Head cylinders majority gasoline engines It is made of aluminum alloy. Aluminum alloy has the advantages in the fact that it is easier than cast iron and has best characteristics thermal conductivity, so that it is easier to cool. However, it has some disadvantages, such as easy damage and higher thermal expansion.
ATTENTION!
When repairing the head of the cylinders, pay attention to the following.
Be careful not to scratch or otherwise do not damage the surfaces of the cylinder head, which is adjusted to the block head gasket and the collector laying,
The cylinder head bolts should be delayed on a cold engine, a predetermined method, in proper sequence with the application of the specified torque. There are two tightening methods - the usual method and method of tightening in the plastic deformation area.
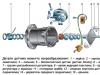
Fig. 1 - device head of the cylinder block.
Valves and parts conjugate with them
1. Valve
Valves are made of special steel, because they are exposed to high pressures and temperatures. The valve is always pressed towards the closure direction of the spring, and when an effort is acting from distribution ValaThe valve moves down inside the valve guide sleeve in the cylinder head to open the intake or exhaust channel. Typically diameter plates inlet valve A little more than the exhaust valve.
In order to provide good seal between valve and saddlevalve the valve cone angle is usually 44.5 ° or 45.5 °.

Fig. 2 - Valve.
2. Spring valve
The valve spring is used to close the valve. Most engines are installed on the valve one spring, but two springs on the valve are used on some engines.
To prevent the valve from the pusher when the engine works on high revolutions, Springs with an unequal step or double springs are used.

Fig. 3 - types of springs valves.
ATTENTION!
The reveuming of the valve from the pusher is caused by the work of the valve spring, not associated with the work of the cam. The valve believes appears when the engine works at the speed of rotation above the maximum permissible. It not only causes an abnormal engine noise, but is the cause of the piston impact on the valve, which can damage these parts. Springs with an unequal step of asymmetric type are installed by coils with a wider step up.
The valve seat is pressed into the head of the cylinders. When the valve closes, the valve plate is tightly adjacent to the valve saddle to maintain the tightness of the combustion chamber. The valve seat also removes heat from the valve to the cylinder head for the valve cooling. Since the valve seat is exposed to hot exhaust gases and repeated contacts with the valve, it is made of special steel having high heat and wear resistance.

Fig. 4 - valve seat.
REFERENCE The valve seat usually has a 45 ° cone form to fit the valve cone. The width of the work chamfer of the valve seat is usually from 1.2 to 1.8 mm. Excessive width of the work chamfer of the valve seat probably will cause carbon penetration between the valve and the saddle, although the cooling effect will be high. If it is too narrow, it will improve the tightness, but the cooling effect will decrease.
The valve guide bushing is usually made from cast iron and pressed into the cylinder head. The valve guide sleeve sends the valve so that its working surface is properly adjacent to the valve seat. The conjugate surfaces of the valve rod and the valve guide sleeve are lubricated with engine oil. To prevent a large amount of engine oil into the combustion chamber through the gap between the valve rod and the guide sleeve, in the upper part of the valve guide, the oil seal is provided.
The non-defective movement or stirring of the valve rod in the valve guide sleeve is called the "valve jamming". It appears when the gap between the valve rod and the valve guide sleeve is too small or when they are not lubricated enough.
If the oil seal of the valve rod is destroyed or hardens, or if the clearance between the valve rod and the valve guide sleeve is excessive, motor oil It will fall into the combustion chamber. This oil will burn in the combustion chamber and emit through exhaust pipe. As a result, motor oil consumption will increase.
Typically, the oil is easier to enter the combustion chamber through the intake valve.
5. Valve turning mechanisms.
On some engines, the valve rotation mechanisms are used instead of the springs plates.
The valve rotation mechanism rotates the valve, thereby preventing a loose fit to the valve saddle caused by lead or by naigar compounds deployed on the working surface of the valve during the combustion of eaten gasoline.
Typically, the valve rotation mechanisms are installed on exhaust valves.
The valve rotation mechanism consists of a mechanism housing, a spiral spring, a flat spring and a lock.
The ring-shaped spiral spring is installed in the groove in the housing of the mechanism and is slightly flattened with a flat spring when the valve spring is installed.

