The ability to prevent drift and keep on the road sliding sideways has always been considered a sign of driver skill. To master this skill, an ordinary motorist should be driving not one hundred kilometers. Thanks to the introduction of a new course stability system (the generally accepted name - Abbreviation ESP), many cars "are able to" leave such situations independently. To figure out how the function acts in practice, you need to understand general device and principle eSP work.
How is the system arranged?
This abbreviation is decrypted as Electronic Stability Program, which translated into Russian means "electronic stabilization system". It should be noted that for budget cars this function is not available, and in the machine of the average price category is set to optionally. Only dear cars equipped with ESP B. basic configuration, Later you will understand why.
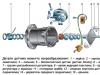
The main element of the scheme is a separate electronic control unit (it is the controller, ECU), which interacts with the following sensors:
- the rotation meter of the front wheels;
- the same for rear wheels;
- the determinant of the position of the steering wheel;
- sensor of dynamic side loads (another common name - G-sensor, angular acceleration meter).
Who has been able to deal with the principle of the anti-lock system (ABS), will probably see familiar parts in the list of rotation meters that transmit the information to the ABS controller.
The ESP electronic unit also controls the anterior and rear brake hydraulic cylinders valves plus connected to the main "brains" of the vehicle feeding fuel into the engine cylinders. In a car with a similar set of electronics, a separate controller of the anti-slip system is simply not needed, since ABS is part of the ESP and receives commands from the main computer.
 To maintain coursework passenger car ESP must interact with other electronic "assistants" of the driver:
To maintain coursework passenger car ESP must interact with other electronic "assistants" of the driver:
- system preventing the protrusion of the drive wheels (ASR);
- free differential automatic locking devices (EDS);
- the system distributing brake force depending on the conditions of movement (EBD).
Reference. In premium cars, the ESP class is closely connected with one "assistant" - adaptive cruise - control, capable of fully controlling the movement of the car along the highway and in urban conditions.
It is not difficult to guess that in budget cars, the above electronic "filling" is absent, and in the car-based price category manufacturers put anti-lock wheels and a couple of other systems (depends on the brand and configuration vehicle). That is why ESP is not available for each new car.
Principle of action of electronic stabilization
During the movement of the car, the course stability system works constantly, and regardless of the mode - in the process of overclocking, braking and driving at a constant speed. Collecting data from a group of sensors and other helping systems, the controller compares the resulting picture with the reference laid in its own memory. Finding deviations that threaten the safety of the car and passengers, the electronic unit interferes with the management and tries to correct the situation.
The ESP work algorithm should be shown on the example of the side demolition of the machine in the left turn:
- The fact of the drift marks the angular acceleration sensor (G-sensor) and transmits information to the controller.
- Additional data of the ECU receives from wheel rotation sensors and the position of the ram.
- By the combination of the received signals, the electronic unit "understands" the speed of the side displacement and its direction. As a result electromagnetic valves Hydrock Suggested the team to slow down the left rear wheel With a certain effort.
- At the same time, the signal is sent to the main car controller to reduce the feed combustible mixture In cylinders, in order to reduce the transmission of torque on the master axis.
- Result: Regardless of the driver's actions, the car slows down and aligns in turn.
 When ESP interacts with other electronic "helpers", the car stability of the car can be provided with additional means - the temporary blocking of the free differential (inter-axis and inter-track), the inclusion of the anti-slip system and the exact distribution of braking effort. In a machine equipped with an automatic transmission with electronic control (robot, variator), ESP can switch to a reduced speed or enter the winter mode.
When ESP interacts with other electronic "helpers", the car stability of the car can be provided with additional means - the temporary blocking of the free differential (inter-axis and inter-track), the inclusion of the anti-slip system and the exact distribution of braking effort. In a machine equipped with an automatic transmission with electronic control (robot, variator), ESP can switch to a reduced speed or enter the winter mode.
Note. If problems with violation of the course stability arise under the control of adaptive cruise - control, the latter will act synchronously with the rest of the system - to handle the front wheels in the desired direction.
