All models Raf. 2019: the lineup cars Raf, prices, photos, wallpaper, specifications, modifications and configuration, reviews of the Raf owners, the history of the brand Raf, review of the RAF models, video test drive, the archive of RAF models. You also find there discounts and hottest offers from official dealers RAF.
History of the brand RAF / RAF
Riga bus factory, RAF (Latvian. Rigas Autobusu Fabrika, Raf) - Soviet and Latvian minibus manufacturing enterprise. In 1949, on the basis of the Riga Car Repair Plant No. 2, which was located in the former workshops of Dezmanis and drove on the street. Terbatas, "Riga Plant of Bus Body" (RZAC) was created. The activity of the plant was the production of medium buses. In 1951, Rzak was combined with the "Riga experimental automotive factory" (react). In 1953, the plant released the first 25 RAF-651 buses. Capotic RAF-651 was a copy of the Gaza-651 Gazhkovsky bus on GAZ-51 cargo, accompanied 25 passengers and had 16 seats. On June 10, 1954, the order of the Ministry of Motor Transport was reorganized into the "Riga Experienced Bus Plant", but already on September 30, 1954, it was renamed again - and this time received the final name: "Riga bus factory" (RAF). In 1955, the release of buses was established own development. New bus RAF-251 was also based on the GAZ-51 chassis, but already had a wagon layout.
In 1957, Raf employees got acquainted with the minibuses of the Volkswagen brand and decided to organize the production of small comfortable buses in Riga. Chief Engineer Lymons Klege (Laimonis Klege), Designers Ya. Ositis (J. Ositis), G. Sils (G. Sils) and 4 more enthusiasts created the first car RAF-10 in an initiatory order. In honor of the VI World Festival of Youth and Students in Moscow, Raf-10 received the name "Festival" (Latvian. Festivals). RAF-10 was built on the platform a passenger car GAZ-M20 "Victory", had a wagon layout, steel carrying body and 10 seating (corresponds to the model index). The initial construction of the body caused a lot of complaints and in 1958 was changed. The car also received the engine from GAZ 21 "Volga". On November 20, 1958, the plant began a serial release of the Minibus RAF-10 "Festival", 11 copies were made by the end of the year. The experience gained in the development and conclusion of RAF-10 and RAF-08 was realized in the RAF-977 model "Latvia" (Latvi. Latvija), built on the chassis of the car GAZ-21 "Volga". In 1958, the first 10 copies were released, since 1959, full-scale mass production was deployed. In 1960, the first generation machines were replaced by the upgraded RAF-977V.
In 1976, a new plant was commissioned in the city of Yelgava under Riga, designed for production of 17 thousand cars per year. Here, the production of 11-seater minibuses RAF 2203 "Latvia" on the aggregates of GAZ-24 "Volga" began. A lot of modifications were produced at its base, and the Finnish company Tamro created a resuscitation car. In the 1980s, excursion trains on the basis of RAF-2203 worked at the VDNH in Moscow. By 1986, the decline in the quality of production RAF caused public resonance to the USSR, which caused the resignation of the former leadership of the plant. In the spirit of restructuring reforms, in 1987, the appointment of the new director was preceded by his election by the plant by the plant from the list of proposed candidates. Victor Bosser won in the elections. This man served as director RAF until 1990. On September 6, 1991, RAF reorganized the joint-stock company. In the same year, Latvia became independent, an end to the Soviet planned economy came. After deploying in March 1996, on gas of large-scale production of minibuses of the GAZ-3221 family, "Gazelle", in many respects exceeding RAF products, the export of Latvian minibuses to Russia was rapidly sued. In 1997, production at the RAF plant stopped. The owners declared bankruptcy in 1998. As of 2010, most of the production corps are destroyed, leased retail areas are located in their place.
Let's see what happened to the automotive plants that produced equipment during the USSR.

Yerevan Automotive Factory
On December 31, 1964, the Order of the Armenian SSR No. 1084 was decided "On an organization in the city of Yerevan in the factories of the Forklift plant under construction of a car for car vans with a carrying capacity of 0.8-1.0 tons." It was there that the charming vans Eraz were created, the brothers of the Latvian Rafikov.
In November 2002, the plant was declared bankrupt, and two years later his premises were sold at auction. The new owner was the company "Mc Metal", which produces reinforcement, nails and other products made of metal. So the plant looks in our day.

