Let's see what happened to the automotive plants that produced equipment during the USSR.

Yerevan Automotive Factory
On December 31, 1964, the Order of the Armenian SSR No. 1084 was decided "On an organization in the city of Yerevan in the factories of the Forklift plant under construction of a car for car vans with a carrying capacity of 0.8-1.0 tons." It was there that the charming vans Eraz were created, the brothers of the Latvian Rafikov.
In November 2002, the plant was declared bankrupt, and two years later his premises were sold at auction. The new owner was the company "Mc Metal", which produces reinforcement, nails and other products made of metal. So the plant looks in our day.

Riga automotive factory
Well, the Rafa themselves began to release from 1953 on the basis of the Riga automotive factory, which was built in 1949 at the site of the "Riga Author Repair Plant No. 2". Until 1954, the plant wore the name of Rzak - Riga Plant of Bus Body. The most bright years of his years fell on the 50s-70s, but after the release of Latvia from the USSR, the plant began to die.
The company was declared bankrupt in 1998 and now the plant's area was partially looted and destroyed, and partially given under warehouse and office rooms. Ironically, the last cars of the plant were created for funeral services.

Kutaisa Automotive Factory
Let the name "Kolkhida" and became the synonym for an unreliable truck in the Soviet Union, the cars under this brand were produced until 1993. Later, attempts were made to revive the production of agreements with GM, Mahindra, HTZ, but they did not lead to anything concrete. As a result, since 2010, the plant, which was built in 1951, is idle. Most of its equipment is plundered and cut into metal, only an administrative building remains in the "live" state, which is protected (in the photo).

Vilnius Vehicle Factory
The forge of the fastest Ralone cars of the Soviet Union, located in Vilnius, was created in the late 70s on the basis of the Vilnius Authororer. The new enterprise received the name of the Vilnius Vehicle Factory (VFTS) and has long existed for a long time after the USSR has become a story, switching to the construction of rally cars according to individual projects.
Now the territory where VFTS was located is occupied by the Volkswagen service station, and there is little reminded about the last rally of magnitude.

Lviv Bus factory
The last large order of the Lviv bus factory, which since its construction in 1945, revealed many magnificent cars, was the delivery of a batch of buses and trolley buses to the city of Ukraine, which took Euro-2012's football championship. Today the plant is a huge empty premises, of which almost all equipment for the assembly took out.

Rousseo Balt.
The automotive department on the basis of the Russian-Baltic Wagon Plant appeared in 1908, however, during the First World War, the company "went on" on other corners of Russia for evacuation purposes. In the native walls of the car, there were not so long - only seven years. And on July 1, 1917, the "Second Automotive Plant Rousseo Balt" began working. Now the plant in Riga looks like this. And let his condition seems to be veterging, there are still former greatness in these walls.

Dux
YOUR HISTORY The plant "Dux", which this year marks 124 years old, started from the release of bicycles, but soon expanded production to cars and aircraft. The first "dead loop" performed by Nesterov was performed just on the aircraft "Dux". Now on the territory of the plant complex, which in 1993 returned the historical name "Dux", produce weapons for air-air aircraft.
Part of the complexes of the complex at the address: Moscow, Street Pravda 8 is transferred to office space and trading platforms.

Plant named after Likhachev
Muscovites are well aware of what happened to Zil. One of the oldest auto plants founded in 1916, under the influence of urban processes turned out to be nobody unnecessary. As a result, the factory premises were equalized with the Earth and in its place it costs the residential complex "Zilart", next to which the Park "ZIL" will appear next to the fall.
The highlight of this park will be the terrace in the form of a conveyor line - as a tribute to the historical past.

Moskvich
Construction of the plant at the intersection of the current small rings of Moscow railway And Volgograd Avenue started in 1929, and already in the 1930th enterprise began its activities. The dawn of the plant, subsequently the name "Moskvich", fell on the post-war years. But by the beginning of the "perestroika" over the "Moskvich", clouds began to thicken, in 2001, production was stopped, and in 2010 the procedure of bankruptcy of the enterprise was completed.
One of the workshops of the plant, in which the engines were planned, now belongs to Renault Russia. On the territory of another Radius Group planned to open a cryptocurrency mining farm.

Yaroslavl Automotive Factory
101 a year ago, Vladimir Lebedev began producing crossley cars in Russia - under license. What posted the beginning of the plant, which is now known as the Yaroslavl Motor Plant. Where the eyelids collected a copy of the British cars, now they make diesel engines.
In the interval between these epochs at the enterprise gathered a variety automotive technology, including trucks of the series I and Trolleybuses Yatb.
Article about minibuses RAF: history of creation, model range, evolution of technology, features, interesting Facts. At the end of the article - video about the history of RAF.

The content of the article:
The minibuses of the RAF series for the first time came off the conveyor since 1976 and instantly separated throughout the Soviet Union. What caused so phenomenal popularity of these cars and mass use in all areas of activity?
German inspiration

The Soviet-Latvian enterprise was founded back in 1949. Since 1953, when the plant has united with an experimental automotive factory, he began the active release of medium buses. Before the triumphal procession of the most popular models - 223 and its modifications - was a number of experiments.
You should start with RAF-10, the pre-trip of future minibuseswho has become ideological inspirations and a kind of "test bench" for many technical developments. Although he was based on the chassis "Victory", it was a full-fledged minibus, before creating designers carefully studied and inspired by the simplicity and reliability of the design of Volkswagen production cars.
They saw their Soviet specialists during a trip to Europe to exchange experience, where the German auto industry was gaining momentum and was almost reference to other automakers.
For the development of RAF-10, which was produced from 1956 to 1958, the Volkswagen model of the first generation model was "spied". The Soviet car received a steel bearing of the body, the wagon layout and accompanied 10 passengers. However, this design received a number of complaints, and therefore was significant in 1958.

