction depending on the modification of the rolling stock and the organization of its work - (1) table. 2.9;
K3 - coefficient of adjustment of standards depending on natural and climatic conditions and aggressiveness of the environment - (0.9)
A list of the required equipment with an indication of the power of the pantographs:
 2. Settlement part.
2. Settlement part.
2.1. Calculation of the wage fund for repair workers.
To determine the cost of remuneration of repair workers, a time-based bonus system of remuneration is proposed.
Calculation of the number of main workers.
The number of repair workers at the design facility, Nrr people, is determined by the formula:
![]() people we accept 3 people. (one)
people we accept 3 people. (one)
where; Tob.pr. - labor intensity at the design object, person / hour;
FRV - fund of working time of one worker, hour
FRV = [Dk - (Dv + Dpr + Dot + Db + Dgo)] * tcm - (Dpv + Dpr) * t, (2)
where; Dk - the planned period, Dk = 365 days;
Dv - weekend, Dv - 52 days;
Дпр - holidays according to the calendar, Дпр = 11дп;
DB - days of absence from work due to illness and other good reasons, DB = 5 days;
Dgo days of absence from work in connection with the fulfillment of general economic and state tasks, Dgo = 1 day;
Dot - vacation days; Dot - 31 days
tcm - shift duration; tсm - 12.6
Dvp - pre-weekend days (Saturdays); DVP - 52 days
Дпр - pre-holiday days according to the calendar;
t - The time of the shortened working day. 1 hour.
FRV = * 12.6 - (52 + 11) * 11.6 = 2070 hours.
2.2 We make the distribution of workers by categories in accordance with the types of work performed.
Table No. 1
Calculation of the average discharge Rav, is performed according to the formula;
![]() (1)
(1)
where; N 1 - N 6 - respectively, the number of repair workers, people;
R 1 - R 6 - corresponding digits;
Npp - the number of repair workers, people.
![]()
When calculating the hourly tariff rates for repair workers of 2-6 categories, we make the calculation according to the formula:
![]() (2)
(2)
where; - hourly tariff rate of the 1st category;
Ktar is the tariff coefficient of the corresponding category.
 |
Hourly tariff rate of the 3rd category Hour, rub., Is calculated by the formula:
Hourly tariff rate of the 4th category Hour, rub., Is calculated by the formula:
The calculation of the average hourly wage rate with a fractional value of the average category of rubles is carried out according to the formula;
![]() (3)
(3)
where; Cm - tariff rate of the lower of two adjacent categories, rubles;
Sat - tariff rate of the largest of the adjacent categories, rubles;
Кр - fractional part of the category.

Wage fund at the tariff rate.
The calculation of the payroll at the wage rate of the federal budget, rubles, is carried out according to the formula:
FZPt = Ssr * Tob.p., (4)
Where; Сср - average hourly tariff rate, rubles;
Tob.p. - labor intensity at the design object.
FZPt = 7.47 * 5896.4 = 44,046.1 rubles.
Calculation of surcharges and bonuses.
 Additional payments for unfavorable working conditions Dnebl.usl.t. - 10% in jobs with difficult and hazardous working conditions. Calculation of additional payments for repair workers, according to the formula;
Additional payments for unfavorable working conditions Dnebl.usl.t. - 10% in jobs with difficult and hazardous working conditions. Calculation of additional payments for repair workers, according to the formula;
where; Сч - average hourly wage rate of a repair worker, rubles.
FRV - working time fund, hour
Pnebl.service.t. - percentage of additional payment for unfavorable working conditions,%
Npp - and the number of repair workers, people.
Calculation of additional payments for work in the evening hours.
The surcharge is calculated using the formula;
where; 20 - the amount of additional payment for work in the evening,%
TWh - the number of hours worked by one in the evening, i.e. from 18 to 22 hours.
Drvch - the number of working days per year with work in the evening, days.
Npp - number of repair workers working in the evening hours, hour.
Сч - average hourly tariff rate, rub.
Award for exceeding quantitative indicators and quality of work.
The amount of the premium P, rubles, is calculated by the formula;
![]() (7)
(7)
 where; FZPt - payroll according to the tariff, rubles; npr - premium rate, n = 50%
where; FZPt - payroll according to the tariff, rubles; npr - premium rate, n = 50%
![]()
Calculation of basic wages.
The calculation of the basic salary of FOZPrr, is calculated by the formula:
FZPrr = FZPt + D + P (8)
where; FZPt - wage fund at the tariff rate, rubles;
P - premium for repair workers;
D - additional payments.
D = 4123.44 rubles.
FOZPRr = 44046 + 4123.4 + 22023 = 70192 rubles.
Calculation of additional wages.
The rate of additional wages Ndop. %, calculated by the formula;
![]() (9)
(9)
where; Dot - duration of paid vacation, 31 days;
Dk - calendar period, 365 days;
Dv - the number of Sundays, 52 days;
Дпр - quantity holidays, 11 days.
Additional wages fund FD, rubles, is calculated by the formula;
![]() (10)
(10)
where; FOZPRr - basic wages fund for repair workers, rubles,
Ndop - the rate of additional wages.
 |
2.1.1. Calculation of the wage fund for repair workers.
The calculation of the wage fund payroll, rubles, is made according to the formula:
FOTrr = (FOZPrr + FDZPrr) * 1.5 (11)
where; FOZPrr - basic wages fund for repair workers, rubles;
ФДЗПрр - fund of additional wages of repair workers, rubles;
1.5 is the sum of the regional coefficient (1.2) and the seniority bonus (30%).
FOTrr = (70192.4 + 8703.8) * 1.5 = 118344.31 rubles.
Calculation of the average monthly wage of one worker, salary, rub. produced by the formula:
![]() (12)
(12)
where; FOTrr - payroll fund;
Npp is the number of workers;
12 - the number of months in a year.
![]()
2.1.2. Calculation of the wage fund for auxiliary workers, foremen and employees.
The wage fund for auxiliary workers at the wage rate of FZPvr, rubles, is calculated by the formula;
 (13)
(13)
 |
Where; Tvr - the wage rate of the auxiliary worker;
Tob.p. - labor intensity at the design object;
20 - the rate of labor intensity of auxiliary work,%.
Auxiliary worker bonuses.
The calculation of bonuses to auxiliary workers Pr.vr., rubles, is carried out according to the formula;
![]() (14)
(14)
where; nвр - the rate of bonus for auxiliary workers, 10% lower than that of repair workers (40%).
FZP time. - wage fund for auxiliary workers at the tariff rate, rubles.
Basic wages of auxiliary workers.
The calculation of the basic wages fund for auxiliary workers of the FOZPvr, rubles, is carried out according to the formula;
FZPvr = FZPvr + PR.vr. (15)
where; ФЗПвр - wage fund for auxiliary workers at the tariff rate, rubles;
Prvr. - bonus to auxiliary workers, rubles.
FOZPvr = 3523.68 + 8809.22 = 12332.9 rubles.
Additional wages for auxiliary workers.
 The calculation of the additional wages fund for auxiliary workers of the FDZP, rubles, is made according to the formula:
The calculation of the additional wages fund for auxiliary workers of the FDZP, rubles, is made according to the formula:
![]() (16)
(16)
Ndop - the rate of additional wages, is taken the same for repair and auxiliary workers, 11.44%.
The wage fund for auxiliary workers.
The calculation of the wage fund for auxiliary workers of the payroll, rubles, is carried out according to the formula:
FOTvr = (FOZP = FDZPvr) * 1.5 (17)
where; FOZPvr - fund of basic wages of auxiliary workers, rubles;
ФДЗПвр - additional wages fund for auxiliary workers, rubles;
FOTvr = (12332.9 + 1529.2) * 1.5 = 20793.5 rubles.
Calculation of the wage fund for foremen and employees.
The wage fund of the FZPm.s. is calculated by the formula:
FZPm.s. = 0.05 * Npp * Report * Nmonth. (eighteen)
where; 0.05 - the rate of foremen and employees per worker;
Npp - the number of repair workers, people;
Dokl - monthly salary of one employee, rub. We accept; RUB 2500
Nmonth - the number of months, 12 months.
 |
FZPm.s. = 0.05 * 3 * 2000 * 12 = 3600 rubles.
Awards for craftsmen and employees.