In fact, the active stabilization system eliminates the car enthusiast from the need to study extreme ride. Entering the turn, the driver simply rotates the beam, placing other actions on the ESP. But it should be remembered that the possibilities of electronics are not limitless and not all emergency situations is capable of preventing.
Advantages and disadvantages of ESP
The electronic car stabilization system is invented with the sole purpose of improving the safety of driving, regardless of the level of training of the driver. As mentioned above, it is always on guard and at any time ready to adjust the actions of the motorist in the right direction.
The main advantage of this technology is that the speed of the electronics reaction to changes in the conditions of movement is much higher than that of any person. Sensors fix the skid at the initial stage, and the triggering of distributed brakes takes a fraction of a second. An additional bonus is an increase in comfort in management when driving for long distances, when the driver's fatigue plays a big role.
 The shortcomings of the car stabilization system in the process of movement look like this:
The shortcomings of the car stabilization system in the process of movement look like this:
- At the moment, the course stability controller does not know how to "pull out" the front-wheel drive car from the drift by increasing the torque on the front wheels. This is a very effective technique practiced by experienced drivers.
- The same applies to SUVs and passenger cars, equipped fully drive on 4 wheels. Under certain conditions (for example, ice), the reasonable pressing of the accelerator pedal can give best resultThan braking and reducing power on the drive axis.
- ESP does not particularly confidently behave in specific conditions - when driving along a loose snow either by slippery dirt road.
- Many manufacturers in the operating instructions of the vehicle warn that the stabilization electronics will act incorrectly if the auto tires of different dimensions or cylinders are not puppied properly.
For the overwhelming majority of motorists (especially newbies), the system of course stability is very useful. But some categories of ESP drivers deliver inconvenience, for example, "knead dirt" fans outside asphalt or just experienced motorists who are accustomed to ride without interference. To this case, auto manufacturers provide for the system shutdown by a special button or a separate mode activated by the automatic transmission selector.
Just a couple of dozen years since the first system appeared electronic stabilizationAnd the market has already proven the ESP of the ninth generation.
EVOLUTION ESP.
ESP-Evolution Für PRESSEBILD 10 "2014_dt und engl.ai
To begin with, let's go back in the distant 1978 year. Then, for the first time on the car, the ABS system was serially installed (anti-lock system), which did not allow the wheel during braking to be completely blocked. Thus, the driver has received the opportunity to control the trajectory of movement. It is difficult to appreciate the importance and necessity of this system, but the one who at least once in life is inhibited by "into the floor", crossed four bands diagonally, without having the opportunity to adjust the direction of movement, the benefits of ABS is aware of fully.
8 years have passed, and they began to install cars tCS system (Traction Control System) - anti-test brake system. It prevents wheel slip when starting. These systems, ABS and TCS, use the same sensors and executive mechanisms, Difference only in software. Finally, in 1995, the first ESP stabilization program appears. Electronics began to control not only the lock and slip of the wheels, but also the rotation of the car around the vertical axis - the engineers were able to curb the car. Moreover, if the first ESP consisted of 11 elements, then in a modern stabilization system of them only four.
The main task of this system is the car should go to where the steering wheel is rotated, while the skid and ruck are excluded. It works like this: the driver with the helm sets the trajectory of movement, the rotation angle sensor transmits data into the control unit, along with them there comes there from ABS sensors, acceleration and corner rotation of the body. The last two are now combined into one case and are placed directly on the hydraulicone. It is easier, cheaper and more reliable.
Once the data from one or more sensors exceeds the critical values \u200b\u200brecorded in the control unit database, the program according to the specified algorithm of action will begin to adjust the car trajectory. Now it can be done only by short brake impulses, slowing down the wheel around which the car should turn and change the trajectory of his movement. If this is not enough and the speed of entry in turn is large, the system can slightly "strangle" the engine, thereby reducing the thrust on the wheels. Many active "drivers" do not like this, but for an ordinary driver is a good help.