The next stage was the release of RAF-977, which existed immeasurably longer than his "fellow" - from 1958 to 1976. His chassis was borrowed from GAZ-21, the minibus itself was used everywhere: for freight and passenger traffic, such as transport for medical services, but mainly - as a service bus of various state organizations. In all areas, he has established himself as a reliable car, and, in addition, for that time more than comfortable.

The famous RAF-2203 was produced from 1976 to 1997, and left the market only under pressure of ever increasing competition from the Gorky Automobile Plant.
The automakers began a fierce rivalry since the beginning of the 90s, modernizing and promoting each of their own models - "Gazelles" and "Rafa". Unfortunately, the first in their characteristics and cost exceeded Latvian creations, and therefore became leaders in the Russian car market.
Noteworthy fact - initially planned to make the body of a minibus from fiberglass, but then they refused from this idea.

The best creation of the automobile plant - model 2203 - was manufactured with a carrier or frameless power base, which included:
- spars;
- front shield;
- wheeled arches;
- carriage or disabled body layout.
The engine for a minibus, bridges and suspension are borrowed from the GAZ-24 car, in later versions - from GAZ-24-10. The brake system has two contours, all the wheels are equipped with brake drums, and the hydraulic amplifier of the brakes is taken from Moskvich-412.
Like a complex designer, it consisted of a variety of elements taken from others. domestic cars. Even it seems to be a unique steering, still developed with the borrowing of parts from the passenger models of gas. The engineering design team of the plant explained such an approach to the simplicity of car service.
Tires were used original, specially designed for RAF-2203, although the wheels from GAZ-21 were fitted. "Exclusive" buses for the minibus produced tire factory In Yaroslavl, and after the disintegration of the Union, they began to install any suitable on the landing diameter and height of the wheel.
Modifications

During the production, several modifications of the minibus were developed, characterized by technical characteristics, as well as the possibility of operation. Not all the developed versions were reached by mass production, it was especially concerned with the options that worked in 1990-1995.
Some versions were simply not suitable for practical applicationlike, for example, modification with original rear lanternswho did not imply a separate replacement of lamps. Thus, in the event of a malfunction of one lamp, it would have to change the entire flashlight, which seemed to be extremely uncomfortable and costly.
Therefore, this modification never went into mass production.
Some varieties were made in small-sector to cover the specific needs of the national economy. Preferably, some technical elements have changed and modified, most often the suspension that increases the level of comfort. Objectively, between different modifications No radical changes were noted.

The first version of the RAF-2203 bus is considered basic and has two main modifications. The first is with the original dashboard and subharbones from GAZ-24. The second used the dashboard from GAZ-24, as well as the standard optical devices from other serial buses for those years.
The first generation of this car was produced until 1986, after which the quality of the copies produced rapidly began to deteriorate. A lot of complaints came from medical organizations where minibuses were used as an ambulance card.
During operation it turned out that even absolutely new models obtained literally from the conveyor could break on the road without visible reasons. An example of poor quality is the TAT fact that in February 1986 the State Commission did not accept 13% of these cars.
There are ideas, no resources

The result of the dispute about the quality was the technical re-equipment of the plant and the subsequent issue new modification RAF, which included certain novelties of that time. Unfortunately, the power of the plant did not allow to introduce all conceived innovations, therefore engineers had to stay at key moments:
- enhanced body;
- hatch in the roof and side windows on the rear windows;
- disk brakes on the front wheels;
- front suspension type "swinging candle".
After the collapse of the USSR, the demand for minibuses fellAlthough the plant's management tried to do on the basis of RAF-2203-01 very demanded at the time all-metal van and a version in the form of a pickup. These cars liked these cars, but the plant did not have enough resources to completely translate the conveyors for the assembly of new models.
Safe Raf

In 1994, another modernization was performed. It is difficult to call global, but she made the minibus RAF-22038-02 as the safest in the country. He received the following changes:
- one brake amplifier instead of two, which made it possible to reduce the risk of failures;
- modified carburetor, more efficiently supplying fuel;
- modern air filter;
- new heating system;
- inertial seat belts;
- spherical rearview mirrors;
- noise insulation of the motor.
The last refinement, which had enough resources, became whole-flame bumper. In 1997, production was stopped in connection with the market loss.
Mass distribution