Calculation of the premium for masters and employees PM.s. rub., is carried out according to the formula;
![]() (19)
(19)
where; FZPm.s. - salary fund for foremen and employees by salary, rubles;
nm.s. - premium rate, 10% higher than that of repair workers (60%).
![]()
Basic wages for foremen and employees.
The basic wages fund for foremen and employees, rubles, is determined by the formula:
FOZPm.s. = FZPm.s. + Pm.s. (twenty)
where; FZPm.s. - ITS wage fund by salary, rub.
Pm.with. - award for engineering and technical employees.
FOZPm.s. = 3600 + 2160 = 5760 rubles.
Additional salary.
The additional wages fund for foremen and employees of FDZPm.s, rubles, is determined by the formula;
![]() (21)
(21)
where; Ndop - the rate of additional wages of foremen and employees,%; 12.4%
 FOZPm.s. - Fund of basic wages for foremen and employees, rubles.
FOZPm.s. - Fund of basic wages for foremen and employees, rubles.
2.1.3. Salary fund for foremen and employees.
The calculation of the wage fund for foremen and employees of the FOTm.s., rubles, is carried out according to the formula;
FOTm.s. = (FOZPm.s. + FDZPm.s.) * 1.5 (22)
where; FOZPm.s. - Fund of basic wages for foremen and employees, rubles.
FDZPm.s. - fund of additional wages of foremen and employees, rubles;
1.5 - the sum of the regional coefficient and the seniority bonus.
FOTm.s. = (5760 + 771.84) * 1.5 = 9797.76 rubles.
General payroll fund.
The general wage fund, rubles, is determined by the form;
PHOTObs = PHOTO.r. + PHOTOV.r. + PHOTM.s. (23)
where; FOTm.s. - wages fund for foremen and employees, rubles;
FOTvr - fund for the payment of auxiliary workers, rubles;
FOTrr - fund for wages of repair workers, rubles
FOTtotal = 9797.76 + 118344.31 + 16191.36 = 148,935.07 rubles.
2.2. Unified social tax.
 The calculation of the unified social tax Sesn., Is made according to the formula;
The calculation of the unified social tax Sesn., Is made according to the formula;
![]() (24)
(24)
where; PHOTotch - general wage fund, rubles;
H is the tax rate as a percentage. 26%.
We enter the calculation in table number 2
The structure of the wage fund.
Table No. 2.
| Name |
Value, rub. |
||
| Repair workers |
Auxiliary workers |
Craftsmen and employees |
|
| 1.wage fund at the tariff rate (salary) |
|||
| 2.extra payments for unfavorable working conditions |
|||
| 3. additional payments for work: |
|||
| * in nighttime |
|||
| * in evening time |
|||
| 4. surcharges for brigadier |
|||
| 6.fund of basic wages |
|||
| 7.fund of additional wages |
|||
| 8. wage fund, rub. |
|||
| 9. general wages fund, rub. |
|||
| 10.uniform social tax (UST) |
|||

2.3. Calculation of costs for spare parts and repair materials.
Spare parts costs.
Spare parts costs rubles, calculated by the formula;
where; Nzch - the rate of costs for spare parts per 1000 km, mileage, rubles;
(8.17 rubles) [page 30 annex No. 4. (1)]
Ltot - annual mileage of a car of this brand, km; (LiAZ-5226)
Ltot = 153 * 123 * 365 = 8544285 km;
K1, K2, K3, - correction factors (K1 = 08, K2 = 1, K3 = 0.9) [page 26, page 27, 2].
Kinf - inflation rate, we take equal to 25%.
Nuch.z.ch. - the percentage of costs for spare parts attributable to this section is 8%
The cost of repair materials.
The calculation of the cost of repair materials Srm, rubles, is made for each brand, is determined by the formula;
 (26)
(26)
where; Нрм - the norm of expenses for repair materials per 1000 km. mileage, rub. (8.13 rub.) p. 30;
Nuch.rm - the percentage of costs for repair materials attributable to this area%, if zones EO1, TO1, TO2, TP, this percentage is not accepted.
Kinf - inflation rate, we take equal to 25% .;
Ltot is the annual mileage of a car of this brand, km.
The costs are summed up.
The calculation results are summarized in table No. 4.
Table No. 4.
| Rolling stock brand name |
Total mileage, km |
Cost rate |
|||
| Zap. parts, rub. |
Rem. mater., rub. |
Zap. parts, rub. |
Rem. mater., rub. |
||
2.4. Calculation of overhead costs.
Electricity calculations.
The annual consumption of power electricity Qes, kW, is determined by the formula;
![]() (27)
(27)
 where; Rob is the sum of the equipment power, 3.9 kW;
where; Rob is the sum of the equipment power, 3.9 kW;
FRVob - equipment working time fund;
K3 - equipment load factor, 0.5 - 0.8, we take equal to = 0.5;
Kc is the demand coefficient, 0.3 - 1, we take equal to = 1;
Кnс - loss coefficient in networks, 08 - 0.9, we take equal to = 0.8;
Кng - coefficient of losses in the engine, 09 - 0.98, we take equal to = 0.9;
Rob = 0.4 + 1.5 + 1.5 + 0.5 = 3.9 kW. (the sum of the equipment power).
Fund of working time of equipment FRVob., Is determined by the formula;
FRVob = Dr * tcm * ncm; (38)
where; Dr - days of work of the unit, days. 365days:
tcm - the duration of the equipment operation, we take 6 hours;
ncm - the number of shifts. One-shift.
FRVob = 365 * 6 * 1 = 2190;
Annual electricity consumption for lighting Qeos, kW, is determined by the formula;
![]() (29)
(29)
where; 25 - the rate of electricity consumption per 1 m 2, W;
Foc - lighting area, (plot area - 36 m 2);
Tos - hours of lighting per year.
 Lighting hours per year Tos, h, are determined depending on the shift of work:
Lighting hours per year Tos, h, are determined depending on the shift of work:
Tos = Dr * tos; (thirty)
where; tos - lighting time per day, hour, we take 8 hours;
Dr - days of operation of the site per year, days, we accept 365 days.
Tos = 365 * 8 = 2920 hours.
![]()
The calculation of the cost of electricity, Se, rubles, is made according to the formula;
Se = (Qes + Qeos) * CkW; (31)
where; CkW - the price per 1 kW in current prices, we take 1.5 rubles;
Qes - annual power energy consumption, kW;
Qeos - electricity for lighting, kW.
Se = (5931 + 2628) * 1.5 = 12838.5 rubles.
Heating costs.
Heating costs Sotop., Rubles, are calculated by the formula;
Sotop = Fuch * C * M (32)
where; Fuch - the area of the site, we take 36 m 2;
C - the price for heating 1m 2, we accept 14 rubles;
M - the number of heated months in a year, we take 7 months.
Sotop = 36 * 14 * 7 = 3528 rubles.
Water supply costs.
 The calculation of the cost of water supply Sv, rub., Is made according to the formula;
The calculation of the cost of water supply Sv, rub., Is made according to the formula;
Sv = (Nr * Npp + Nm 2 * F) * Dr * Tsl; (33)
where; Нр - the rate of water consumption per one worker for 1 shift, we take 30 liters;
Npp - the number of repair workers on the site, 4 people;
Nm 2 - daily rate of water consumption per 1 m 2 production area, we accept 1.5 liters.;
F - area of the site, we take 36 m 2;
Dr - days of work of the site per year, 365 days;
Tsl - the price of 1 liter of water in current prices, we accept - 0.4 rubles.
Sv = (30 * 3 + 1.5 * 36) * 365 * 0.4 = 21024 rubles.
Depreciation of fixed assets.
The calculation of the depreciation of the AZD building, rubles, is carried out according to the formula:
![]() (34)
(34)
where; nzd is the rate of depreciation of buildings and structures; we accept 3%;
Сzd - the cost of buildings, rub.
The cost of buildings Szd, rubles, is calculated by the formula:
Szd = F * Tsm 2; (35)
where; F - the area of the production site, we take 36 m 2;
Tsm 2 - the book value of 1m 2 of the area, we take 3000 rubles.
Сzd = 36 * 3000 = 108000 rubles.
![]()
 |
Depreciation of equipment Aob, rub., Is calculated by the formula;
![]() (36)
(36)
where; Sob - the book value of the equipment, rubles, we accept 250,000 rubles;
nob - the norm for equipment depreciation, we take 5%.