Riga automotive factory
Well, the Rafa themselves began to release from 1953 on the basis of the Riga automotive factory, which was built in 1949 at the site of the "Riga Author Repair Plant No. 2". Until 1954, the plant wore the name of Rzak - Riga Plant of Bus Body. The most bright years of his years fell on the 50s-70s, but after the release of Latvia from the USSR, the plant began to die.
The company was declared bankrupt in 1998 and now the plant's area was partially looted and destroyed, and partially given under warehouse and office rooms. Ironically, the last cars of the plant were created for funeral services.

Kutaisa Automotive Factory
Let the name "Kolkhida" and became the synonym for an unreliable truck in the Soviet Union, the cars under this brand were produced until 1993. Later, attempts were made to revive the production of agreements with GM, Mahindra, HTZ, but they did not lead to anything concrete. As a result, since 2010, the plant, which was built in 1951, is idle. Most of its equipment is plundered and cut into metal, only an administrative building remains in the "live" state, which is protected (in the photo).

Vilnius Vehicle Factory
The forge of the fastest Ralone cars of the Soviet Union, located in Vilnius, was created in the late 70s on the basis of the Vilnius Authororer. New enterprise got the name Vilnius Factory Vehicle (VFTS) and for a long time it existed even after the USSR became a story, switching to the construction of rally cars according to individual projects.
Now the territory where VFTS was located is occupied by the Volkswagen service station, and there is little reminded about the last rally of magnitude.

Lviv Bus factory
The last large order of the Lviv bus factory, which since its construction in 1945, revealed many magnificent cars, was the delivery of a batch of buses and trolley buses to the city of Ukraine, which took Euro-2012's football championship. Today the plant is a huge empty premises, of which almost all equipment for the assembly took out.

Rousseo Balt.
The automotive department on the basis of the Russian-Baltic Wagon Plant appeared in 1908, however, during the First World War, the company "went on" on other corners of Russia for evacuation purposes. In the native walls of the car, there were not so long - only seven years. And on July 1, 1917 began working "the second automotive factory Rousseno Balt. " Now the plant in Riga looks like this. And let his condition seems to be veterging, there are still former greatness in these walls.

Dux
YOUR HISTORY The plant "Dux", which this year marks 124 years old, started from the release of bicycles, but soon expanded production to cars and aircraft. The first "dead loop" performed by Nesterov was performed just on the aircraft "Dux". Now on the territory of the plant complex, which in 1993 returned the historical name "Dux", produce weapons for air-air aircraft.
Part of the complexes of the complex at the address: Moscow, Street Pravda 8 is transferred to office space and trading platforms.

Plant named after Likhachev
Muscovites are well aware of what happened to Zil. One of the oldest auto plants founded in 1916, under the influence of urban processes turned out to be nobody unnecessary. As a result, the factory premises were equalized with the Earth and in its place it costs the residential complex "Zilart", next to which the Park "ZIL" will appear next to the fall.
The highlight of this park will be the terrace in the form of a conveyor line - as a tribute to the historical past.

Moskvich
Construction of the plant at the intersection of the current small rings of Moscow railway And Volgograd Avenue started in 1929, and already in the 1930th enterprise began its activities. The dawn of the plant, subsequently the name "Moskvich", fell on the post-war years. But by the beginning of the "perestroika" over the "Moskvich", clouds began to thicken, in 2001, production was stopped, and in 2010 the procedure of bankruptcy of the enterprise was completed.
One of the workshops of the plant, in which the engines were planned, now belongs to Renault Russia. On the territory of another Radius Group planned to open a cryptocurrency mining farm.

Yaroslavl Automotive Factory
101 a year ago, Vladimir Lebedev began producing crossley cars in Russia - under license. What posted the beginning of the plant, which is now known as the Yaroslavl Motor Plant. Where the eyelids collected a copy of the British cars, now they make diesel engines.
In the interval between these epochs at the enterprise gathered a variety automotive technology, including trucks of the series I and Trolleybuses Yatb.
new 1989 RAF 2203 "Latvia" - with storage
RAF-2203 "Latvia" - Minibus, produced by the Riga Bus factory in 1976-1997.

Minibuses of this type were widely used as route taxis, emergency cars and in the role of official transport until the mid-90s, then in Russia were gradually ousted by "gazelles", and in Latvia, Mercedes minibuses and other foreign cars.