The so-called "raffiki" in the USSR was made only for state structures and enterprises, without acting in free sale. In this regard, the models were divided into several basic series, part that were intended for strictly limited use:
- sanitary cars;
- route taxis;
- olympic series specially designed to work in Moscow of 1980;
- militia cars.
The most common modification was medical. This version of RAF-22031 was labeled and was originally made on some assembly lines with the rest of the varieties. Later, a separate conveyor was allocated under the assembly of sanitary cars.
The main difference from the "civilian" versions was the upholstery of the cabin, which was made of light brown dermatina. Also there was a partition between the passenger compartment and the driver, equipped with a sliding glass. Two lamps with a red cross were mounted on the roof, as well as a crawler lamp designed to search for the address at night. Mandatory was a blue flashing beacon.
There were also more specialized models, for example, for blood transfusion or reanterate. But they produced extremely limited parties.
To work as passenger buses of low capacity, more known as "minibuses", used standard modifications. Also, the experiment existed specially developed RAF-22032, which had a ticket office, a circular layout and distinctive signs of accessories to passenger transport. But in the series such buses were not received, mainly minibuses were based on RAF-2203.
In the early 1990s, the RAF-22039 version was performed, especially for route taxis. It was distinguished by an increased capacity and fiberglass roof. This allowed to reduce the mass of the car, and also increased the profitability of routes.
There was a separate modification for mobile laboratories, it had additional batteries to power the devices.
Limited circulation was made by traffic police cars and boat buses.
Olympic series

It was Rafik who was honored to become the official vehicle of the Olympiad-80, so such a significant sporting event was developed special versions cars. The most interesting among them can be called the following:
- Judge electric car - Designed for transportation of judges during marathon races. Accepted up to 30 km / h and had a power reserve on one battery to 100 km.
- Raf-3407 saddle tractors - To move athletes capable of towing to two passenger cars.

The main advantage of raffikov was the unification of components with other popular cars at that time, which simplified the service. In addition, the advantage of the minibus was excellent maneuverability, even despite a fairly wide base from Volga. The disadvantages include poor weighing and caused complaintious quality assembly, which led to problems with the operation of even new cars.
In 2018, information about the restoration of the plant was leaked to the press. It is assumed that in conjunction with European manufacturers, minibuses and urban electric automobiles, compact buses with electric motors and even trolley buses will be made there.
The plans also - the creation of a series of vehicles built on a single base and having characteristics at the same time trolley buses and a bus. An unusual design will be able to move both on its own reserve, so recharge from the city power grid.
If the investment in the production accumulates itself, you can count on the new "golden age" of the Baltic miracle - minibus RAF.
Video about the history of Raf:
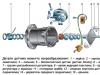
The bus of a particularly small class of general purpose is manufactured by the RAF minibus factory since 1987 the body is a whole metal, carriage-type, 4-door (two doors in the front compartment, one side for the entrance to the salon and one behind). Front engine location. The driver's seat is adjustable in length and tilt back. The heating system is a liquid, using the heat of the engine cooling system. Previously, the RAF-2203 bus (1976-1987) was produced (1976-1987), characterized by the use of the mod engine. CMP-24D lower power and some separate elements of the body (bumpers, doors, mirrors).
Modifications:
RAF-22031-01 - Linear emergency room;
RAF-2203-02 - working on liquefied gas.
Engine.
Maud. ZMZ-402.10, gasoline, inline, 4-cyl., 92x92 mm, 2.445 l, compression ratio 8.2, work order 1-2-4-3, power 72.1 kW (98 hp) at 4500 / min, torque of 180.4 N-M (18.4 kgf) at 2400-2600 rpm; K-126GM carburetor; Air filter - inertia-oil.Transmission.
The clutch is one-piece, shutdown drive - hydraulic. Gearbox 4-st., Transmit. Numbers: I-3.50; II-2.26; III-1.4 5; IV-1.00; Zh-3,54; Synchronizers on all transmissions of the front turn. The cardan transmission consists of two shafts with an intermediate support. Main transmission - single, hypoid, transmit. number 3.9.Wheels and tires.
Wheels - disk, rims 5k-15 or 5 1 / 2j-15, fastening on 5 studs. Tires 185/82p15 mod. I-288, tread pattern - road, pressure in front wheels 3.2-3.3 tires, rear - 3.7-3.8 kgf / cm. sq. The number of wheels 4 + 1.Suspension.
Front - independent, spring, with transverse levers, two shock absorber, rear suspension - dependent, on semi-elliptic springs, two shock absorber.Brakes.
The working brake system is two contour, with a hydraulic drive with two vacuum amplifiers, drumming mechanisms (diameter 280 mm, the width of the pad 50 mm), spin the cam. Parking brake - on the brakes of the rear wheels, with a mechanical drive.Steering.
The steering mechanism is a global worm and a three-grass roller, transmitted. number 19.1.Electrical equipment.
Voltage 12 V, AK. 6T-60EM battery, G16.3701 generator with voltage regulator 13.3702, Starter St230-B1, Sensor-distributor 19.3706, ignition coil B116, Candles A14-B. Fuel tank - 55l, gasoline AI-93;Cooling system - 13l, water or Tosol A-40;
The lubricant system is 6l, the All-season M-6 / 10G, in the summer M-12G, in winter M-8G;
Carter of the steering mechanism - 0.40 l, TAP-15B or TAD-17 and;
gearbox - 0.95 l, TAD-17 and or TAP-15B;
Carter of the leading bridge - 1.20 l, TAD-17I or TSP-GUI;
Hydraulic brake and clutch - 0.95 l, brake fluid BSK;
Shock absorbers:
Front - 2x0,14,
Rear - 2x0.2 1 l, oil spindle AU;
Windshield washer tank - 2 l, water or niiss-4 liquid in a mixture with water.
Mass of aggregates (kg).
Engine with equipment and clutch - 185,gearbox - 26.5;
Cardan shaft - 12;
Rear axle - 85.5;
Body - 890;
wheel assembly with a bus - 25;
Radiator - 12.6.
SPECIFICATIONS
| Capacity: | |
|---|---|
| number of seats | 11 |
| total number of seats | 11 |
| number of service seats | 1 |
| Curb weight | 1815 kg. |
| Including: | |
| on the front axle | 980 kg. |
| on the rear axle | 835 kg. |
| Full mass | 2710 kg. |
| Including: | |
| on the front axle | 1275 kg. |
| on the rear axle | 1435 kg. |
| Max. Sign | 125 km / h |
| Overclocking time up to 60 km / h | 14 p. |
| Max. overcome. climb | 25 % |
| Flood from 60 km / h | 600 m. |
| Brake Path with 50 km / h | 32 m. |
| Control fuel consumption at 60 km / h, l / 100 km | 11.8 liters. |
| Radius of rotation: | |
| by external wheel | 5.5 m. |
| overall | 6.2 m. |
new 1989 RAF 2203 "Latvia" - with storage
RAF-2203 "Latvia" - Minibus, produced by the Riga Bus factory in 1976-1997.