![]()
Equipment repair: R about = 10000 / 0.07 = 7000 rubles.
The costs of maintaining and repairing inventory SINV, rubles, are calculated using the formula;
![]() (37)
(37)
where; Npp - number of workers, 2 people;
Synv - the book value of the inventory, we accept 20,000 rubles;
Ninv - the norm for the restoration of inventory, we accept 4%.
![]()
Labor protection and safety costs.
Labor protection and safety costs Sot. and tb., is calculated by the formula;
![]() (38)
(38)
where; PHOTotch - general wage fund, rubles;
no. and TB. - the norm for labor protection and safety measures, we accept 2%.
![]()
 Other costs.
Other costs.
Other costs Spr, rub., Are calculated by the formula;
![]() (39)
(39)
where; - the sum of all costs, rubles;
0.05 is a percentage factor.
The sum of all costs, rubles, is calculated by the formula;
Se + Sotop + Sv + AZD + Aob + Srob + Sinv + Sot and TB. (40)
where; Сэ - electricity costs, rubles;
Sotop - heating costs, rubles;
Sv - the cost of water supply, rubles;
АЗД - the cost of depreciation of the building, rubles;
Aob - equipment depreciation costs, rubles;
Сrob - expenses for the current repair of equipment, rubles;
Synv - the cost of restoring inventory, rubles;
Cell and TB - the cost of labor protection and safety precautions, rubles.
21024 + 3528 + 12838.5 + 3240 + 5000 + 7000 + 2400 + 2978 + 2900.4 = 60908.9 rubles.
 We enter the calculations in table number 5.
We enter the calculations in table number 5.
Overhead costs for the site.
Table No. 5
| Expenditure |
Value, rub. |
Share of expenses,% |
| Water supply costs |
||
| Electricity costs |
||
| Heating costs |
||
| Depreciation costs of a building |
||
| Equipment depreciation costs |
||
| Equipment maintenance costs |
||
| Inventory maintenance costs |
||
| Health and safety costs |
||
| other expenses |
||

2.1.5. Cost calculation.
The cost calculation is carried out in table 6.
Table 6.
Cost of impact per 1000 km. mileage, calculated by the formula;
![]() (41)
(41)
where; - the sum of all costs;
Car mileage 
![]()
In this course project, the cost of work was calculated on the site for the repair of electric starters. The amount of costs at cost is 456,277.9 rubles. The site employs 3 people. By analyzing the calculation, we determine overhead costs (106,290.41 rubles) and social costs. their deductions amounted to 38723.1 rubles. Analyzing table 6, we see that the largest percentage of the prime cost was the wage fund for repair and auxiliary workers, ITS - 32%. The wage fund can be reduced by reducing the working time of employees from 12.3 hours. up to 8 hour working day and consequently the unified social tax will be reduced (it will be unnecessary to pay for processing). Due to the reduction in working hours, electricity consumption (table No. 5) will decrease, which is 21%, in the total amount of overhead costs. You can also reduce energy consumption by introducing energy-saving technologies, upgrading equipment. Refuse from centralized heating and switch to autonomous. Practice shows that costs are significantly reduced by about 15%, due to the fact that in the absence of people at night, the boiler is set to standby mode. Fuel consumption is decreasing.
Bibliography.
1. Methodological guide for the implementation of term paper.
2. Regulations on the maintenance and repair of the rolling stock of road transport. MOSCOW "TRANSPORT" 1986
3. L.Yu. Astansky, S.I. Ilyin et al. "Economics, organization and planning of production building materials»MOSCOW 1988
4. V.A. Tanygin "Fundamentals of standardization and quality management" MOSCOW 1989.
5. Enterprise economics. Textbook. UNITY MOSCOW. 1996 V.Ya. Gorfinkel, E.M. Kupryanov.
6. Marketing. Textbook. UNITY MOSCOW. 1995 A.N. Romanov.
7. The course of the market economy. UNITY MOSCOW. 1995 Ruzavin G.I. Martynov V.T.
8. The economy of an industrial enterprise. Textbook. MOSCOW. 1998 "INFRA - M" N.L. Zaitsev.
9. Labor rationing. MOSCOW 2005 "ALPHA - PRESS". M.I. Petrov.
We have adopted a planned preventive system in our country. maintenance and repair of cars... The essence of this system is that maintenance is carried out according to plan, and repairs - as needed.
The fundamental principles of a planned preventive system for the maintenance and repair of vehicles are established by the current Regulation on the maintenance and repair of rolling stock of road transport.
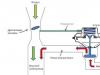
Maintenance includes the following types of work: cleaning and washing, control and diagnostic, fastening, lubrication, filling, adjusting, electrical and other work, performed, as a rule, without disassembling the units and removing them from the car individual nodes and mechanisms. If during maintenance it is impossible to make sure that individual units are in full serviceability, then they should be removed from the car for control on special stands and devices.
By frequency, car maintenance according to the current Regulation, it is divided into the following types: daily (EO), first (TO-1), second (TO-2) and seasonal (CO) maintenance.
The regulation provides for two types of repairs of cars and its units: current repairs (TR), carried out in motor transport enterprises, and overhaul (CR), carried out at specialized enterprises.
Each type of maintenance (MOT) includes strictly fixed list(nomenclature) of works (operations) to be performed. These operations are divided into two parts, control and performance.
The control part (diagnostic) of maintenance operations is mandatory, and the executive part is performed as needed. This significantly reduces material and labor costs for maintenance of rolling stock.
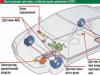
Diagnostics is part of the maintenance workflow (MOT) and maintenance(TR) vehicles, providing the initial information about the technical condition of the vehicle. characterized by the purpose and place in the technological process of maintenance and repair.
Daily maintenance (EO) is carried out every day after the vehicle returns from the line between shifts and includes: control and inspection work on mechanisms and systems that ensure traffic safety, as well as on the body, cab, lighting devices; cleaning and drying and cleaning operations, as well as refueling the car with fuel, oil, compressed air and coolant. Car wash is carried out on demand, depending on weather, climatic conditions and sanitary requirements, as well as on the requirements for the appearance of the car.
First maintenance. TO 1
TO-1 consists in an external technical inspection of the entire car and the performance in the prescribed amount of control and diagnostic, fastening, adjusting, lubrication, electrical and refueling work with checking the operation of the engine, steering, brakes and other mechanisms. The complex of diagnostic works (D-1), performed at or before TO-1, serves to diagnose mechanisms and systems that ensure the safety of vehicle movement.
TO-1 is carried out between shifts, periodically at set intervals for mileage and should ensure the trouble-free operation of units, mechanisms and systems of the vehicle within the established frequency.
In-depth diagnosis of D-2 is carried out 1-2 days before TO-2 in order to provide information to the TO-2 zone about the upcoming volume of work, and if a large amount of current repairs are detected, redirect the car to the current repair zone in advance.
Second maintenance. TO2
TO-2 includes the performance of fastening, adjusting, lubricating and other works in the established volume, as well as checking the operation of units, mechanisms and devices during operation. TO-2 is carried out with the removal of the car for 1-2 days from operation.
At ATP D-1 and D-2 are combined in one section using combined stationary stands. At large ATP and at centralized service bases, all diagnostic tools centralize and optimally automate the repair and maintenance of the vehicle.
Determination of the place of diagnostics in the technological process maintenance and repair of cars allows you to formulate and the basic requirements for its funds. To diagnose the D-1 of mechanisms that ensure traffic safety, high-speed automated diagnostic tools are required brake mechanisms and steering.
To diagnose the car as a whole (D-2) and its units, stands with running drums are needed to determine the power and economic indicators, as well as the state of systems and units, which maximally approximate the conditions for their diagnosis to the operating conditions of the car. For diagnostics combined with maintenance and repair, mobile and portable diagnostic tools and devices should be used.
Seasonal maintenance
CO is carried out 2 times a year and is the preparation of the rolling stock for operation in cold and warm seasons. Separately, JI is recommended to be carried out for rolling stock operating in a cold climate zone. For other climatic zones, CO is combined with TO-2 with a corresponding increase in the labor intensity of the main type of service.
Car repair and maintenance
Routine repair and maintenance of the car is carried out in motor transport companies or at ONE HUNDRED and consists in the elimination of minor malfunctions and car failures, contributing to the fulfillment of the established vehicle mileage up to overhaul.