2. Is it worth overpaying for ESP when buying a new car?
Since mid-2014, all new cars produced in Europe should have ESP in basic configuration. We still have everything so strictly: new cars that first get oligation must be equipped with this system, and if they only prolong the certificate, it is optional. It should be borne in mind that if you need various assistants, such as a drock help system, imitation of differential blocking, parking assistant, etc., without electronic stabilization. Those who do not want to drive with an "electronic collar", you can advise you to choose the old Good classics (until 1995), but find such a car in good condition Today it is very problematic. It is even better to buy a new one, but with the disabled ESP system. As an example, you can bring the MITO model of Alfa Romeo. Depending on the mood and movement conditions, you can select one of the three basic settings. Dynamic is the most aggressive, security system works at the last moment, allowing you to get full pleasure from driving. All Weather Mode is sharpened to safety, all electronic assistants work quickly and at the maximum. Natural is an intermediate setting designed for everyday ride.3. Is it possible to retail the car equipped with ABS, ESP system?
Very tempting - buy missing sensors, install them on a car with ABS and get a car equipped with ESP! Is it possible? After reviewing several forums, they were convinced that no more "Kulibins" did not translate. Owners Ford Focus The second and third generations are actively discussing the topic and share the instructions for the alteration of the car. From an economic point of view, this is a fairly costly event, it is necessary to buy a new hydraulic unit, missing sensors and tubes, and the most important thing is to have access to the programs of the control unit and correctly installe them.Bosch's specialists do not advise to engage in similar experiments: Even if the wiring is to match, hydroblocks and control units will still be different. Moreover, even the ABS versions may differ and, accordingly, different software will be loaded in the control blocks. In addition, other components of the brake system can also differ. Alteration of system active security in garage conditions May have dangerous consequences. Still, specialists should be engaged in complex systems, not lovers.
4. Are there any differences between ESP systems that are installed on cars of different classes?
Of course, there is, and this concerns not only mechanics, but also software. For example, the difference between the ESP 9 Plus hydroblocks from Premium - in the amount of pistons that create pressure: more expensive premium their six instead of two ESP 9 Plus. Budget car No need to do business car without anything. Additional options He strongly affect the cost of the entire system. Easy to present Renault Logan. without drying brakes, but the absence of this option in the equipment list Mercedes-Benz E-Class unacceptable.5. How will the security system develop in the near future?
The main objective for the next decade is to create a car with a fully autonomous control system and run it into the series.
For this there are almost all the necessary prerequisites and developments. Prototypes have already been created, which can move in the usual stream of machines without the participation of the driver, make various maneuvers and take passengers to the final point. But such cars, firstly, very expensive, secondly, not yet completely reliable. Initially, autopilot will work on highways, then gradually be used on ordinary roads in cities. True, for this you need to solve a number of problems.
Sensors providing surroundings for 360 0
In essence, it is required to create a system that will analyze the environment and issue the right decision. The first step has already been made: active cruise control uses radar and video sensors to track road situation Ahead of the car.
Backup system architecture
The car will soon become much safer, he, like modern aircraft, will appear various duplicate systems. This, first of all, is necessary so that the sudden failure of one of the systems does not lead to an accident.
Bosch specialists have already developed a backup brake technology technology. The electromechanical amplifier of the IBOOSter and ESP brakes (electronic system of course stability) allow you to stop the car independently of each other.
High-precision cartographic data
Now the accuracy of the positioning of modern navigation systems is within one meter. For safe autopilot, accuracy should be raised at least once every ten. In addition, the actualization of maps should occur more often. Our habit of installing new signs for the time of repair of the road, and then forget to remove them can drive crazy the cybernetic brain of the car. For example, when the camcorder locks "brick", and navigation will determine the road as one-sided. Where to move? After all, the ban violate the rules road It will be basic in artificial intelligence.
We only listed three problems while on the way to creating autopilot them dozens! And yet there is hope that in ten years we will be able to go early in the morning at the cottage on the "smart" car, and on the way you can safely sleep in the driver's seat.
This year is executed exactly 20 years since the first electronic car stabilization system (ESP). We asked Bosch specialists to help figure out what was done over the years and answer the five most common issues relating to this and future system.
Many of you, for sure, more than once heard such an alphabetic combination as an ESP, which is an electronic Stability Program abbreviation, literally "electronic stabilization system", meaning a system of dynamic stabilization of the car. This system can be denoted by the following letters: DSC, VDC, DSTC, ESC, VSC, and, you know, ESP, - different manufacturers Assign her letters to her, but the essence does not change.