Minibuses of this type were widely used as route taxis, emergency cars and in the role of official transport until the mid-90s, then in Russia were gradually ousted by "gazelles", and in Latvia, Mercedes minibuses and other foreign cars.

The creation of a new Rafov minibus (instead of the RAF-977 model) began in 1965. The development of a new promising car was led by two groups of four designers, one - under the guidance of Mason, the other - under the leadership of Eyster. In fact, the development was carried out in the competition-competition mode between two groups of engineers. The groups worked completely independently of each other. The projected minibus was to meet two requirements: he had to be twelve and had to be based on GAZ-21 car units.

As a result, two prototype vehicles were created: RAF-982-I Group of Mason and RAF-982-II of the Eyster Group. The first minibus had a half-door layout, this car was called "cyclone". The second promising car had a wagon layout.

Both cars were sent to Moscow to pass the interdepartmental commission. As a result, the Commission found the best RAF-982-I. However, director of Rafa, Ilya Poznyak, was dissatisfied with the decision of the ministry. He considered Futuristic ( wagon layout Buses then was in a novelty) RAF-982-II more promising model. Rafov prototypes were again sent to Moscow. After the "second round" test, the test was made about the future production of RAF-982-II.

On July 25, 1969, the construction of a new plant of Rafa began in Jelgava. After the completion of the new plant was supposed to start the release of new minibuses. Raf-982-II prototype finishes were carried out during the construction of the plant.

The new plant began work in February 1976. From his conveyor, the minibuses of RAF-2203 "Latvia" began to go. Such an official designation received new minibuscreated during the progress of the prototype RAF-982-II. In contrast to the prototype, the serial RAF-2203 used the aggregates from a newer "Volga" - GAZ-24.

Modifications
| Model | Purpose | Years of release |
|---|---|---|
| 2203 | Basic model. Used as service transport. | 1976-1987 |
| 22031 | A ambulance, differed in the presence within medical equipment. | |
| 22032 | Car to work as route taxiThe seats in the passenger compartment were located along the sides. | |
| 22033 | Service car for the police. In a specially equipped cabin, there was a penny on 2 detainees, a place for a dog, 3 seats and a pyramid for weapons. | |
| 22034 | Service car for firefighters. Designed for transportation 5 firefighters and 5 sets of equipment. A small experienced party was released, mainly the basic minibuses with the forces of firefighters were converted. | |
| 22035 | Special car for the transport of donor blood. | |
| 22036 | Special car having together ambulance and the police. A single experienced sample was released. | |
| 2912 | Small-sector version - window laboratory. | |
| 2909 | Small-sector "Olympic" version - Picap-bibliovoz with a double-round cabin and an awning. | 1979-1980 |
| 2911 | Small-sector "Olympic" version with a referee board on the roof. | 1979-1980 |
| 2910 | Small-sector "Olympic" version - a judicial electric car. | |
| 2907 | Small-sector "Olympic" version of the maintenance of a runner with the Olympic flame, the cooling system was appropriately finalized. | 1979-1980 |
| 3407 | Small-sector version - Park road train from saddle tractor and one-two trailed open beables RAF-9225/9226. | |
| Raf-Tamro. | Resuscitation car with the equipment of the Finnish company "Troo". He had a high roof and stained in a bright yellow color with orange stripes. | 1979-1989 |
| 2203-01 | Transitional model from RAF-2203 to RAF-22038. | 1987-1990 |
| 22031-01 | Ambulance transition car. | 1987-1990 |
| 2921 | Small-sector passenger version with a high roof for transportation of disabled. | |
| 22038 | The updated model with a new suspension system and some other aggregates had a modified radiator grille, there were no subcords. | 1989-1997 |
| 2915 | Ambulance on the basis of RAF-22038. | 1991-1997 |
| 22039 | Car to work as a route taxi. | 1993-1997 |
| 2914 | Reanimobile on the basis of RAF-22038 by type Toro-Raf. | 1989-1993 |
| 2916 and 2924-Toro | The small version is a chapeless van (postal, mobile shop, catatball, etc.). | |
| 33113 | Pickup with a double-shot cabin and awning. | |
| Long bead pickup with a single-row cab and an awning. | ||
| 33111 | On-board mini-row cabin. | 1991-1993 |
| 2920 | Minigurizer-van with a single-row cabin and kung. | |
| 3311 | On-board minigar with a two-round cabin. | 1991-1993 |
| 33114 | Minigurizer-van with a double-shot cabin and kung. | |
| 2926 | Minigurizer-van with a double-round cabin and isothermal kung. |
Evaluation of the project
DignityCompared to the preceding Rafa model (RAF-977), RAF-2203 was a spacious minibus. It raised the level of passenger comfort and had paramount importance for the use of RAF-2203 as an ambulance car: in the Body RAF-2203 there was enough space for the most important medical equipment. In addition, RAF-2203 had a soft smooth move.
disadvantagesToo heavy engine, hosted above the front axle, created a bad wave (over 55% of the mass accounted for the front axle), which led to increased wear and even damage front Bridge, as well as bad manageability of an unloaded minibus on a slippery road and significantly worsened the permeability (because of this, the back of the minibus was sometimes loaded with ballast). The body was different not too high quality welds and paint, as well as bad anti-corrosion properties. The bottom was made plywood (except the latest version of the route taxi 22039), which also aggravated the problems of operation. Significant problems were with the quality of the aggregate base from the GAZ-24 Volga car. Due to the features of the driver's location and gearbox, the gear shift was uncomfortable.