The purpose of diagnostics during routine repair is to identify a failure or malfunction and establish the most effective way their elimination: on site, with the removal of the unit or units with their full or partial disassembly or adjustment. Routine repair and maintenance of a car consists in carrying out disassembly, locksmith, welding and other works, as well as replacing parts in units (except for basic ones) and individual components and assemblies in a car (trailer, semitrailer), which require, respectively, current or overhaul of the car.
During current repairs, the units on the car are changed only if the repair time for the unit exceeds the time required to replace it.
Car overhaul
KR of cars, units and assemblies is carried out at specialized repair enterprises, factories, workshops. It provides for the restoration of the operability of cars and units to ensure their mileage until the next major overhaul or write them off, but not less than 80% of their mileage from the mileage norms for new cars and units.
During the overhaul of a car or unit, it is completely disassembled into units and parts, which are then repaired or replaced. After completing the parts, the units are assembled, tested and sent to the assembly of the car. With an impersonal repair method, the car is assembled from previously repaired units.
Cars and buses are sent for overhaul, if overhaul of its body is necessary. Trucks are sent for overhaul, if overhaul of the frame, cab is necessary, as well as overhaul of at least three main units.
As a rule, a complete vehicle undergoes one major overhaul during its service life.
The purpose of overhaul diagnostics is to check the quality of the repair.
Working programm
by discipline MDK 01.02 Maintenance and repair of road transport
for basic training
specialty 02.23.03 Maintenance and repair of road transport
graduate qualifications technician
form of education full-time
1.1. Scope of the program
Program (further working programm) - is a part of the main vocational educational program of SPE in accordance with the Federal State Educational Standard in the specialty of SPE 02.23.03 Maintenance and repair of road transport(basic training) in terms of mastering the main type of professional activity (VPA) and the corresponding professional competencies (PC):
PC 1.1. Organize and carry out maintenance and repair work for vehicles.
PC 1.2.
1.2. Goals and objectives of the MDK - requirements for the results of mastering the MDK
In order to master the specified type of professional activity and the corresponding professional competencies, the student in the course of mastering the MDC must:
have practical experience:
development and assembly of vehicle units and assemblies;
technical control of the operated transport;
implementation of maintenance and repair.
be able to:
develop and implement a technological process for the maintenance and repair of vehicles;
carry out technical control of vehicles;
evaluate the efficiency of production activities;
carry out an independent search for the necessary information to solve professional problems;
analyze and assess the state of labor protection at the production site.
know:
device and foundations of the theory of rolling stock of road transport;
basic circuits for switching on elements of electrical equipment;
properties and quality indicators of automobile operating materials;
rules for the preparation of technical and reporting documentation;
qualifications, basic characteristics and technical parameters of road transport;
methods of assessment and quality control in professional activities;
the main provisions of the current regulatory documentation;
fundamentals of the organization of the enterprise and its management;
rules and norms of labor protection, industrial sanitation and fire protection.
MDK 01.02:
total -720 hours, including:
the maximum study load of the student is 720 hours, including:
compulsory classroom teaching load of the student - 480 hours;
independent work student - 240 hours;
laboratory and practical - 92 hours;
training practice - 288 hours.
2.Results of mastering MDK 01.02
The result of mastering the program is the mastery of students by the type of professional activity (VPA) Maintenance and repair of vehicles, including professional (PC) and general (OK) competencies:
| Name of the learning outcome |
|
| Organize and carry out maintenance and repair work for vehicles. |
|
| Carry out technical control during storage, operation, maintenance and repair of vehicles. |
|
| Organize your own activities, choose standard methods and ways of performing professional tasks, evaluate their effectiveness and quality |
|
| Make decisions in standard and non-standard situations and be responsible for them. |
|
| Search and use the information necessary for the effective performance of professional tasks, professional and personal development |
|
| Use information and communication technologies to improve professional performance |
|
| Work both individually and in a team, communicate effectively with colleagues, management, consumers |
|
| Set goals, motivate the activities of subordinates, organize and control their work with taking responsibility for the result of completing tasks |
|
| To independently determine the tasks of professional and personal development, engage in self-education, consciously plan professional development |
|
| Navigate in the face of frequent technology changes in professional activities. |
|
| Perform military duty, including using the acquired professional knowledge (for young men) |
3. STRUCTURE and content of MDK 01.02
3.1. Thematic plan
| Professional competency codes | Names of sections of the professional module | Total hours | Amount of time allotted for mastering the interdisciplinary course (s) | Practice |
|||||
| Compulsory classroom study load of the student | Student's independent work | Educational, | Production (according to the profile of the specialty), (if dispersed practice is envisaged) |
||||||
| Total, | incl. laboratory work and practical exercises, | Total, | including, term paper (project), |
||||||
| PC 1.1-1.3 | Section 1. | ||||||||
| PC 1.1-1.3 | Section 2. | ||||||||
| PC 1.1-1.3 | Section 3. Diagnostics of technical means of cars | ||||||||
| PC 1.1-1.3 | Section 4. Car repair | ||||||||
| Industrial practice, (according to the profile of the specialty), hours (if a final (concentrated) practice is provided) Study practice ..... | |||||||||
| Total: | |||||||||
| Names of sections of interdisciplinary courses (MDC) and topics | Clock volume | Development level |
|||||
| Section 1. | |||||||
| MDK 01. 02. Maintenance and repair of road transport | |||||||
| Introduction | |||||||
| Topic 1.1.Fundamentals of maintenance and repair of rolling stock | |||||||
| Reliability and durability of the car | |||||||
| The system of maintenance and repair of rolling stock. | |||||||
| Regulations on the maintenance and repair of the rolling stock of road transport | |||||||
| Fundamentals of diagnosing the technical condition of cars | |||||||
| Topic 1.2.Technological and diagnostic equipment for technical maintenance and repair of cars | ||||
| General information about technological and diagnostic equipment, fixtures and tools. | ||||
| Equipment for harvesting, washing and cleaning works. | ||||
| Inspection and handling equipment. | ||||
| Equipment for lubrication and filling works. | ||||
| Equipment, fixtures and tools for disassembly and assembly works. | ||||
| Diagnostic equipment | ||||
| Topic 1.3. Technology of maintenance and repair of rolling stock of road transport | ||||
| Daily car maintenance | ||||
| Diagnosing the engine as a whole | ||||
| Maintenance and running repairs of crank and gas distribution mechanisms. | ||||
| Maintenance and repair of cooling and lubrication systems. | ||||
| Maintenance and current repair of the power supply system of carburetor engines. | ||||
| Maintenance and current repair of the diesel engine power supply system. | ||||
| Maintenance and routine repair of the power supply system for gas-fueled engines. | ||||
| Maintenance and current repair of electrical equipment. | ||||
| Maintenance and current repair of transmission. | ||||
| Maintenance and running repairs of the chassis and car tires. | ||||
| Maintenance and current repair of control mechanisms. | ||||
| Maintenance and current repair of bodies, cabins and platforms. | ||||
| Car diagnostics at the posts of general and element-by-element diagnostics. | ||||
| Laboratory works | ||||
| Engine diagnostics using built-in devices. | ||||
| Maintenance and running repairs of the crank mechanism. | ||||
| Maintenance and current repair of the gas distribution mechanism. | ||||
| Maintenance and repair of the cooling system. | ||||
| Maintenance and routine repair of the engine lubrication system. | ||||
| Maintenance and current repair of power system devices removed from the engine | ||||
| Maintenance and routine repair of devices for cleaning and supplying fuel, air and exhaust gases. | ||||
| Identification and elimination of malfunctions in the power supply system carburetor engine... Carburetor adjustment. | ||||
| Diagnostics, maintenance and current repair of fuel cleaning and supply devices, power systems diesel engine. | ||||