Fig.5 - Valve turning mechanism

Fig. 6 - work mechanism
When the valve opens, the valve spring is compressed and its effort becomes large. This causes the outdoor portion of the flat spring slightly bending up, while the spiral spring is flattened even more. This, in turn, makes the mechanism body turn.
At this time, the point A slides, but the points in and with do not slide.
When the valve closes, that is, when the valve spring is expanding, the valve spring force is weakening.
Bending a flat spring so it becomes smaller and the spiral spring returns to its original state. This causes sliding at points in and C, whereas at the point and the sliding does not occur. Therefore, the corps of the rotation mechanism remains in the same position as with the open valve.
Toyota Motor Corporation
The abbreviation of the CBC is decrypted as the head of the cylinder block, this is one of the most important nodes of any engine. internal combustion. Know what the CCC is in the car, the principle of its work and the features of the design, should every owner of the car. This will help notice in time possible malfunction, as well as provide stable work power aggregate In various modes.
GBC, this is the upper part of the internal combustion engine cylinder block. It is attached to it with bolts or special studs. The main purpose of the head is to control the flow of fuel in working cylinders, ensuring its combustion, control and distribution of gases. It is from the accuracy of adjustment separate nodes GBC depends the power and stability of the work of the entire engine as a whole.
What does the cylinder head look like
For various power units, the heads of the cylinder block are produced from cast iron or aluminum-based alloys. It is aluminum GBC that are installed on most modern carswhich allows you to slightly reduce the total weight of the power unit.
For engines with inline cylinder arrangements, a single cylinder is used, and for V-shaped power plants, separate heads are used for each row. There are no other constructive differences.
Video about GBC
How the cylinder head is arranged
The housing of the GBC (Carter) is obtained by casting and subsequent metalworking (milling, drilling). In the body of the product, there are channels for circulating the coolant, oil-carrying for lubrication of the main nodes, separate combustion chambers for each of the cylinders. In addition, in the crankcase there are holes for installing spark plugs or nozzles (for diesel engines). According to its design, the head is considered a complex unit that includes several different mechanisms.
- Gas distribution mechanism, providing removal gases. The valve of the gas distribution system opens in a clear sequence depending on the steps of each individual cylinder.
- The drive of the gas distribution mechanism that provides the opening of the valves at the required moment.
- Places for fastening intake and exhaust collectors providing fuel supply and waste gases.
- Failure elements of the GBC include guide sleeves and valve seat. These elements provide sealing of the gas distribution mechanism. The installation of these parts is carried out by the method of hot crimping, it is almost impossible to perform it without special equipment, especially in a private garage.
Each of the above nodes is responsible for the engine performance as a whole, and the yield of any of them becomes the cause of a more serious breakage. On the video clip at the bottom you can observe the work of all the elements of the GBC in motion.
How to install a GBC correctly

Cylinder Head, Gasket (Head Gasket) and Engine Block (Engine Block).
Considering the fact that the GBC has many channels for the movement of the lubricant, coolant, exhaust gases, the most important condition for the correct installation is reliable sealing in the connection site with the cylinder block. This is done by installing a special gasket made of reinforced asbestos. Such material is able to withstand high temperature and significant pressure of working fluids and exhaust gases. Consider the fact that the gasket of the GBC is disposable, reuse will not be able to guarantee reliable sealing of the connection location with the cylinder block.
The tight fit of the head and the compression of the asbestos gasket is achieved by tightening fastening bolts or nuts on the heels. Take into account the fact that any skew when performing these operations will lead to insufficient sealing of the compound. That is why the tightening should be carried out with a certain force, which must be monitored using a dynamometric key. At the same time, each stud should tighten strictly in a certain order, the violation of which will also be the reason for the emergence of problems with insufficient sealing.
With permanent operation, it is necessary to pay attention to the density of the adjustment of the GBC to the surface of the cylinder block. The appearance of oil flows, coolant indicates unreliable sealing of the compound. In this case, it is necessary to cover the head on the new one.
For maintenance Be sure to check the state of the most loaded GBC elements. Understand the state of the valves, the camshaft, do not miss the type and integrity of the sealing glands.
All work related to the repair of the head of the cylinder block or the replacement of individual mechanisms can be performed individually if there are appropriate experience. Remember, any negligence and non-compliance with the installation technology will cause more serious engine breakdowns. And the cost of such repairs will be significantly greater. Therefore, trust the repair of the GBC is only a professional auto show that has experience and appropriate equipment.
The head of the cylinder block is an essential detail for each modern staffing absolutely. power plants, be it diesel car or gasoline. Of course, there is a difference between them - and the type of fuel, however, the device and the principle of operation of the head of the block are not changed. Therefore, today we will analyze the overall design of this element.
and principle of work
Despite its importance in the engine, the head of the cylinder block has a completely simple design. This mechanism consists of parts such as:
- valves of gas distribution, namely inlet and graduation;
- spark plugs (in the case of gasoline) or nozzles (in the case of a diesel engine);
- block combustion chamber fuel-air mixture.
Based on the photo provided at the very beginning of the article, we see that it is a structural part of the engine (in fact, a large aluminum lid) with pressed valve beds and guide bushings. It should be noted that the axes of these parts should fully coincide with each other, otherwise, otherwise, the entire crank-connecting mechanism fails.