The historical predecessors of the plant, the products of which along with Liaz buses, Trolleybuses ZiU, trams Škoda. and taxi "Volga" was the face of the Soviet public transport The seventies and eighties were two completely different enterprises ...
The first of them - formed on the basis of private auto repair shops of Deitzmanis and dried on Terbatas Street Riga Author Repair Plant # 2 (Rarz), in turn, subsequently transformed into the Riga Plant of Bus Body (Rzak) - was anything particularly noticeable Soviet auto repair plant. Thousands of such enterprises acted across the country overhaul Government, and in certain moments of history - and private, car, trucks and buses, over time, sometimes we are going to release our own unique models (the so-called "Barbuhak"), as a rule, built on what either the finished chassis or set of aggregates.
Much more interesting from any point of view was the second predecessor RAF-A - located in Riga on Alkyshnya Street Riga Experimental Automobile Factory (Rafe, Reaf), created in 1947 under the leadership of Vsevolod Bakhchivanji, who had a native brother Hero of the Soviet Union, Test Test Gregory Bakhchivanji, who died during the war years on the tests of an experienced missile fighter-interceptor. The full retelling of the story of this is not quite traditional for the "Format" for the Soviet Automobile Watering of the enterprise would not be here to the place, it will be enough to mention that the activities of Bakhchivandzhi and K ° under the auspices of the Latvian Communist Number one Vilis Latis today is considered by many today as uniform " Poured "allocated to the development of a small car of a car - which, however, is not the only possible interpretation of events. In any case, the design and design of Raef clearly talk about, at least, outstanding abilities and eruditions of his author (authors?).
This story once again illustrates the fact that in the Stalin USSR for the "simple person from the street" (let, in this particular case - and the hero's brother) quite existed the opportunity to "break down" my idea and at least attempt to establish its practical implementation, with the allocation for this modest, But the adequate task of financial and material and technical means. It is in this way that, in particular, in the twenties and thirties, many famous Soviet Aviation Design Bureau rose from amateur groups of enthusiasts. And in the automotive industry, the same group of enthusiasts was developed on the basis the graduation project young engineer Konstantin Sharapova and launched in production at the state factory (alone and alonery) first soviet car We are-1. It was only necessary to direct their private Initiative so that it coincides with the interests of the big common Cases - and, of course, enjoy the appropriate set of professional and business qualities characteristic of any private entrepreneur.
 But all this will be later, in the meantime - in 1959, a ten-seater minibus model RAF-977 went to the series, built on the basis of the Volga aggregates of GAZ-21. In contrast to prototypes that had bearing body, it was built on the frame-joint power scheme - that is, it had a full-fledged frame integrated into the power elements of the body and constructively inseparable from it. Aggregates from GAZ-21 barely enough for the car with full massI have no alternatives for 2.5 tons, but there were no alternatives at that time.
But all this will be later, in the meantime - in 1959, a ten-seater minibus model RAF-977 went to the series, built on the basis of the Volga aggregates of GAZ-21. In contrast to prototypes that had bearing body, it was built on the frame-joint power scheme - that is, it had a full-fledged frame integrated into the power elements of the body and constructively inseparable from it. Aggregates from GAZ-21 barely enough for the car with full massI have no alternatives for 2.5 tons, but there were no alternatives at that time.
 For a long time, the release of minibuses remained semi-pedars, piece. The mass conveyor production was deployed only in 1962, simultaneously with a small restyling, which included the new front panel, with a wide radiator grille and a solid bent windshield instead of the old two half, as well as other changes ...
For a long time, the release of minibuses remained semi-pedars, piece. The mass conveyor production was deployed only in 1962, simultaneously with a small restyling, which included the new front panel, with a wide radiator grille and a solid bent windshield instead of the old two half, as well as other changes ...
 As a result, the appearance of a car was finally established, which was produced with several modernizations in Riga until 1976, and ERAZ-762 created on its database, which was produced in Armenia on Yerevan factoryAt which all relevant documentation was transferred at the beginning of the sixties - then until 1996.
As a result, the appearance of a car was finally established, which was produced with several modernizations in Riga until 1976, and ERAZ-762 created on its database, which was produced in Armenia on Yerevan factoryAt which all relevant documentation was transferred at the beginning of the sixties - then until 1996.
As can be seen, despite the sixties and seventies that occurred at the turn of the sixties and seventies, the change of generations of the basic model at the Gorky factory, in Riga were not too in a hurry with the update model Row. The fact is that the old production capacity of the plant was not designed to assemble a large number of cars and barely coped with current orders - their absolute limit was 5 thousand cars per year. Meanwhile, the need for the only minibus in the country extended far from this figure.
Therefore, in 1969, the construction of a fully new plant began to build a completely new plant near Riga, in Jelgava, designed for three large volumes of release. The transfer of production there was planned to be carried out only by the middle of the seventies and combine with the update of the model range, while the design team of the plant had plenty of time to bring his brainchild.
By themselves, work on a new minibus began in 1965. They were conducted in the form of a competition between the two design teams, numbering four people each, by the group A. Mason, who operated on the sample of RAF-982-I, and the group A. Eiser, who developed the RAF-982-II project. The task given to them was exclusively general: only the capacity of the future car was set - 12 people - and the use of GAZ-21 as a base as a base.
The concepts adopted by competing groups fully reflected two at that time in the world of approach to a car of this class.
 Collected by 1967 RAF-982-I, also known called Cyclone., was the realization of the classical half-door layout, from this point of view (but with no other) recalling then Ford Transit.
or Polish "Vyu". The design of the design of the car was obviously not, continuing the defined RAF-977 traditions of ascetic functionality, but had a number of serious advantages from a practical point of view - first of all, more successful weighing over the axes, which causes a more sparing operation for passenger front suspension. In addition, the engine made far forward contributed to the improvement of the acoustic comfort of the cabin and, potentially passive security.
Collected by 1967 RAF-982-I, also known called Cyclone., was the realization of the classical half-door layout, from this point of view (but with no other) recalling then Ford Transit.
or Polish "Vyu". The design of the design of the car was obviously not, continuing the defined RAF-977 traditions of ascetic functionality, but had a number of serious advantages from a practical point of view - first of all, more successful weighing over the axes, which causes a more sparing operation for passenger front suspension. In addition, the engine made far forward contributed to the improvement of the acoustic comfort of the cabin and, potentially passive security.
 Almost a year later, the RAF-982-II was built on the wagon layout, with the engine completely inside the cabin - between the driver's seats and the front passenger. Created under the leadership of Arthur Eiser's artist, he was distinguished first by catching, even bold for his time design, although, on the subjective opinion of the author of these lines, more resembled the product "Avtosham" than the serial car, and clearly demanded significant finishes before the start of mass release - Take at least the absence of bumpers!
Almost a year later, the RAF-982-II was built on the wagon layout, with the engine completely inside the cabin - between the driver's seats and the front passenger. Created under the leadership of Arthur Eiser's artist, he was distinguished first by catching, even bold for his time design, although, on the subjective opinion of the author of these lines, more resembled the product "Avtosham" than the serial car, and clearly demanded significant finishes before the start of mass release - Take at least the absence of bumpers!
It is not quite clear what specific considerations were guided in the sectoral ministry, but the fact remains a fact - after some oscillations, the second prototype was recognized more promising. Probably, in addition to the design, it also affected the fact that it was the car of the carriage layout to the greatest extent that resembled the small, but still bus.
It is usually indicated that final choice It was already made at the end of the sixties, and by the time of the bookmark of the new plant in Jelgava on July 25, 1969, it was already known what the car would be on it. Meanwhile, photographs of the prototype of a minibus of a half-door layout on the aggregates of GAZ-21 are also known, unambiguously dated as much as 1971:
 Thus, you can come to the conclusion that even after the decision to prepare for serial production, it was RAF-982-II for some time of work actually conducted over the car of the semicapidate layout. However, judging by the rifling ratio of the bridges and the body width in the photo depicted a bus prototype higher than RAF-982, class, so both versions are not mutually exclusive.
Thus, you can come to the conclusion that even after the decision to prepare for serial production, it was RAF-982-II for some time of work actually conducted over the car of the semicapidate layout. However, judging by the rifling ratio of the bridges and the body width in the photo depicted a bus prototype higher than RAF-982, class, so both versions are not mutually exclusive.
It is curious to note that the design of this prototype was very reminded by the "Nosted" American Wanets of the semi-door layout, which will go into a series only by the mid-seventies, such as the third generation Ford Econoline. (1975—1983).
 Meanwhile, RAF-982-II evolved, successfully managed to adapt to the new aggregate base from GAZ-24, and about 1974 already acquired quite familiar according to the serial model. exterior appearance, as well as the serial index - RAF-2203. Is it necessary to say that by this time the futuristicity of the spectacular prototype almost completely "evaporated", and the "dry residue" turned into a rather ordinary minibus of the mid-seventies in the stylistic solutions? But the incurable flaw in favorite at the layout design stage - chronic overload of the front axle - remained with new model forever and ever.
Meanwhile, RAF-982-II evolved, successfully managed to adapt to the new aggregate base from GAZ-24, and about 1974 already acquired quite familiar according to the serial model. exterior appearance, as well as the serial index - RAF-2203. Is it necessary to say that by this time the futuristicity of the spectacular prototype almost completely "evaporated", and the "dry residue" turned into a rather ordinary minibus of the mid-seventies in the stylistic solutions? But the incurable flaw in favorite at the layout design stage - chronic overload of the front axle - remained with new model forever and ever.
In her finished form, the Riga bus was a real "USSR national team" on the range of used aggregates.
 The car body was performed according to a power scheme with a carrying basis, which includes the spar of the spar frame and the floor panel with wheel arches and the front panel (the floor of the passenger salon was to relieve and simplify repair, which, by the way, often I am experiencing the Iron Body itself).
The car body was performed according to a power scheme with a carrying basis, which includes the spar of the spar frame and the floor panel with wheel arches and the front panel (the floor of the passenger salon was to relieve and simplify repair, which, by the way, often I am experiencing the Iron Body itself).