The creation of a new Rafov minibus (instead of the RAF-977 model) began in 1965. The development of a new promising car was led by two groups of four designers, one - under the guidance of Mason, the other - under the leadership of Eyster. In fact, the development was carried out in the competition-competition mode between two groups of engineers. The groups worked completely independently of each other. The projected minibus was to meet two requirements: he had to be twelve and had to be based on GAZ-21 car units.

As a result, two prototype vehicles were created: RAF-982-I Group of Mason and RAF-982-II of the Eyster Group. The first minibus had a half-door layout, this car was called "cyclone". The second promising car had a wagon layout.

Both cars were sent to Moscow to pass the interdepartmental commission. As a result, the Commission found the best RAF-982-I. However, director of Rafa, Ilya Poznyak, was dissatisfied with the decision of the ministry. He considered Futuristic ( wagon layout Buses then was in a novelty) RAF-982-II more promising model. Rafov prototypes were again sent to Moscow. After the "second round" test, the test was made about the future production of RAF-982-II.

On July 25, 1969, the construction of a new plant of Rafa began in Jelgava. After the completion of the new plant was supposed to start the release of new minibuses. Raf-982-II prototype finishes were carried out during the construction of the plant.

The new plant began work in February 1976. From his conveyor, the minibuses of RAF-2203 "Latvia" began to go. Such an official designation received new minibuscreated during the progress of the prototype RAF-982-II. In contrast to the prototype, the serial RAF-2203 used the aggregates from a newer "Volga" - GAZ-24.

Modifications
| Model | Purpose | Years of release |
|---|---|---|
| 2203 | Basic model. Used as service transport. | 1976-1987 |
| 22031 | A ambulance, differed in the presence within medical equipment. | |
| 22032 | The car to work as a route taxi, the seats in the passenger compartment were located along the sides. | |
| 22033 | Service car for the police. In a specially equipped cabin, there was a penny on 2 detainees, a place for a dog, 3 seats and a pyramid for weapons. | |
| 22034 | Service car for firefighters. Designed for transportation 5 firefighters and 5 sets of equipment. A small experienced party was released, mainly the basic minibuses with the forces of firefighters were converted. | |
| 22035 | Special car for the transport of donor blood. | |
| 22036 | Special car, having together ambulance and police. A single experienced sample was released. | |
| 2912 | Small-sector version - window laboratory. | |
| 2909 | Small-sector "Olympic" version - Picap-bibliovoz with a double-round cabin and an awning. | 1979-1980 |
| 2911 | Small-sector "Olympic" version with a referee board on the roof. | 1979-1980 |
| 2910 | Small-sector "Olympic" version - a judicial electric car. | |
| 2907 | Small-sector "Olympic" version of the maintenance of a runner with the Olympic flame, the cooling system was appropriately finalized. | 1979-1980 |
| 3407 | Small-sector version - Park road train from saddle tractor and one-two trailed open beables RAF-9225/9226. | |
| Raf-Tamro. | Resuscitation car with the equipment of the Finnish company "TRORO". He had a high roof and stained in a bright yellow color with orange stripes. | 1979-1989 |
| 2203-01 | Transitional model from RAF-2203 to RAF-22038. | 1987-1990 |
| 22031-01 | Ambulance transition car. | 1987-1990 |
| 2921 | Small-sector passenger version with a high roof for transportation of disabled. | |
| 22038 | The updated model with a new suspension system and some other aggregates had a modified radiator grille, there were no subcords. | 1989-1997 |
| 2915 | Ambulance on the basis of RAF-22038. | 1991-1997 |
| 22039 | Car to work as a route taxi. | 1993-1997 |
| 2914 | Reanimobile on the basis of RAF-22038 by type Toro-Raf. | 1989-1993 |
| 2916 and 2924-Toro | The small version is a chapeless van (postal, mobile shop, catatball, etc.). | |
| 33113 | Pickup with a double-shot cabin and awning. | |
| Long bead pickup with a single-row cab and an awning. | ||
| 33111 | On-board mini-row cabin. | 1991-1993 |
| 2920 | Minigurizer-van with a single-row cabin and kung. | |
| 3311 | On-board minigar with a two-round cabin. | 1991-1993 |
| 33114 | Minigurizer-van with a double-shot cabin and kung. | |
| 2926 | Minigurizer-van with a double-round cabin and isothermal kung. |
Evaluation of the project
DignityCompared to the preceding Rafa model (RAF-977), RAF-2203 was a spacious minibus. It raised the level of passenger comfort and had paramount importance for the use of RAF-2203 as an ambulance car: in the Body RAF-2203 there was enough space for the most important medical equipment. In addition, RAF-2203 had a soft smooth move.
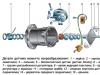
disadvantagesToo heavy engine, hosted above the front axle, created a bad wave (over 55% of the mass accounted for the front axle), which led to increased wear and even damage front Bridge, as well as bad manageability of an unloaded minibus on a slippery road and significantly worsened the permeability (because of this, the back of the minibus was sometimes loaded with ballast). The body was different not too high quality welds and paint, as well as bad anti-corrosion properties. The bottom was made plywood (except the latest version of the route taxi 22039), which also aggravated the problems of operation. Significant problems were with the quality of the aggregate base from the GAZ-24 Volga car. Due to the features of the driver's location and gearbox, the gear shift was uncomfortable.