The main task of this electronics is to control the transverse dynamics of the machine, and at the right moment, the preservation of the trajectory of movement and course stability, as well as the stabilization of the position of the car during the fulfillment of the maneuvers. That is why it is often referred to as the "system of maintaining courseworthy" or "bonus".
The principle of ESP operation.
The system of maintaining the course stability is associated with the car motor control unit, its anti-slip system and ABS, more about the anti-lock system. In fact, all these components in the complex are a single system of contraloan activities. The ESP system itself includes a block controller (processing all signals) and various sensors (position of the steering wheel, pressure in the brake system and wheels of rotation of the wheels and others).
The main and most important are the two main sensors - this is a transverse acceleration sensor, called another G-sensor, and an angular velocity sensor from the vertical axis. It is they who catch the occurrence of lateral slip, evaluate it and transmit further instructions. The block controller estimates these signals by comparing them with embedded in the program. It is due to the ESP sensors know exactly what the vehicle speed is accurate, the rotation of the steering wheel, the number of engine speeds at this second, is there a side slip and other motion characteristics. If the movement of the car begins to differ from the calculated in the program, this block understands this, as the risk of an emergency situation, and is making actions to prevent.
These actions are to select the wheels selectively. One thing will be a wheel or a few, front or rear, external or inner to turn, the system solves itself, focusing on the situation. The resolution itself is carried out through the ABS hydromodulator, which creates pressure in. At the same time, or a little in advance, a signal is fed to the engine control unit, the fuel supply is reduced, and, therefore, the torque on wheels is reduced.
Moreover, the ESP system is always running, regardless of which mode is the car: overclocking, braking or movement along the rolled. The most interesting thing is that in each specific situation and in accordance with the type of car drive, the system works in different ways. I will cite an example: the angular acceleration sensor on the turn has been recorded rear axis, the control unit responded to this information to a decrease in fuel supply if these measures did not help, using ABS system slows down the external front wheel, Well, and so on.
 By the way, the ECP system in cars with an automatic transmission switched by electronic control is able to even correct the operation of the transmission, lowering the transmission or including. Excellent system, isn't it?! But experienced drivers who are accustomed to ride the limit of opportunities, this system is disliked, they say, she interferes with them. After all, such situations may arise when to get out of the drift, you need to gazal well, and the electronics does not make it possible. Fortunately, for such professionals, many cars are equipped with a function forced shutdown This system. And in some models of the car, in general, the system itself provides for the assumption of small drifts, which allows drivers, so to speak, a little to lose weight, but in case a really dangerous situation, the ESP stabilization system will come to help.
By the way, the ECP system in cars with an automatic transmission switched by electronic control is able to even correct the operation of the transmission, lowering the transmission or including. Excellent system, isn't it?! But experienced drivers who are accustomed to ride the limit of opportunities, this system is disliked, they say, she interferes with them. After all, such situations may arise when to get out of the drift, you need to gazal well, and the electronics does not make it possible. Fortunately, for such professionals, many cars are equipped with a function forced shutdown This system. And in some models of the car, in general, the system itself provides for the assumption of small drifts, which allows drivers, so to speak, a little to lose weight, but in case a really dangerous situation, the ESP stabilization system will come to help.
Thus, without ESP, it is impossible to present a comprehensive active system car security. It allows you to correct many mistakes allowed by motorists in the control of the machine. Thanks to her, we do not need to master the skills of extreme driving, we only turn the steering wheel in the right direction, and the car does everything for us. All this can not but rejoice. But this does not mean at all that it is not necessary to fear anything. Nobody canceled the laws of physics. And at least ESP is able to reduce the risk of many accidents, the "head on the shoulders" is still needed to have.