The engine and gearbox almost without alteration switched from the Volga GAZ-24. They also accounted for one of the most significant drawbacks of the car: despite the increase in the characteristics of the engine compared to 75-strong from GAZ-21, it was not necessary to talk about the special dynamism of the fully loaded Raffa, and the engine working with constant overload worn significantly faster than on sedans - Actually, he was somewhat small and for the "Volga" itself. In addition, due to the strong engine takeaway back, switching gear by a regular lever of the box, which even with a specially designed drive stacked out of the floor in the area of \u200b\u200bthe driver's seat back, turned out to be far from a trivial operation with some elements of acrobatics. On RAF-977, the base model of which - GAZ-21 - initially had a drive shift drive, this task at one time found a more successful solution - the lever was conveniently located right under the right hand of the driver.
The cardan transmission was made according to GAZ-21, with two shafts and intermediate support.
The front suspension almost completely swallowed with the Volga gas-24, but received a new steering trapezium, designed to locate the steering mechanism before, and not behind the axis of the front wheels. Soft suspension Provided the "raffika" rather smooth move, however, the same softness in combination with a specific waveguard guaranteed the permanent suspension tributes when driving along an uneven road, and therefore the accelerated wear of it with such emergency operation. The steering mechanism itself was constructively similar to Volgovsky. The hydraulic power steering in the design did not appear, although with such a coupling weight on the front wheels would not hurt it.
The rear suspension combined the items from GAZ-24, "Seagulls" GAZ-13 and original, designed specifically for a minibus. The main pair of the rear axle remained Volgovsky, with a gear ratio of 4.1: 1.
15-inch wheel disks With the caps are preserved from the previous model, unified with the "Volga" GAZ-21.
 The brake system was the original creativity of Latvian designers - I must say something more successful than the original GAZ-24 system. From the brake pedal, the force through the equalizer was simultaneously transmitted on the rods of two completely separate main cylinders, and a hydraulic amplifier from Moskvich-412 was embedded in each of the resulting independent contours. As a result, it turned out quite reliable system, ensuring the full separation of contours and a fairly effective stopping of the car while maintaining a reasonable effort on the pedal. True, the capacity of the regular Volgovsky drum brake mechanisms nevertheless was not enough, and their pads were very low in such conditions - but it is no longer disadvantages of the design as such, but the costs of excessive unification with base model. Drive unit manual brakes Initially repeated it on GAZ-24.
The brake system was the original creativity of Latvian designers - I must say something more successful than the original GAZ-24 system. From the brake pedal, the force through the equalizer was simultaneously transmitted on the rods of two completely separate main cylinders, and a hydraulic amplifier from Moskvich-412 was embedded in each of the resulting independent contours. As a result, it turned out quite reliable system, ensuring the full separation of contours and a fairly effective stopping of the car while maintaining a reasonable effort on the pedal. True, the capacity of the regular Volgovsky drum brake mechanisms nevertheless was not enough, and their pads were very low in such conditions - but it is no longer disadvantages of the design as such, but the costs of excessive unification with base model. Drive unit manual brakes Initially repeated it on GAZ-24.
The controls and equipment of the salon were the maximum unified with the same "Volga".
Complemented the picture door handles and rectangular headlights from Moskvich-412, farls with turn signals, and then fog lights, GAZ-24, as well as ingenious in its simplicity, rear lighting, scattered from individual diffusers in the form of color squares.
Although individual experienced minibuses of the new model were collected and passed to operation since around 1973, mass production was started only after starting the plant in Jelgava, in February 1976. Being designed for a production of 15-17 thousand cars per year, RAF was stably loaded with orders by 100%, and at the end of the eighties even exceeded its calculated power, each year collecting up to 18 thousand minibuses, who dreamed throughout the country.
The main field of activity for them, of course, was the route taxi service. Despite twice the greater dachshum than in ordinary flight buses - 10 kopecks instead of 5 - this type of transport enjoyed great popularity in all cities where it was presented.
The second in the mass of the area of \u200b\u200bapplication of these machines was the emergency service - reanterate on their basis gave 100 points forward much more closely on the "Volga" -Niversal.
In addition, minibuses RAF were often used as service vehicles for personnel delivery, consisting of the most various organizations - from the Soviet Army and People's Militia to research institutes, factories and educational institutions.
Shortly after the launch in the series, the car was crash under the method of seventies (concrete cube, full overlap, 50 km / h) - with a slightly predictable result for the machine such a layout.
In the early middle of the eighties, a series of cars on GAZ-3102 aggregates (forkar engine, disc brakes) was released in the semicreimental order - they were mainly enrolled in various government agencies.
 In 1987-88, the minibus was upgraded using aggregates from GAZ-24-10, receiving the designation of RAF-22038. This modification has received a significantly more modern appearance (surprisingly restyling turned out to be, perhaps even better than the original option) due to aluminum bumpers and plastic facing front, new door handles, a new instrument panel with an original design, in which the instrument shield from "Volga" was practically unrecognizable , and even your own steering wheel with your own factory emblem.