The dynamics of modern standards is modest. Seventy five horse power The engine for a thousand seven hundred with nuts of kilograms of the exhaust mass is not much at all. But in the sixties it was enough. Some European analogs have been loose more. And now Raf, even if it is not fast, you can take it to quite sufficient for urban speeds. We just need not to forget that the brakes are not at all modern here: drum and without amplifier. Of course, they try, as they can restrain the car, but it is not necessary to put pressure on the pedal, and the slowdown is still not the god of the news.
Roured also requires skills. Even on a straight rate at 50 km / h, "Rafik" begins to swim a little, demanding constant infringement. By the way, the car can rather confidently can go and at a speed of 100-110 km / h, but such a pace is not a rustling of the 977th Rafa.
In rapid turns, the high minibus is noticeably cubed, but the stroke is soft. In general, in the 1960s, and in the early 1970s, the comfortable RAF-977 was undoubtedly the best Soviet serial nurse and a car, quite comparable in many of the parameters with imported analogues.
Latvija from Latvia
Minibuses of UAZ and RAF, including in the sanitation, appeared in the country almost simultaneously. Such machines doctors were very necessary. After all, until the end of the 1950s, the main sanitarian was the Paz-653 - a booth on the chassis of the GAZ-51 truck, as well as the ZIS-110. The car on the chassis cargo was spacious, but very shaking. ZIS and winters went softly, but the doctors were closely in them: you can carry the patient, but you will not find serious help on the road, and you will not place the necessary equipment. In addition, the cost of sanitaries on the basis of a large expensive sedan, especially a governmental melk-sector limousine, was very high.UAZ was performed primarily for rural areas and at first in very small quantities. So the main urban machine for hospitalization of patients was RAF. In the early 1960s, the challenges, however, began to leave and fast on the basis, but they are again less comfortable for physicians.
It was small, and it is not too great. By the way, the cars collected were drowning on the stands with wheels and pushed along the rails - a shaped hand conveyor. Before the construction of a new plant in Jelgava, there were still almost two decades, so the natives and minibuses on the units of the 21st Volga did only a small Riga plant. In order not to reduce their production, the release of vans was transferred to Yerevan.
The first samples of medical machines were made from 1958 on the basis of RAF-977B. In the large series in 1962, the sanitary raf-977 was launched - this is a modification of the RAF-977D minibus. After modernization in 1968, who touched the main body (it was once again strengthened, the side windows changed), the medical machine received the index RAF-977. The car on which I managed to ride exactly such.
Foreign analogs |
||
| Volkswagen T2, 1967-1979. Engines: gasoline, 48 hp, later - from 67 to 71 hp Volkswagen T2, 1967-1979. Engines: gasoline, 48 hp, later - from 67 to 71 hp | RENAULT ESTAFETTE, version 1968-1980. Engine with a capacity of 43 hp RENAULT ESTAFETTE, version 1968-1980. Engine with a capacity of 43 hp | Ford Transit. (second generation), 1965-1978. Engines: gasoline, power 75-83 hp, as well as diesel in 70 hp Ford Transit (second generation), 1965-1978. Engines: gasoline, power 75-83 hp, as well as diesel in 70 hp |
Cabinet number 977.
Of course, the suspension from the Volga worked on a heavy car at the limit of possibilities (especially the front), but the course of "Rafa" is very soft. And this, believe me, is important and those who are taken, and those who are lucky. At one time I experienced a sanitary gazelle, and then an imported minibus. Difference, I share you, huge! And the raf in the smoothness of the stroke is about in the middle between them, and certainly more comfortable gazelles with a rigid cargo suspension.
The doctor here, of course, is much more convenient than in the 22nd Volga, - Mésta plenty. The sanitary "rafiki" was very different from each other with a complete set, but in any case, the medical compartment was accompanied by everything necessary and possible equipment in those years, including an artificial respiratory unit. In this sense, the car was quite modern. He would have a high roof ... the first similar soviet cars appeared on the basis next model - RAF-2203, and even at first only Finnish production.
How many lives saved such rafs, no one knows. They diligently worked in all corners of the Union, in large and small cities. Of course, Raf, especially the sanitary worked during the day and night almost without breaks, demanded constant attention. The details of the already remembered Volgovsky suspension and steering, not the most durable and durable was carrying the body. However separate cars served in the early 1980s, when a completely new, powerful and quite modern at that time, the Yelgava plant was already far from the first year released a new model.The sanitary 977th was shot in dozens, and even in hundreds of Soviet films - in drams, detectives, household stories from medical life. Thanks to this, the connoisseurs of the Soviet retro today can learn how such cars looked and were staffed. By the way, this RAF, on which we went to the challenge today (of course, fictional), participates in filming, helping more accurately recreate the long-stayed era. In general, a car in good health and is ready for this work. We assume that it is not retired, but simply in stock.