The ESP (ESP) electronic stabilization system is installed on cars within 15 years. Depending on the manufacturer, the abbreviation may be different: ESC, VSC, DSTC, VDC, DSC. However, regardless of the name, it has one destination: to maintain control in driving a car when maneuvers at high speeds and on the roads with slippery coating. Despite the very fact of the existence of this system, many motorists have a very weak idea of \u200b\u200bhow the ESP (ESP) works. And some say that the excess electronics them do nothing, they are quite satisfied aBS system (Although ESP is considered as an extended ABS option), others, on the contrary, are completely trusted by the system, not attacked in the principle of its action.
For curious let's try to shed light on it quite interesting electronic device. The system of control of the course stability (KSU) massively began to be introduced in the late 1990s. The impetus for this was the scandalous case, which occurred in the history of Mercedes, when tested in the fall of 1997 mercedes-Benz car A-Class, without stabilization system. When passing the so-called enemy test, when at high speed it was necessary to drive around the obstacle suddenly and return to the former strip of movement, the car lost control and turned over. It was after this incident that it was decided to supply cars with electronic stabilization system. Initially, it was planned to apply it in representative and business class machines, but with the ESP time and its analogues were accessed for budget budget cars.
Currently, KSU has become an integral part in electronic support for cars, since the end of 2011. And in 2014, in the United States, Canada, Australia and Europe, all new cars are planned to supply ESP.

How else does the ESP work? The ultimate goal set before the electronic stabilization system (ESP) - in the extreme situation to keep the car towards the movement of the front wheels. Constructively, the device is made of several sensors designed to control the vehicle in space, an electronic control unit and a pump controlling a pump brake systems Each wheel. The latter is also involved in the functioning of the system that prevents the ABS wheel lock. Sensors that are mounted in each wheel read the angular velocities of the wheels with a frequency 25 times per second. The next sensor located on the steering column tracks the angle to rotate the steering wheel. And finally the last sensor ECP is set as close as possible to the axial center of the car (Yaw Sensor), is made structurally in the form of a gyroscope (in modern systems Accelerometers are used) and fixes the rotation of the car around the vertical axis.
IN electronic block The wheel rotation speeds are compared, plus the angular speed of rotation (lateral acceleration) with an angle of rotation of the wheel, and if there is no synchronization, then the fuel supply and pressure systems in the brake lines are adjusted. Here it is necessary to take into account that the stabilization system itself does not prevent a safe trajectory of movement, its task is to direct the machine in the direction where the steering wheel is turned. At the same time, it does what it is impossible to do physically: performs independent from each other inhibition of the wheels of the machine. Also limited fuel supply, stopping the acceleration of the vehicle, which allows it to instantly stabilize.
There are two options when the car deviates from the intended trajectory. This is a skid - a clutch loss case with a road with a side slide of the rear wheels and demolition, when the side slide of the front wheels occurs when the clutch is loss. The threat of drift often occurs when leaving the rotation on cars with rear wheel drive With a sharp press on the gas pedal. In this case, the rear wheels begin to slip and move in outdoor side turn. In this position, the CSU system slows down the external front wheel and the skid stops. The demolition occurs when maneuver is performed at high speed at the time of losing the adhesion of the front wheels with the road, as a result of which the car does not respond to the rotation of the steering wheel and then continues movement in a straight line. To avoid this, the system slows down internally to turn the rear wheel, thereby preventing demolition.
In some cases, it is possible to apply the dynamic stabilization of the car when braking not only one wheel. In practice, it is used to stop two and even three wheels at the same time, except for the external front.
For motorists who believe that this system interferes with movement, visual example, refuting such an opinion, serves the simplest experiment conducted at the ice track. When moving along such a road at the average driver, the chance to fly off the track without a stabilization system will increase, not to mention the fact that he can only dream about the best time. Most of all disbeliefs of the ESP system arises from drivers who do not want to understand simple truth: the electronic stabilization system is trying to direct the car in the direction where the wheels are turned.
ESP may be unnecessary only when you have a desire with the effect of twist a wolf, or you experienced a racer, who wants to install a new record on the racing track. Here, of course, the stabilization system will be a hindrance that does not allow the use of controlled driving for turning, and the limited fuel supply will not allow you to quickly dial the speed at lateral slides.