| Diagnostics, maintenance and current repair of air purification devices, diesel engine power systems. | ||||
| Diagnostics, maintenance and current repair of injectors, AMOVT injection pump. | ||||
| Determination and elimination of malfunctions of the diesel engine power supply system. | ||||
| Maintenance and current repair of the power supply system of engines from gas-cylinder installations. | ||||
| Diagnostics, maintenance and current repair of power supply system devices. | ||||
| Diagnostics, maintenance and current repair of ignition system devices. | ||||
| Diagnostics of electrical devices using a tester. | ||||
| Diagnostics, maintenance and current repair of engine electric start devices. | ||||
| Diagnostics, maintenance and current repair of sound and light alarm devices, additional equipment and lighting devices. | ||||
| Diagnostics, maintenance and current repair of the clutch. | ||||
| Diagnostics, maintenance and current repair of gearboxes, cardan drives and driving axles. | ||||
| Diagnostics and installation of angles adjustment of wheel alignment angles, pivot pivot angles. | ||||
| Checking and adjusting the clearances in the pivots, ball bearings and wheel bearings, maintenance of the chassis. | ||||
| Vulcanization of chambers. Routine tire repair. | ||||
| Assembly and disassembly pneumatic tire... Wheel balancing. | ||||
| Diagnostics, maintenance and current repair of steering. | ||||
| Diagnostics, maintenance and current repair of power steering. | ||||
| Diagnostics, maintenance and routine repair of brake systems with hydraulic drive and parking brake. | ||||
| Diagnostics, maintenance and routine repair of pneumatic brake systems. | ||||
| General car diagnostics. | ||||
| Element-by-element diagnostics of cars. | ||||
| Topic 1.4.Organization of storage and accounting of rolling stock and inventory. | ||||
| Storage of rolling stock of road transport. | ||||
| Storage, accounting of inventories and ways to reduce the cost of material and fuel and energy resources. | ||||
| Topic 1.5.Organization and management of maintenance and repair production. | ||||
| Classification of trucking companies | ||||
| General characteristics of the technological process of maintenance and current repair of rolling stock. | ||||
| Organization of work of repair workers. | ||||
| Organization of vehicle maintenance. | ||||
| Organization of current car repairs. | ||||
| Organization of quality control of maintenance and current repair of cars | ||||
| Topic 1.6. Automated control systems in the organization of maintenance and routine repair of road transport | ||||
| Forms and methods of organization and production management | ||||
| Automated control systems in the organization of maintenance and routine repair of cars | ||||
| Analysis and modeling of the production process of maintenance and routine repair of cars | ||||
| Automated workplace workers of the technical service of a motor transport company. | ||||
| Laboratory works | ||||
| Drawing up a daily shift assignment for the repair team. | ||||
| Drawing up a plan for the dispatcher's report. | ||||
| Drawing up a shift-daily assignment for a production preparation site | ||||
| Calculation of the production program of maintenance and current repair on a computer using simulation programs. | ||||
| Analysis and solution of tasks of the type: AWS equipment for rolling stock, drawing up a reporting sheet. | ||||
| Topic 1.7.Basics of designing production sites of motor transport enterprises. | ||||
| Fundamentals of technological design of production sites of motor transport enterprises. | ||||
| Independent work in the study of section 1 | ||
| Fulfillment of assignments for the preparation and design of sections of the course project. Implementation of individual assignments using technical and reference literature. |
||
| Correction of standards for maintenance and current repair of cars. Installation of ignition on a car. Automatic transmission. Diagnostics and maintenance of an automatic transmission. Modern equipment for running gear diagnostics passenger cars... Shock test benches. Car tire markings. Anti-lock braking system (Anti-lock braking system). Traction control system air wheels, (stabilization system). Bodywork... Body restoration after a traffic accident. Applied equipment. Means for anti-corrosion treatment of the body (brands and application technology). Cleaning and washing equipment classification scheme. Lift classification. Factors affecting the progressiveness of technology maintenance and current repair of cars. Means of technical diagnostics of systems that ensure the safety of the car. Means of technical diagnostics of the engine, its systems and operating properties. Repair of electrical equipment. Repair of transmission units and parts. Repair of units and parts of the chassis of the car. Repair of units and parts of control mechanisms. Car tire repair. Cab, body repair. Development of schemes for the restoration of parts. Solving problems for standardization. Calculation of the main users for the design of repair production areas. Working out the sections of the course project and making drawings. |
| MDK 01.02. | |||||
| Introduction | |||||
| Topic 2.1. Automotive fuel | |||||
| Chemical composition of fuel and lubricants. Methods for obtaining petroleum fuels. | |||||
| Automobile gasolines. | |||||
| Automotive diesel fuels. | |||||
| Gas and oil motor fuels. | |||||
| Laboratory works | |||||
| Evaluation of gasoline according to the passport, external signs. Analysis for the content of water-soluble acids and alkalis. Determination of the density of gasoline. Determination of the fractional composition of gasoline. | |||||
| Grade diesel fuel according to passport data. Assessment of the presence of mechanical impurities and water. Determination of the kinematic viscosity of diesel fuel at 20 ° C. Determination of the pour point of diesel fuel. Determination of the brand of diesel fuel in accordance with GOST and the solution of the issue of its use. | |||||
| Topic 2.2.Automotive lubricants. | |||||
| Automotive lubricating oils. | |||||
| Automotive greases. | |||||
| Laboratory works. | |||||
| Evaluation of engine oils according to passport data. Determination of the presence of mechanical impurities. Determination of kinematic viscosity of oil at 50 ° C and 70 ° C. Determination of the viscosity index. Determination of the viscosity grade according to GOST and the solution of the issue of its application. Determination of the presence of water in engine oil. | |||||
| Evaluation of grease according to passport data. Test of grease for solubility in water and gasoline. Determination of the camp drop temperature of the lubricant. Establishing the brand of grease in accordance with GOST and resolving the issue of its use. | |||||
| Topic 2.3.Automotive special liquids | |||||
| Laboratory works | |||||
| Evaluation of antifreeze sample according to passport data. Definition appearance and the presence of mechanical impurities. Determination of the composition and freezing point of antifreeze. |
|||||
| Topic 2.4.Organization of rational use of fuel and lubricants in road transport. | |||||
| Organization of rational use of fuel and lubricants at road transport. | |||||
| Topic 2.5.Construction and repair materials. | |||||
| paints and varnishes | |||||
| Construction and operational materials | |||||
| Topic 2.6. Safety and environmental protection when using automotive operating materials. | |||||
| Safety and environmental protection. | |||||
| Independent work when studying section 2 Systematic study of class abstracts, educational and special technical literature (on questions, paragraphs, chapters of textbooks compiled by the teacher). Preparation for laboratory / practical exercises using methodological recommendations drawn up by teachers. Registration of reports on the performed laboratory work / practical exercises and preparation for their defense. Independent study of electronic resources. Execution of abstracts. Preparation of messages, reports on topics set by the teacher individually. Use of Internet resources. | |||||
| Themes of extracurricular independent work Development automotive industry in Russia. Suspension of the car and power unit. Timing with lower valve arrangement. Coolants. Oils for engines. Crankcase ventilation. Motor gasolines: neutralization of exhaust gases. Fuels for gas-cylinder vehicles. Diesel fuels. Detonation, the influence of various factors on detonation. Glow ignition. Exhaust gas toxicity. Ways to reduce toxicity. Features of the application of automotive operating materials in modern conditions. The main indicators of the quality of diesel fuels. Alternative fuels. Classification engine oils SAE and API. Transmission oils. Fluids for cooling systems. Fluids for hydraulic systems. The main measures to save fuels, oils, technical fluids in road transport. The influence of the quality of fuel and lubricants on the operation of the rolling stock of road transport. Paints and varnishes. Toxicity and flammability of fuel and lubricants. Environmental monitoring. |
|||||
| Section 3 Diagnostics of technical means of cars. | ||||
| MDK 01.02. | ||||