COLLEAGUESSectional doctors at home calls in the USSR took all models on Muscovites, starting with the "four hundred." Simultaneously with RAF-977, several other domestic models worked in the ambulance service. |
||
| GAZ-22D, 1962-1970. Sanitary Volga could carry a lying patient and two passengers sitting next to him. A similar gas-24-03 car came to the change of this model, created on the basis of the GAZ-24-02 universal. GAZ-22D, 1962-1970. Sanitary Volga could carry a lying patient and two passengers sitting next to him. A similar gas-24-03 car came to the change of this model, created on the basis of the GAZ-24-02 universal. | ||
Hi-minibus in Riga began to be engaged shortly after the serial release of RAF-977 began. Already in 1963, Rafa designers were developing a new model, whose body was planned to perform not from traditional metal, but from reinforced glass fiber. Such a direction in those years was quite popular - it is possible to remember both the petrolery, and other experimental models with fiberglass bodies.
Alternative material was selected for several reasons. First, the Chemical Industry of the USSR at that time actively engaged in innovative materials for widespread use - and this meant that fiberglass could also be used in the automotive industry. Secondly, the use of plastic instead of a traditional sheet metal would theoretically make a car not only much easier, but also more durable - after all, from the point of view of corrosion resistance, the plastic body would be "eternal". Finally, such a reception enulged a good saving of steel sheet, which, on the scale of the country, it seemed a very promising option to reduce the cost of production.
However, for a number of reasons, the development of fiberglass as a material for the manufacture of body parts was suspended. The change in the country's leadership meant the revision of priorities and trends - including this and the chemical industry. In addition, experiments with fiberglass showed that this material does not have sufficient mechanical strength and loses metal in the stability of the characteristics.
Two options
After the fiberglass work was finally minimized, the designers returned to a more traditional metal from which the body of the future minibus should have been manufactured. The technical task at the end of the sixties has not yet been specifically formed, but everyone in the Riga bus factory was understood that the car should be based on the aggregate base of the same "twenty-first" Volga. The only limitation is passed: minibus eventually had to get twelve.
In a specially organized competition, two creative groups of factory designers took part, each of which was to build two prototypes of their own design. The prototypes differed only by the "added" digit in the index: Group A. The Arise was built by RAF-982-1, and the team A. Bergs - RAF-982-2.
1 / 5
2 / 5
3 / 5
4 / 5
5 / 5
The team of the Giazisis tried to escape from the wagon layout to the half-door - about the same scheme was performed newest Ford. TRANSIT Sample 1965. An important difference between such a scheme - the driver and the passenger did not sit "on the wheel", like the first minibus RAF, and behind the front axle (as on modern gazelles). At the same time, the minibus according to the appearance turned out to be rather heavy and obsolete. The effect only intensified by a small area of \u200b\u200bglazing and highly raised lateral line.
1 / 2
2 / 2
But the option that designed the Bergs group turned out to be completely different. Not retreating from the familiar wagon layout with the location of the driver and passenger over the front axle, the second team was able to create a very unusual outwardly single-visuous car, which, thanks to a large glazing area and a strong slope. windshield It looked unconventional and at the same time very modern.
At the end of the sixties, a member of the Union of Artists of the USSR, Arthur Eiser, RAF-982-2 looked at the same "aliel out of the future" - a minibus, who won his time.
1 / 2
2 / 2
Indeed, even a foreign car industry at that time did not release cars with such a bold and distinctive appearance. And the most amazing thing that with all the nontriviality of the minibus turned out to be very attractive - harmonious aesthetically and simply beautiful.
The interdepartmental commission of the Mainstoprom at the show of the first copies of each group carefully examined both options and, together with representatives of the Ministry of Health and the specialists, we concluded that a more traditional and usual version of the feature in terms of launching in mass production looks preferable. However, by the next "Watching" in 1971, the Bergs group was able to prepare an improved version of RAF-982-2, having relocated its prototype from the most obvious deficiencies. At the same time, the appearance of the car deliberately slightly "landed", which subsequently had a favorably on the perception of the "Concept".

The "second edition" was made better than the first, and the Commission made his verdict: a car created on the basis of the prototype 982-2 will be produced in Latvia. True, it was first necessary to ... Build a new plant, since the Riga factory in terms of technology and production facilities did not meet the requirements that were laid at the stage of developing a new minibus project. Therefore, the second generation raf should have been released not in Riga himself, but in the neighboring Yelgave, where the construction of a new auto plant soon began.

The future RAF-2203 appeared on the cover of the journal "driving" in 1974, but in 1971 the photography of the prototype flashed on the pages of the publication!
Since at the beginning of the seventies, the automotive industry was on the rise, at the new enterprise, installed the most modern presses, stamping and painting equipment. At this time, in Armenia, it was just actively changing the equipment for production, but the factory in Jelgava was not exceeded by the Yerevan Plant in terms of technology, then in terms of future production was an order of magnitude higher, in one moment becoming the largest manufacturer of minibuses in the USSR.
But at the time of starting the construction of a new auto plant in Latvia, work on the minibus itself was not yet completed. Specialists from us, whose task was to make the Machine "Self" on the technical characteristics, reliability and even competitiveness in foreign markets were connected to bringing the new design. Finally, it was necessary to cover the entire range of modifications, because the future minibus was to master the mass of professions and appear in a wide variety of hypostatas. Unlike the previous rafts and already mentioned Erazov, the minibus of the new generation also had to become the most massive car of this type - and this means that the technology of its production, and the design was to "hide" under this important nuance.
1 / 4
2 / 4
3 / 4
4 / 4
In the process of finishing, the minibus was far away from his prototype - the first version of Bergs with an index 982-2 is guessed in the serial RAF-2203, but not more than that.
At the same time, during the development of a new model and a conveyance cycle, the Rafa appeared a new "donor of the aggregates" - in the bitter instead of the familiar and already outdated GAZ-21, the release of a more modern Volga GAZ-24 began. Of course, for the Latvian new items decided to use the nodes and units "Twenty-four" - good, structurally differed from the components of the predecessor not so much so that it requires major changes in the design or layout of the minibus.
New "Rafik"
Compared to RAF-977D, the second-generation minibus has become not only modern externally, but also more comfortable. Thanks to other proportions, the car has noticeably reduced the center of gravity, which has favorably affected the ravings and, as a result, manageability and sustainability. The safety of RAF-2203 answered a more modern two-door brake actuator system, and convenient separate seats for all passengers appeared in the cabin; Metal interior elements covered with soft linings.
1 / 4
2 / 4
3 / 4
4 / 4
Interesting detail: A new minibus has received its own ... The emblem, consisting of a stylized silhouette of the car, in which the Latin was "entered" the factory abbreviation RAF. Therefore, some Soviet citizens at first were confident that this minibus was manufactured "abroad", and the effective design of the novelty only strengthened such an impression.