In 1987-88, the minibus was upgraded using aggregates from GAZ-24-10, receiving the designation of RAF-22038. This modification has received a significantly more modern appearance (surprisingly restyling turned out to be, perhaps even better than the original option) due to aluminum bumpers and plastic facing front, new door handles, a new instrument panel with an original design, in which the instrument shield from "Volga" was practically unrecognizable , and even your own steering wheel with your own factory emblem.
This car in the version, re-equipped under the requirements for vehicle Categories B, sold in private hands, initially under the program of support for large families - but later they received the distribution and as workers' cars, which came very by the way after the removal of restrictions on individual labor activities in 1986. At its base, the cargo van RAF-2916 was developed and was produced in small quantities, and even the RAF-3311 truck, however, who did not receive special distribution.
Rafik was produced until 1996 - the beginning of 1997, although in the past few years the production has constantly bounced due to the destruction of the decades of the established links between the plant and suppliers of aggregates and other components, which caused the various sides of the new state borders. However, after the appearance of his own minibus in Russia, the Gazelles - the Riga plant and was essentially doomed. Its the last products became - which is very symbolic - a party of isothermal vans for the transport of corpses of the RAF-2926 model, purchased by Moscow ambulance.
Currently, the plant in Jelgava is completely abandoned, negotiations with several interested in its acquisition by Russian companies were not crowned with success. In particular, Latvians did not let the gas in Yelgava, who was going to establish the assembly of their gazelles there. Like many dead businesses soviet eraThe territory of the Riga bus factory turned out to be partially turned into a trading platform.
Nevertheless, working in the rapter taxi "Rafiki" could be seen before the beginning of the 2000s, and in some corners of the former union - even in early 2010. You can meet them as a delivering car for cargo and personnel.
Oddly enough, in recent years there has been a revival of interest in the old Soviet minibuses, now - mainly as houses on wheels for long journeys. Unification with a common model passenger cars It turns out that positive feature, allowing you to practically do not experience problems with spare parts.
From the standpoint of today, it will be quite difficult to give a general assessment of the products of the Riga bus factory - in the end, any alternative to her just did not exist until the middle of the nineties, so it is difficult to judge how they would lead themselves in the same conditions, let's say Similar automobiles of foreign production, not necessarily not created to work in the route taxi.
In any case, the practice of exploitation of RAFs almost unequivocally showed that the idea of \u200b\u200bbuilding a flight of a minibus on the basis of the serial aggregates of the middle-class passenger car was unsuccessful, which is specially concerned with the chassis aggregates in general. Abroad, such a unification was still justified - most of the minibuses were there in private hands and was operated in a relatively gentle mode, almost never having a full load. In the conditions of the same daily exploitation In the route taxi mode, non-needed passenger aggregates could not ensure the required reliability and durability. It was doubly concerned and built on the same aggregate base of freight vans.
It is difficult to say to what extent here the original selection of wagon layouts with an increased loading of the front axle has been born. The dispute between it and the half-door continues until now with a variable success, although in our time, very concerned about security issues, the last seems to be starting to defeat more confidently.
It seems, however, that the next-generation minibus developers are not at all challenges - from the very beginning, he created a half-door car, while going on a more complex way and refusing to seem to be doubly tempting for the factory of the Volga's manufacturer of unification with the passenger model, instead of What to develop a full-fledged chassis with a separate frame and spring suspensions. More "passenger" minibuses of the Sobol family were also built not directly at the Volgov aggregate base, and on the basis of the aggregates developed for them from scratch.
Yes, and the employees of the Riga bus in the new generation developed at the turn of the eighties and the ninetieth generations decided to abandon excessive unification with a passenger car by turning on the front suspension of the "swinging candle" of special development.
True, it is worth noting that RAF cars operated in more easily conditions did not have such significant problems with longevity. Many of them are still on the go and successfully fulfill their duties.
Does not give an unequivocal response to the question and experience in the production and operation of such cars in other countries. So, many foreign manufacturers went along the same way - for example, Ford Econoline. and Chevrolet Van. Both started their way as minibuses and vans on the basis of serial passenger cars - Odnoklassniki Volga ( Ford Falcon. and Chevrolet Corvair., respectively). But later, both firms refused to unify and began to produce models of this type on their own chassis, borrowing only individual aggregates, mainly engines and transmissions - although retaining their design more "passenger" than our Gazelle.
The experience of the release of minibuses of the same class, but on the stock of full-sized sedans, more appropriate for the reserves of the strength of the aggregates. It is likely that a minibus on the aggregates of the chassis "Seagulls" of GAZ-14 (in many parameters similar, to the Word, on "Sobiolny") - and, it is desirable, with the V6 Gas-Ovsky engine, which would be more successful and durable than built on the obviously overloaded Volgov Raf. At the same time, since the "seagull" itself for work in a taxi was considered unsuitable - he would allow to justify the development and release of this non-none "national economic" application of the machine. You look, I would not have to remove it from production in order to "combat privileges", thus common to most of the country's population ...