The head of the engine and the block are constructively connected to each other with a special refractory stalking gasket. The latter eliminates the possibility of gas output through the place of connection of devices and loss of compression. It should be noted that this gasket, despite its primitive design, is very important for the car. In case of loss of its sealing properties, the operation of the entire engine may worsen. Initially, the phenomenon of compression will occur, the motor will lose its power, and then can stop working at all. Car thrust stops due to unauthorized gas output from the chamber. And considering the fact that inside the internal combustion center is a high compression ratio (about 2 thousand atmospheres on diesel and 100 on gasoline engines), power loss can be substantial.
The head of the cylinder block (Gazelle 3302 including) is also part of the CSM, so its relationship with the engine is direct.

Maintenance features
Each detail, whatever reliable, is, sooner or later subjected to wear, despite the fact that the head of the cylinder block (VAZ-2110 including) can serve from 200 to 400 thousand kilometers. This does not exclude the possibility of its deformation and wear earlier. As a rule, this is due to frequent but the GBC may be broken and due to undime replacement Gaskets. Therefore, that the head of the block served as long as possible, first, do not overheat the motor and do not try to cool it with water from above. Secondly, change regularly and check the layout state. The same applies to fastening bolts. Next, do not forget about the seasonal cleaning of the valves of the intake and graduation clutch, it is Nagar. When complying with these simple tips, your engine will last long and without breakdowns.
An integral part of any piston engine is the head of the cylinder block (GBC), which provides several systems at once. About what is CHC, what are these details, how they are arranged and work, as well as about the right maintenance, choosing and replacing heads - find out in this article.
Purpose of the cylinder head and its place in the engine
(GBC) - one of the main aggregates of all types piston engines internal combustion; One-piece or composite detail, installed on a block of cylinders to form hermetic combustion chambers.

Using the GBC, a number of tasks are solved, ensuring engine functioning:
- The formation of closed combustion chambers - they are formed by the recess in the lower part of the GBC and the bottom of the piston;
- Participation in the functioning of the gas distribution mechanism. In the motors with the lower arrangement of the valves of the GBC, only removal under the valves or short sections of intake and exhaust channels are carrying. In engines with the top arrangement of valves, channels, as well as a part or the entire MRM mechanism (including camshaft) can be placed on the GBC;
- Participation in the operation of the engine cooling system - Channels for coolant are performed in the CCC;
- Participation in the operation of the engine lubrication system - in the GBC with the upper arrangement of the valves or the TRM, oil channels are made for oil supply to rubbing parts;
- Participation in the operation of the ignition system petrol aggregates - ignition candles are mounted in the CBC;
- Participation in the operation of the fuel injection system of diesel and injection motors - nozzles and auxiliary components are mounted in the GBC.
Accordingly, the head for all these systems performs the functions of the housing element, it also contributes to the overall engine rigidity and the preservation of the geometry of its main components.
GBC plays an important role in the work of the power unit, any of its malfunction requires a speedy repair or even full replacement. But for faithful choice This detail must be understood in its existing types and features.
Classification GBC.
Modern GBC can be classified by the location and shape of the combustion chamber, constructive execution, the presence of parts of the gas distribution mechanism and purpose (applicability).
CHCs may have different combustion chamber (COP):
- COP, filled completely in the head. In motors with such a GBC, flat pistons are used, with their approach to VMT, the entire CS volume is formed by the head;
- COP, partially focused in the head and partially located in the piston. In motors with such CHC, pistons have recesses in the bottom, which are part of the COP;
- COP, located completely in the piston. In such motors, the lower head plane is practically flat (with recesses for valves and channels), and the COP is completely formed in the bottom of the piston.
COP may have a different shape that determines the effectiveness of mixing, combustion of the fuel and air mixture, removal of exhaust gases, etc. The most common forms of the COP are the sphere, hemisphere, tent, wedge and half-chain, and others. However, on modern motors, the COP complex (combined) form, combining the best qualities of simple cameras, are increasingly found.
A separate group includes forkamic GBC, in which, in addition to the main COP, a small chamber associated with it is made for preliminary ignition of a combustible mixture.