At the end of 1975, the first batch of minibuses RAF-2203 was collected in Yelgava, and already since 1977, the series launched and modifying the ambulance of RAF-22031. After all, it was the "ambulance" on the volume of issue planned as the main modification of the new model.
1 / 9
2 / 9
3 / 9
4 / 9
5 / 9
6 / 9
7 / 9
8 / 9
9 / 9
Early minibuses (release until 1979) differ from later "rafikov" by some details of the finish. You can visually identify such a car on a round housing of side mirrors and smooth corners front bumper Without individual "fangs", a pair of small bumpers in the corners of the back, "subharbaths" from GAZ-24 and chrome-plated caps from the "twenty-first" Volga. Also cars of the first issues were equipped with the original instrument panel, from which they subsequently refused in favor of the standard Detail of GAZ-24.
Later RAF-2203 is easy to distinguish with "bus" turning signs under the front bumper. It is the same version of "Rafika" (up to 1987) without any special changes.
 "Rafik" was used not only on flight routes, but also as a taxi
"Rafik" was used not only on flight routes, but also as a taxi Despite the fact that in 1979, the products of the Riga bus factory were awarded a state mark of quality, already from the beginning of the eighties to the level of manufacturing and assembling of route taxis and emergency carriage was made a lot of complaints.
1 / 4
2 / 4
3 / 4
4 / 4
When the level of marriage exceeded 10% of the number of cars issued, the plant management was changed, and considerable public funds were identified for the modernization of the minibus.
As a result, RAF enhancements were planned to be made not only modern, but also better. Even at the beginning of the eighties in Riga, a prototype of RAF-22038 was created - as they would say now, the restyled version of the first model. During the update, the body enhancement was planned, improving the ventilation of the cabin due to the presence of a hatch and additional vents, more modern chassis With another front suspension design and a new interior.
1 / 2
2 / 2
However, by the mid-eighties, it became clear that the plant was not able to immediately implement all the innovations, so in 1987 the production of the "transitional" model under the index 2203-01 began. Her main thing technical difference - ZMZ-402.10 engine from the Volga GAZ-24-10, and externally, the model is easily distinguished from the first iteration "Rafa" for a number of characteristic features. Thus, the front "turn signals" moved under the grille, instead of "round" bumpers, parts made of aluminum profile with black side fangs appeared on the car, the front doors were lost to the forces and got large plastic mirrors, and instead of chrome-plated caps in the center wheels Plastic inserts appeared.

In addition to the main modifications ( route taxi and ambulance), in Riga, other versions of a special purpose minibus were developed - a mobile fire headquarters or a machine for the operational service of the USSR Ministry of Internal Affairs. However, subsequently, such "specials" in Latvia were not produced, and various repairs for orders were altered by ordinary passenger RAF-2203.
1 / 2
2 / 2
In 1979, several were issued to serve the upcoming Olympiad-80. The Riga plant has prepared specials and until the beginning of 1980 made about 300 copies of the Olymp Rafikov in the workshop of the small series. Thus, the honorary support of the Olympic Fire from Greece in the USSR (tribute to ancient Greek tradition) was assigned to RAF-2907, in which the responsible keepers, together with spare torches, accompanied the runners. Of course, the specificity of such a low-speed ride for a long time demanded a serious improvement of the cooling system, but RAF coped with the Olympic Mission.
1 / 2
2 / 2
The most unusual option was RAF from the Finnish company Tamro, which by order of the USSR was engaged in re-equipment of "rafikov" in reanimal ambulance. In Finland, there were not so many "reanimations", but in the eighties in the streets of many cities it was possible to meet micro-buses of lemon yellow with bright red stripes and a high fiberglass roof superstructure.
1 / 5
2 / 5
3 / 5
4 / 5
5 / 5
Soviet drivers public transport And Emergency workers quickly fell in love with a small, but comfortable and maneuverable minibus.

Of course, RAF-2203 had disadvantages - except for the flaws of manufacture and assembly, a constructive minibus was not too secure for the driver and the front passenger. After all, with a frontal accident, depring deformation zones, a carrier bodie machine, weakly absorbed the impact energy. Yes, and the "Volgovskaya" platform at maximum load was weak, therefore, the rafiki worked on routes "after 4-5 years of intensive operation required overhaul. At the same time, due to the car layout, the minibus was not very convenient in service, and access to the engine was possible only from the cabin, so any serious intervention required dismantling the power unit.