| Introduction | ||||
| Diagnostics of technical means of cars. | ||||
| Fundamentals and organization of technical diagnostics of cars. | ||||
| Requirements for technical diagnostics of vehicles during operation. Diagnostic parameters and their classification. | ||||
| Construction of a diagnostic algorithm. General requirements for means of technical diagnostics (STD). | ||||
| Nomenclature of means of technical diagnostics. | ||||
| Organization of technical diagnostics of cars at motor transport enterprises. | ||||
| Norms of diagnostic parameters and their standardization. Accuracy and reliability of car diagnostics. | ||||
| Technology for diagnosing the technical condition of cars. | ||||
| General car diagnostics. Diagnostics of the crank and gas distribution mechanisms. | ||||
| Diagnostics of cooling and lubrication systems. | ||||
| Diagnostics of the devices of the power supply system of the carburetor engine and fuel injection systems. | ||||
| Diagnostics of the power supply system of a diesel engine. Diagnostics of preheaters. | ||||
| Diagnostics of power supply devices. Diagnostics of devices of the ignition system. | ||||
| Diagnostics of the starting system and lighting and signaling devices. | ||||
| Diagnostics of transmission mechanisms. | ||||
| Running gear diagnostics. Diagnostics of steering controls. | ||||
| Diagnosis of hydraulic brake systems. | ||||
| Diagnostics of systems with pneumatic drive. Diagnostics of additional equipment. | ||||
| Independent work in the study of section 3 Systematic study of class abstracts, educational and special technical literature (on questions, paragraphs, chapters of textbooks compiled by the teacher). Preparation for laboratory / practical exercises using methodological recommendations drawn up by teachers. Registration of reports on the performed laboratory work / practical exercises and preparation for their defense. Independent study of electronic resources. Execution of abstracts. Preparation of messages, reports on topics set by the teacher individually. Use of Internet resources. | ||||
| Approximate topics of extracurricular independent work Determination of the nomenclature of structural and diagnostic parameters. The choice of diagnostic parameters for assessing the technical condition of vehicles. Development of a block - diagram of structural - effect relationships in the chain of diagnostics. The main indicators of the reliability of technical diagnostics. Drawing up a table of means of technical diagnostics indicating: name, model, purpose. Typical types of express diagnostics. Limit values of the main diagnostic parameters of domestic cars and trucks. Car diagnostics based on parameters that determine braking dynamics. Diagnostics of the tightness of the seating of the valves in the seats. Diagnostics of the crankcase ventilation system. Drawing up a table of the diagnostic parameters of the carburetor with an indication of their nominal and permissible values. Drawing up a table of diagnostic parameters of the diesel power system devices with an indication of their nominal and permissible values. Search for the reasons for the lack of fuel and air supply to the combustion chamber of the heater boiler and the slow warming up of the engine. Execution of the alternator diagnostic circuit. Drawing up a table of diagnostic parameters of devices of a contactless ignition system. Drawing up a table of diagnostic parameters of starter devices. Drawing up a table of permissible and nominal diagnostic parameters of the chassis of the car. Drawing up a technological chart for diagnostics of steering, brake systems with a hydraulic drive and a pneumatic drive of a car. Diagnostics of the pump of the dump truck body lifting mechanism. |
||||
| Section 4 Car repair | ||||
| MDK 01.02. | ||||
| Introduction | ||||
| General provisions for car repair | ||||
| Fundamentals of the organization of overhaul of automobiles. | ||||
| Topic 4.2. Car overhaul technology. | ||||
| Acceptance of cars and units for repair and their external wash. | ||||
| Dismantling of vehicles and assemblies. | ||||
| Washing and cleaning of parts. | ||||
| Fault detection and sorting of parts. | ||||
| Completing parts. | ||||
| Assembly and testing of units. | ||||
| General assembly, testing and delivery of cars from repair. | ||||
| Laboratory works | ||||
| Cylinder block flaw detection. | ||||
| Crankshaft fault. |
||||
| Camshaft fault. |
||||
| Connecting rod defective. |
||||
| Fault detection of spur gears and splined shafts. |
||||
| Fault detection of rolling and plain bearings. Spring fault detection. |
||||
| Completion of pistons with cylinder liners. |
||||
| Completion of parts for the crank mechanism. |
||||
| Practical work. | ||||
| Calculation of size groups when completing pistons with cylinder liners. |
||||
| Topic 4.3. Methods for restoring parts. | ||||
| Classification of methods for restoring parts. | ||||
| Restoration of parts by metalwork and mechanical processing. | ||||
| Restoration of parts by pressure. | ||||
| Restoration of parts by welding and surfacing. | ||||
| Restoration of parts by spraying. | ||||
| Restoration of parts by soldering. | ||||
| Restoration of parts by electroplating. | ||||
| Restoration of parts using synthetic materials. | ||||
| Topic 4.4. Technology for the restoration of parts, repair of units and devices. | ||||
| General Provisions. | ||||
| Development of repair technological processes | ||||
| Repair of parts of the class "body parts" | ||||
| Repair of parts of the class "round rods and rods with a contoured surface" | ||||
| Repair of parts of the class "hollow cylinders" | ||||
| Repair of parts of the class "discs with a smooth perimeter" | ||||
| Repair of parts of the class "non-circular bars" | ||||
| Repair of units and devices of cooling and lubrication systems. | ||||
| Repair of units and devices of power supply systems. | ||||
| Repair of electrical equipment. | ||||
| Car tire repair. | ||||
| Repair of bodies and cabins. | ||||
| Repair quality management. | ||||
| Laboratory works | ||||
| Cylinder block boring. | ||||
| Honing of the cylinder block. | ||||
| Valve seat repair. | ||||
| Course design | ||||
| Engine maintenance and repair. MOT and gearbox repair. | ||||
| Maintenance and repair of gas-powered vehicles. Maintenance and repair of KShM. | ||||
| Maintenance and repair of a starter. Maintenance and repair of the chassis. | ||||
| Maintenance and repair of car cooling systems. Timing maintenance and repair. | ||||
| Maintenance and repair of the brake system of cars. Maintenance and repair of the engine power supply system. | ||||
| Maintenance and repair of car ignition systems. Maintenance and repair of the diesel engine power supply system. | ||||
| Independent work in the study of section 4 Systematic study of class abstracts, educational and special technical literature (on questions, paragraphs, chapters of textbooks compiled by the teacher). Preparation for laboratory / practical exercises using methodological recommendations drawn up by teachers. Registration of reports on the performed laboratory work / practical exercises and preparation for their defense. Independent study of electronic resources. Execution of abstracts. Preparation of messages, reports on topics set by the teacher individually. Use of Internet resources. | ||||
| Themes of extracurricular independent work Restoration of parts to repair size. Reconditioning of parts with additional repair parts. Restoration of parts by welding, surfacing. Restoration of parts by soldering. Restoration of parts using synthetic materials. Restoration of parts by spraying and electroplating. Restoration of parts paintwork... Restoration of engine parts. Repair of units and devices of the engine power supply system. Repair of units and devices of the cooling system. Repair of units and devices of the lubrication system. Repair of electrical equipment. Repair of transmission units and parts. Repair of units and parts of the chassis of the car. Repair of units and parts of control mechanisms. Car tire repair. Cab, body repair. Development of schemes for the restoration of parts. Solving problems for standardization. Calculation of the main users for the design of repair production areas. Development of sections of the course project and the implementation of drawings |
||||
4. conditions for the implementation of MDK 01.02 4.1. Minimum Logistics Requirements
The implementation of the module program assumes the presence of classrooms - "Maintenance and repair of cars"; laboratories - "Electrical equipment of cars", "Automotive operating materials", "Engines internal combustion"," Car maintenance "," Car repair ".
| Car maintenance |
||
| engine models; |
||
| car mockup. |
||
| computers; |
||
| projector, |
||
| Automotive maintenance materials |
||
| jobs by the number of students; |
||
| teacher's workplace; |
||
| technical documentation; |
||
| methodical documentation; |
||
Main sources:
Organization of production of technical maintenance and current repair of cars - a textbook for students of SPO / V.M. Vinogradov, I.V. Bukhteeva, V.N. Repin, A.A. Sokolov - M .: Publishing Center "Academy", 2010.
INFRA-M, 2006
M .: FORUM - INFRA-M, 2006.
Additional sources:
protection. Body. Part 2.
in 2 parts, 2009
5. Monitoring and evaluation of the results of mastering the MDK
| results | ||
| PC 1.1. Organize and carry out works on maintenance and repair of vehicles | Expert assessment of implementation practical assignment Defense of the course project |
|
| Expert assessment of implementation practical assignment Defense of the course project |
||
| PC 1.3. To develop technological processes for the repair of units and parts. | Expert assessment of implementation practical assignment Defense of the course project |
| results | Main indicators for assessing the result | Forms and methods of control and evaluation |
| Understand the essence and social significance of your future profession, show a steady interest in it | ||
| results (mastered general competences) | Main indicators for assessing the result | Forms and methods of control and evaluation |
| Observation and assessment of achievements while performing tasks in laboratory and practical classes, during educational and industrial practice; |
||
| Observation and assessment of achievements while performing tasks in laboratory and practical classes, during educational and industrial practice; Assessment of achievements based on the results of performing extracurricular independent work. |
||
| Observation and assessment of achievements while performing tasks in laboratory and practical classes, during educational and industrial practice. |
||
| Observation and assessment of achievements while performing tasks in laboratory and practical classes, during educational and industrial practice. Observation and evaluation of achievements based on the results of activities in extracurricular activities. |
||
| results (mastered general competences) | Main indicators for assessing the result | Forms and methods of control and evaluation |
| Observation and assessment of achievements while performing tasks in laboratory and practical classes, during educational and industrial practice. |
||
| Observation and assessment of achievements while performing tasks in laboratory and practical classes, during educational and industrial practice. |
||
4. Conditions for the implementation of MDK 01.02
4.1. Minimum Logistics Requirements
The implementation of the module program assumes the presence of classrooms - "Car construction", "Maintenance and repair of cars"; workshops - "Forging and welding", "Turning and mechanical"; laboratories - "Electrical equipment of cars", "Automotive operating materials", "Internal combustion engines", "Maintenance of cars", "Car repair".
Equipment of classrooms and workplaces of classrooms:
| Car maintenance |
||
| jobs by the number of students; |
||
| stands for checking the maintenance of mechanisms and systems; |
||
| engine models; |
||
| car mockup. |
||
| Technical training aids: |
||
| computer desk for the teacher; |
||
| computers; |
||
| projector, |
||
| software general and professional use. |
||
| Workshop equipment and workshop workstations |
||
| Forging and welding |
||
| jobs by the number of students; |
||
| teacher's workplace; |
||
| forge forge; |
||
| anvils, equipment for the production of blacksmiths (hammers, sledgehammers, pliers, etc.) |
||
| welding machines for production welding works(gas, electric) |
||
| consumables (electrodes, carbide, etc.) |
||
| Turning and mechanical |
||
| jobs by the number of students; |
||
| teacher's workplace; |
||
| lathes, milling, sharpening, etc .; |
||
| workpieces for turning work; |
||
| tools; |
||
| Consumables. |
||
| Laboratory equipment and laboratory workstations: |
||
| Electrical equipment of cars |
||
| jobs by the number of students; |
||
| teacher's workplace; |
||
| a set of educational and methodological documentation; |
||
| control and test stands for checking the technical condition of units and parts of electrical equipment of cars; |
||
| chargers for rechargeable batteries; |
||
| demonstration stands of electrical equipment systems; |
||
| nodes and parts; |
||
| instrumentation. |
||
| Automotive maintenance materials |
||
| jobs by the number of students; |
||
| teacher's workplace; |
||
| technical documentation; |
||
| methodical documentation; |
||
| instruments and equipment for determining the quality of fuels and lubricants; |
||
| devices for determining the mechanical properties of fuels and lubricants; |
||
| microscopes, heating ovens, refrigerator; |
||
| samples of tested fuels and lubricants \ |
||
| Internal combustion engines |
||
| jobs by the number of students; |
||
| teacher's workplace; |
||
| technical documentation; |
||
| methodical documentation; |
||
| internal combustion engine; |
||
| stand for taking the traction characteristics of the engine. |
||
| Car maintenance |
||
| jobs by the number of students; |
||
| teacher's workplace; |
||
| stands for checking the maintenance of mechanisms and systems; |
||
| engine models; |
||
| car layout; |
||
| devices and equipment for diagnostics of an internal combustion engine, transmission, running gear, steering and brake systems |
||
| Car repair |
||
| jobs by the number of students; |
||
| teacher's workplace; |
||
| sets of measuring instruments; |
||
| nodes and parts for fault detection; |
||
| workbenches for fastening parts. |
||
The implementation of the module program assumes mandatory industrial practice, which is recommended to be carried out in a concentrated manner.
4.2. Information support of training
Main sources:
Cars: The device of automobile means: a textbook for students. institutions SPO / A.G. Puzankov 6th edition, erased. - M .: Publishing Center "Academy", 2010.
Cars: Design, theory and calculation. Textbook for open source software. Puzankov A.G. M .: publishing center "Academy", 2007.
Quality control of automotive operating materials; workshop: textbook for students of secondary vocational education / Gelenov A.A., Sochevko T.I., Spirkin V.G. - M .: Publishing Center "Academy", 2010.
Automotive operational materials - a textbook for students of SPO / Gelenov A.A., Sochevko T.I., Spirkin V.G. - M .: Publishing Center "Academy", 2010.
Cars: Operational properties: Textbook for stud. higher. uch. institutions / Vakhlamov V.K. - 2nd edition, ster.-M .: Publishing Center "Academy", 2006.
Organization of production of technical maintenance and current repair of cars - a textbook for students of SPO / V.M. Vinogradov, I.V. Bukhteeva, V.N. Repin, A.A. Sokolov - M .: Publishing Center "Academy", 2010.
Car maintenance and repair. Vlasov V.M. Textbook. M .: Academy, 2007.
Peculiarities of maintenance of KAMAZ vehicles with engines of EURO-2, EURO-3 5460-3902901 TO. 2008
Basics of performance technical systems... Automobile transport - textbook / V.G. Atapin - Novosibirsk: NSTU publishing house, 2007.
Maintenance and repair of road transport (Diploma design) / Svetlov M.V. M .: KNORUS. 2011
Car repair (Course design) / Skepyan S.A.M .: INFRA-M. 2011
Professional repair of internal combustion engines. K.L. Gavrilov M .: FORUM. 2011
Organization of production of technical maintenance and current repair of cars - a textbook for students of SPO / V.M. Vinogradov, I.V. Bukhteeva, V.N. Repin, A.A. Sokolov - M .: Publishing Center "Academy", 2010.
Car and engine repair. Karagodin V.I., Mitrokhin N.N. M .: "Academy". 2008
15. The device of the car. Tutorial. / Perederiy V.P. M .: FORUM
INFRA-M, 2006
16. The device of cars. Tutorial. / Stukanov V.A., Leontiev K.N.
M .: FORUM - INFRA-M, 2006.
Additional sources:
Acceptance for repair, repair and release from repair of VAZ car bodies by car service enterprises. Technical conditions. (TU4538-140-00232934-98) (current document).
2. Technological charts, time norms for routine and post repairs of NefAZ 5299 buses, produced on the KamAZ-5297 chassis.
3. Technological maps for the current repair of KamAZ vehicles, models: 5320, 5410, 5511, 4310, 43105 and their modifications (5 parts).
4. Typical execution technology routine maintenance daily first, second and seasonal maintenance of the ZIL-4331 vehicle.
5. Distributed fuel injection systems for VAZ vehicles - device and diagnostics. Maintenance and repair technology.
6. Electronic system control of the engine of cars of the families LADA 110, LADASAMARA, LADA 2105, 2107 with controller М73 EURO-3 - device and diagnostics.
7. Electronic engine control system for cars of the LADAPRIORA, LADAKALINA, LADA 4x4 families with a controller М7.9.7 EURO-3 - device and diagnostics
Fuel and lubricant consumption rates for automobile
VAZ cars. Repair technology, painting and anti-corrosion
protection. Body. Part 2.
VAZ cars. Removal and installation technology. Units and assemblies.
A short automobile reference book. Volume 1. Buses. 2002 2nd
edition, revised and supplemented, 2007
12. A short automobile reference book. Volume 2. Trucks,
13. A short automobile reference book. Volume 3. Cars,
in 2 parts, 2009
14. Instructions for the maintenance and care of buses "Ikarus
15. Catalog of special tools and accessories for technical
maintenance and repair of LADA cars.
18. Typical norms of time for routine repair of family cars
4.3. General requirements for the organization of the educational process
A prerequisite for admission to industrial practice(according to the profile of the specialty) within the professional module "Maintenance and repair of vehicles" is the development of educational material in the relevant sections of the module.
When working on a course project, students are provided with consultations.
4.4. Staffing of the educational process
Requirements for the qualifications of pedagogical (engineering and pedagogical) personnel providing training in an interdisciplinary course (s): the presence of higher professional education corresponding to the profile of the module "Maintenance and repair of vehicles" and the specialty "Maintenance and repair of road transport".
Requirements for the qualifications of teaching staff who manage practice
Engineering and teaching staff: graduates - teachers of interdisciplinary courses.
Masters: the presence of 5-6 qualification categories with a mandatory internship in specialized organizations at least once every 3 years. Work experience in organizations of the relevant professional field is required.
5. Control and assessment of the results of development (type of professional activity)
| results (mastered professional competencies) | Main indicators for assessing the result | Forms and methods of control and evaluation |
| Organize and carry out maintenance and repair work for vehicles. | Performing maintenance and repair work in accordance with technological maps. Practical use of technological and organizational equipment. Compliance with safety requirements and rules and norms of labor protection, industrial sanitation and fire protection | Expert assessment of implementation practical assignment Defense of the course project |
| Carry out technical control during storage, operation, maintenance and repair of vehicles. | quality control of maintenance and repair at various stages using appropriate equipment and tools ability to check the quality and properties of automotive operating materials | Expert assessment of implementation practical assignment Defense of the course project |
| To develop technological processes for the repair of units and parts. | Ability to develop technological processes for the repair of units and parts in accordance with GOSTs, OSTs and TUs. | Expert assessment of implementation practical assignment Defense of the course project |
The forms and methods of monitoring and assessing learning outcomes should allow checking not only the formation of professional competencies in students, but also the development of general competencies and the skills that provide them.
| results (mastered general competences) | Main indicators for assessing the result | Forms and methods of control and evaluation |
| Understand the essence and social significance of your future profession, show a steady interest in it | Demonstration of interest in the future profession in the process of mastering the educational program, participation in research work, Olympiads, festivals, conferences | Observation and assessment of achievements while performing tasks in laboratory and practical classes, during educational and industrial practice; Assessment of achievements based on the results of extracurricular independent work; |
| results (mastered general competences) | Main indicators for assessing the result | Forms and methods of control and evaluation |
| Observation and evaluation of achievements based on the results of activities in extracurricular activities. |
||
| Organize their own activities, choose standard methods and ways of performing professional tasks, evaluate their effectiveness and quality. | Selection and application of methods and ways of solving professional problems in the field of organizing the process; Evaluation of the effectiveness and quality of the performance of professional tasks. | Observation and assessment of achievements when performing tasks in laboratory and practical classes, during educational and industrial practice. |
| Make decisions in standard and non-standard situations and be responsible for them. | The correctness and objectivity of the assessment of non-standard and emergency situations. | Observation and assessment of achievements while performing tasks in laboratory and practical classes, during educational and industrial practice. |
| Search for and use the information necessary for the effective fulfillment of professional tasks, professional and personal development | Effectively search, enter and use the necessary information to perform professional tasks | Observation and assessment of achievements while performing tasks in laboratory and practical classes, during educational and industrial practice; Assessment of achievements based on the results of performing extracurricular independent work. |
| Use information and communication technologies in professional activities | The use of information and communication technologies for solving professional problems | Observation and assessment of achievements while performing tasks in laboratory and practical classes, during educational and industrial practice; Assessment of achievements based on the results of performing extracurricular independent work. |
| Work in a team and in a team, communicate effectively with colleagues, management, consumers | Interaction with students and teachers during training. | Observation and assessment of achievements while performing tasks in laboratory and practical classes, during educational and industrial practice. |
| Take responsibility for the work of team members (subordinates), the result of assignments. | Ability to make joint informed decisions, including in non-standard situations | Observation and assessment of achievements while performing tasks in laboratory and practical classes, during educational and industrial practice. Observation and evaluation of achievements based on the results of activities in extracurricular activities. |
| results (mastered general competences) | Main indicators for assessing the result | Forms and methods of control and evaluation |
| Independently determine the tasks of professional and personal development, engage in self-education, consciously plan professional development | Organization of self-study in the study of the professional module; Planning for students to improve their qualifications in the field of road transport. | Observation and assessment of achievements while performing tasks in laboratory and practical classes, during educational and industrial practice. Assessment of achievements based on the results of performing extracurricular independent work. |
| Navigate in the face of frequent changes in technology in professional activities | Application of innovative technologies in the field of organization of technical maintenance and repair of vehicles. | Observation and assessment of achievements while performing tasks in laboratory and practical classes, during educational and industrial practice. |
| Perform military duty, including with the use of the acquired professional knowledge (for young men) | Show interest in the performance of military duty; The manifestation of logical thinking. | Observation and assessment of achievements during the performance of tasks in laboratory and practical classes, during educational and industrial practice, military training |
Course Description:
The profession of an inspector of the technical condition of vehicles will never leave you without a job, because is in great demand in the modern world, where the number of cars per capita is only increasing every year. To get an education in this profession, you must attend the course "Maintenance and repair of road transport » ... This can be done completely remotely.
The Modern Science and Technology Academy (SNTA) conducts training cycles of professional retraining in technical specialties. You will receive a quality education without leaving your home.
Features of training in the direction "Maintenance and repair of road transport"
Depending on the goals of the specialist, you can take courses in one of two directions:
- Professional retraining;
- Improving professional competencies.
The training cycle for professional retraining is aimed, first of all, at obtaining a completely new direction of work for the listener. Refresher courses, on the other hand, are aimed at improving the already existing knowledge in the specialty.
The main goal of the entire educational cycle is the mastery by the students of basic skills and abilities related to the specifics of work activities, for the implementation of highly qualified independent activities.
The main disciplines that will be studied by students upon admission to the training module in the specialty in question:
- State regulation of transport activities;
- Regulatory support of transport activities;
- The main types of vehicles;
- Car service;
- Types of car repair;
- Practical aspects of vehicle repair.
The main labor duties of mechanics include:
- Ensuring uninterrupted, technically correct operation of devices and equipment;
- Develop vehicle inspection schedules;
- Preparation of technical documentation;
- Carrying out high-quality and timely repair of the vehicle,
- Identify obsolete equipment that requires overhaul;
- Ensuring compliance with labor protection rules during repair work;
- Taking part in the development of measures to create safe working conditions during the operation and repair of equipment and much more.
Training format
The educational cycle at the Academy is carried out according to the traditional full-time and part-time format, using distance educational technologies.
After enrollment, methodological materials are issued containing exclusively relevant and useful information... Distance learning, assumes the absence of the need to visit an educational institution in person. Classes are held from home. All you need is a computer or tablet with Internet access.
It is convenient that there is no need to break away from the production process by leaving for a session, and the students can quickly apply the knowledge gained in their work practice.
At the end of the training cycle, be ready to take online testing, in order to check your knowledge and defend your thesis. But there are no entrance tests for admission.
Learning outcomes
A diploma of completion of training for obtaining a primary specialization is issued to all students who have successfully completed the training module.
We are guaranteed to send documents by Russian post with courier delivery to the door.
Requirements for listeners
Anyone can master a new direction, if they have postgraduate (or secondary specialized) education in the relevant specialty.
Benefits of studying at SNTA
- The Academy operates on the basis of license No. 034268 dated 25.10.2013;
- All educational programs are drawn up in strict accordance with the State, are constantly updated and have only up-to-date information;
- Affordable tuition fees;
- Possibility of training from any locality in Russia;
- After enrolling in the course, each student is assigned a personal curator who, throughout the entire module, helps in mastering the program;
- An individual approach to each student guarantees a high-quality education with maximum accessibility.
Because passing refresher courses is a necessary measure to continue working, at the Academy you can also go through a training cycle to improve professional competencies.
Applications for training can be submitted around the clock.
Still have questions? Contact our call center any in a convenient way... For example, you can order a call through the feedback form, or call directly (the call is free). Or you can send an email to the mail:.
We are waiting for you!
Stock:
Received documents:
Important! The diploma does not indicate the form of study (full-time / part-time).
Established diploma
Conditions of admission:
Training in the direction "Maintenance and repair of road transport" gives an opportunity to get a retraining diploma. Also, for certain areas and specialties, the issuance of additional documents is provided, if they are required by departmental regulations: certificates, books, etc.
In order to become a student of the academy, you must meet several requirements and complete some steps:
- Have a diploma of secondary vocational or higher education in the specialty
- Apply for training under the program of professional retraining or advanced training in the direction of "Maintenance and repair of road transport" in electronic format:
- by email,
- by the feedback form on the website,
- or call the free round-the-clock phone; - Provide documents confirming the identity and the current level of education;
- After signing the contract, take a distance learning course;
- Pass the final testing and receive a retraining diploma or a certificate of advanced training for the program "Maintenance and repair of road transport."