Heads are produced three designs:
- General CCC for all cylinders of an inline engine or one row of a V-shaped power unit;
- Group GBC in line and V-shaped motors closing only part (usually half) of cylinders of one row;
- Separate (individual) GBC for each cylinder.
The widest use of general heads that are used today are used on row and V-shaped small and medium-sized engines. On powerful multi-zeal and multi-cylinder engines, especially diesel, individual GBC is more common - such a solution is dictated by the need to reduce the mass of heads and metal consumption for their manufacture. In addition, the presence of individual heads greatly facilitates and speeds up the process of maintenance and repair of the parts of the cylinder (piston, timing and other).
They are divided into groups on the presence and set of the gas distribution mechanism:
- Without parts of the timing, the GBC of old novel flap and lower multi-cylinder motors include this group, as well as modern two-stroke tangible engines (motorcycles and small equipment);
- With separate parts of the timing valves and valve actuators (rocker and related components);
- With the whole mechanism of gas distribution - this group includes a large number of modern motors, in the CPC of which camshaft is located, valves and their drive, as well as auxiliary mechanisms and sensors.
Finally, the GBC is divided into many groups of applicability and some features:
- For diesel and gasoline engines (as well as for motors with gas-filled equipment);
- For aggregates with liquid and air cooling;
- For motors with various modes of operation (ordinary and forced).
However, regardless of the type and features of the GBC, they all have a similar design and the principle of operation.
Cylinder Block Device

The basis of the GBC design is a solid or milled part of a lightweight aluminum alloy or white cast iron. In GBC. various methods The main details are formed:
- Combustion chambers;
- Intake and outlet channels;
- Channels with velvets pressed in them;
- Valve seat (in many engines - strengthened high frequency currents or in other ways, or in the form of separate parts made of more durable metal);
- Cooling system channels;
- Oil canals;
- Supporting surfaces under the part of the timing of the struts of the rumor axis, the bed of the camshaft and others;
- Threaded holes for installation of spark plugs, fuel injectors, incandescent candles;
- The surfaces of the pairing and mounting holes for the installation of various parts - intake and exhaust manifolds, cylinder caps, a variety of sensors, etc.;
- Through holes for mounting spills / bolts.
All the designated conjugation surfaces are polished to achieve the most dense adjacent parts. Installation of collectors, covers and rows of other parts are performed through sealing elements (gaskets). In the cast iron heads, the installation is usually carried out with the help of bolts, in aluminum - the studs are often used, which are screwed once at the manufacturers and are in the future they do not touch.
The entire lower surface of the GBC is also polished - it forms a flushing surface for mounting on the block and the formation of combustion chambers. Installation of the GBC is also performed through the laying of a certain thickness. Currently, composite strips are most widely used - both traditional paronite (from pressed artificial rubber with asbestos fiber) and modern multilayer metal phones (based on a copper sheet with synthetic inserts).
The GBC assembly is installed on the upper part of the cylinder block, its fixation is carried out using nuts vehicle (in the case of an aluminum block) or written directly to the bolts (in the case of a cast-iron block). A solid or composite lid is installed on the head, providing protection for timing and preventing motor oil losses.
How to choose and replace the GBC

The GBC itself is a reliable and durable item, which can serve many years without any problems. However, it has many details on it, the malfunction of which may require dismantling or other manipulations from the GBC. With normal operation vehicle It is not recommended to remove the head without need, as this leads to a deterioration in the quality of fasteners, and in addition, with a subsequent installation, it is necessary to use a new gasket (which leads to excess costs).
The replacement of the GBC will have to think in case of serious damage - through cracks, chips and fears, changes in geometry, etc. To replace, you need to choose the head of the same model (and most importantly - catalog number) that was installed on the engine earlier. The "NOTOR" head simply will not rise in its place and will not provide the necessary characteristics of the engine. However, it should be noted that the GBC of other types is often used when tuning the engine, but this work is much more complex to replace the parts and is performed only by professionals, so we do not consider it here.
It is purchased complete with a gasket and a set of seals (for collectors, covers, sensors, etc.), the use of old sealing elements is unacceptable! Installation of the new head should be carried out in strict accordance with the instructions for the repair of the vehicle, special attention The order of tightening of nuts / bolts and the effort attached to them should be given. Failure to comply with these recommendations can lead to a failure of the GBC.
In the future, the GBC requires minimal attention (which cannot be said about the details established on it), and proper montage and careful operation It will ensure reliable operation of the motor.
The head of the cylinder block is the main constructive node car Engine. Malfunctions in its work can lead to serious consequences, up to overhaul Motor. You can learn more about this device from this article.
[Hide]
The concept of GBC
What is a GBC in the car, which is a decoding this device? Cylinder cylinder head or head is an integral part of the power unit. This device is designed to control the combustion process of the fuel-air mixture in the power unit, as well as the derivation of the exhaust gases. GBC is the cover of the power unit, which is mounted from above directly block. This node can be made of aluminum alloy or doped cast iron.
After the completion of the casting, the production of artificial aging is undergoing the production of CCB, this is removed to remove residual voltage from the device. If the car motor is single, then it uses one GBC. If we are talking about W-shaped units, in this case, a separate Cylinder Cylinder will be used for each series of cylinders. The lower part of the design is wider, it is necessary for reliable fixation node on the unit. In order to seal a block with a GBC in the car, a sealing component is applied - the gasket (video is removed and published by the KVS theory channel).
Installation and fastening of the device on the motor is carried out through guide pins, which fix the cylinder engine on the engine. The pins on the head are twisted in a certain order, which is determined for each brand of the car, and the moment of tightening the device is particularly important. For tightening applied dynamometric Keywhich determines this moment - if you twist the pins by force, without observing the moment, there is a chance of damage to the device. The deformation of this design will cause its replacement.
Constructive features of the GBC.
Earlier, the GBC was made of cast iron, but today this material is not used for production. Cast iron heads are still installed on many cars. The use of this material is due to the fact that cast-iron GBC better Work under hard temperatures. Cast iron heads are better coping with severe heat and reduced temperatures, and aluminum devices are more susceptible to shrinkage and deformation when working in such conditions (Alexander Skripchenko).
One of important elements Cup of the car is considered to be a gasket that is performed from reinforced asbestos. Thanks to the use of this material, the gasket allows you to cope with your tasks at elevated temperatures, and also withstands high pressure. Gaskets made of asbestos allow you to provide good tightness of the mains of the cooling system, combustion chambers and oil wire.
Below are the main components of the GBC of the automotive engine:
- Gasket.
- Gas distribution mechanism.
- Crankcase. The crankcase contains all the elements and nodes of the device, including the cooling and oil channel channels. Here is the combustion chamber.
- Technological connectors for installing nozzles or candles.
- Same Camera combustion. This node is used to ensure the ignition procedure of the fuel mixture of the engine.
- Drive gas distribution mechanism.
- Planting places with threaded holes. They are installed collectors - intake and graduation.
Valves available on the GBC are installed in the same row on the design. Valves are installed at an angle of 20 degrees. Constructive features In various cars, especially modern production, may differ, but usually valves are in the same row.
In the front of the head of the cylinder head, there is a technological surface for mounting the timing of timing, as well as a belt tensioner or timing chain. The combustion chambers of the automotive motor are mounted tightly to the cylinder itself, they are mechanically processed to ensure reliable adjustment. As for the dimensions, the compression chamber area will be lower than the dimensions of the bottom of the piston. This makes it possible to ultimately improve the combustion process of the fuel and air mixture in the engine cylinders.
On the left side of the block head, 4 technological holes are located in which the candles are installed or engine nozzles. On the other hand there is a flange, collectors are mounted on it. In close proximity to the flange there are highways of the cooling system, the refrigerant circulates. The block heads are located on top of the block, the guide elements are mounted, the puis bearings, the camshaft bearing devices are mounted. Also on the top mounted the lid fixed using pins.
Full elements are installed on the GBC:
- valve saddles used to ensure the timing tightness;
- valve guide elements.
Full elements are mounted by pressing the structure of the block head. The dismounting process and replacement of these devices is performed using thermal equipment and tools that can be found on specialized stations. At home, their replacement will be impossible.