ESP can also play a cruel joke with the owners of crossovers with the next conquest of a difficult-scale area of \u200b\u200brough terrain or the road without asphalt coating (in the most responsible moment when the wheel is needed, in order to cling to something, the stabilization system, on the contrary, slows down and overlaps Fuel). So, if necessary, ESP can, and in some cases it is necessary to disable. Just not worth it to do inexperienced drivers, or if the bus bower is going to go to the country road, where he plans to move at high speed.
However, in order to master the car control skills on a slippery road, you need to learn driving with the stabilization system. Only in this case you can correctly determine the time of the start of the drift or demolition, and correctly select the speed for maneuver. If the manufacturer has not provided a shutdown of the system offline, then, as an option, you can turn off one of the speed sensors from one of the wheels or remove the ABS pump fuse. But at the same time, you should not forget that the anti-lock brake system will be turned off.
Modern car is a complex system in which many elements are combined. Automakers in their struggle for comfort and security are developing and implemented various new systems. Now one of the key systems in new models used to enhance security is the ESP system.
If it is easier to speak, then this is a course stability system. Almost no car, among those that come from conveyors in recent years, do not cost without this technology.
So what is it? And how does the ESP system work?
Answers to these questions will allow better understanding of all the features of the car, and also greatly facilitate the operation of the operation. After all, to get the maximum that manufacturers offer, it is necessary to understand what it is necessary to deal with.
Features of technology

ESP (Electronic Stability Program) is a system of dynamic stabilization of the car. Sometimes there are other abbreviations, but this is most often found precisely. Various companies sometimes implement their designations. However, this fact Not at all affects how the ESP system works.
The active introduction into production was started in 1994 on top models. Now it has become quite affordable for everyone, therefore, the direct dependence on the class class is no longer traced.
What is necessary for this system

Its main purpose is to improve safety in various critical situations, due to an increase in the control of the transverse dynamics of the car.
Thanks ESP car Much less is at risk of breaking into a skid or exit lateral slip. The position of the car on the road is stabilized and the initial course stability is saved even on sophisticated areas Trails and during turns.
From here, the integral name of the ESP system was "bonus".
However, not everyone understands how the ESP system works.
Principle of operation

In the car, as a rule, there are several similar systems. In particular, we are talking about ABS - anti-passing system. They are closely interrelated. A separate unit control reads information from many sensors, based on which this or that solution is accepted. Thus, ESP is only part of one single "body" vehicle.
The control unit reads several parameters:
Rotation speed of wheels;
Steering wheel position;
Pressure in the brake system.
On the basis of this, it is possible to obtain accurate and reliable information as to how correctly and steadily the position of the car on the road.
But the most important parameters give two other sensors:
Corner Speed \u200b\u200bSensor;
Transverse acceleration sensor (the so-called G-sensor).
In the event of a risk of falling into a skid, it is these two sensors initially fix the start of the lateral slip and determine the potential danger. After that, the control unit gives the necessary commands.
At this point, the ESP system already has the necessary information about how speeding the machine is moving, in which position it is in which engine is running, etc. Various sensors Constantly fix this information. If the actual position of the car is different from the calculated, therefore, something goes wrong.
Next, the controller practically instantly processes information and makes the necessary decision based on the program. All this is aimed at automatically align the position of the vehicle on the road.
However, how exactly does the ESP system work? In other words, how do she manage to provide the necessary stability and save the transport with drivers and passengers from entering the skid?
After making a solution, the car unit automatically controls the rotation of the wheel. At this point, they begin to rotate not synchronously. Some wheels slow down towards driving, others, on the contrary, are released.
Here the other element is entering into the case - ABS Hydromodulator.
As already mentioned, these two systems work inextricably with each other.
Now there are quite complex ESP systems, which, for example, are able to even monitor the features of the work. automatic box Transmissions. They work at any time of movement, so they are always ready to join. In some cases, motorists do not even notice how the ESP system works - it simply gently adjusts the course stability. Naturally, in many similar situations, the driver is simply not able to quickly take the necessary solution, so it significantly increases the safety of motion. Now many companies began to establish such systems to their models, and motorists in turn look at their presence when choosing a vehicle for themselves and their family.




Video
Story about the ESP system in video format: