The prototype of the PAZ family buses known to the entire population of the post-Soviet space was the PAZ-665 model, developed by the designers of the Pavlovsk Bus Plant back in 1966.
The history of the appearance of buses of the PAZ-3205 series
The bus was developed in two versions - a city bus with two double-folding doors, and a tourist version of the same car, which differed from the basic version by the presence of comfortable seats in the cabin and one manually opened door. The body design and layout of the prototype model vaguely resembled the PAZ-3205, the production of which was launched much later.
In 1967, the tourist version of the bus, which received the PAZ-665T index, was demonstrated in Paris, at the international motor show, where it was awarded the Great Silver Medal of the French High Commissioner for Tourism and the medal of the motor show.
At the same time, the plant was preparing for the production of another bus model - PAZ-672, developed several years ago. The Ministry of the Automotive Industry of the USSR decided to manufacture this particular model, as a result of which the international prize-winner PAZ-665 did not go into the series, remaining an experimental model.
Later, the plant created several more experimental models with a layout identical to the PAZ-3205. So, in the 70s, several modifications were developed based on the PAZ-3202. Their launch into mass production was planned for 1979, but production problems that arose at ZiL, which is the main supplier of components for the Pavlovsk bus, prevented the existing plans from being implemented.

Experimental PAZ-3202. It was not released into the series.
To get out of this situation, it was decided to change the base supplier and switch to components and assemblies supplied by the Gorky Automobile Plant. As a result, a new model was developed, which received the PAZ-3205 index, the first prototypes of which appeared in 1981. Many flaws were found in the design of the new model, the elimination of which took several more years. Only in 1986 small-scale production of PAZ-3205 was launched, and finally, in 1989, the bus went into production, replacing the obsolete 672 model.

The new bus was significantly different from its predecessor. PAZ-3205 received a spacious, comfortable, bright interior with a large glazing area. Nevertheless, in terms of its technical characteristics, the model was somewhat inferior to the previously developed version 3203, since the parts and assemblies supplied by GAZ were inferior to the ZiL counterparts.
 The bus was equipped with a ZMZ-5112 engine with a capacity of 125 horsepower, and was not much different from the engine that was equipped with the 672nd model. The gearbox, braking system and axles were supplied from GAZ, the steering mechanism was produced at the Minsk Automobile Plant.
The bus was equipped with a ZMZ-5112 engine with a capacity of 125 horsepower, and was not much different from the engine that was equipped with the 672nd model. The gearbox, braking system and axles were supplied from GAZ, the steering mechanism was produced at the Minsk Automobile Plant.
From the beginning of serial production until 1991, the bus was supplied to all the republics of the USSR, the pace of production was constantly increasing. However, the collapse of the USSR and the subsequent long crisis that followed, led to a sharp decline in production at PAZ. Nevertheless, even in crisis conditions, the factory workers managed to put on the conveyor the urban modification PAZ-32051, and in 1995 the modernized PAZ-3205-07 with the diesel engine MMZ D 245.7 produced by Belarusian machine builders.

PAZ-3205 special order 10 pcs. for the 27th Congress of the CPSU Central Committee
By the second half of the 90s, production growth began again at the plant, which, paradoxically, was facilitated by the ongoing crisis in the country. The fact is that many automobile enterprises engaged in passenger transportation, due to the high cost, did not have the opportunity to purchase large, roomy buses, and replaced them with much more affordable PAZs. True, in the same period, cases of serious accidents with the participation of these buses became more frequent, which was associated with numerous violations of the operating rules and the low reliability of the hydraulic brake system.

PAZ 3205 1989, LUX grade
By the beginning of the 2000s, Pavlovsk Automobile Plant, basically, overcame all the difficulties of the transition period and began to produce better and more reliable modifications of buses. A single-door PAZ-32053 and a two-door PAZ-32054, equipped with axles produced by the Ryazan Automobile Unit Plant and new pneumatic brakes, appeared in the model range. By 2002, these models were refined and equipped with ABS anti-lock brakes. Gradually, the new Pavlovsk buses replaced the outdated PAZ-3205 and PAZ-32051 models.

PAZ-32051 bus
In the same 2002, some changes appeared in the appearance of buses. So, the rear emergency door, previously located at floor level, was brought to the level of ground clearance, and the area of the emergency door glazing was slightly reduced. Also in the passenger compartment there are handrails covered with a polyurethane coating.
A few years later, in 2007, Pavlovsk buses underwent a very serious modernization. The most problematic units, which caused complaints from operators, were replaced with imported counterparts. Thus, a Ukrainian-made compressor was replaced by a similar unit manufactured by a German company. The same fate was awarded to the ABS "Ekran" system of Belarusian production.
In addition to replacing the units, work was done to improve the quality of the assembly. So, the joints of the body elements began to be glued with tape that protects the metal from corrosion, the front of the buses received a new plastic lining.
 Not without changes in the interior of the bus. The floor was covered with plywood impregnated with a special compound, the chipboard sheathing was replaced with plastic, the doors were made of galvanized steel.
Not without changes in the interior of the bus. The floor was covered with plywood impregnated with a special compound, the chipboard sheathing was replaced with plastic, the doors were made of galvanized steel.
The driver's workplace was now separated from the passenger compartment by an incomplete partition, the headlight switch from the floor was moved to the steering column, and electrically heated mirrors appeared. Customers were able to order various color options for the interior and exterior of cars in accordance with different finishing schemes.
Nevertheless, despite the regular improvements and modernizations, it should be admitted that the PAZ-3205 bus has long been hopelessly outdated. The ancient gearbox from the GAZ-53, the power units ZMZ and MMZ that do not meet modern environmental requirements, the outdated design - all this persistently and urgently required replacement.
Test drive PAZ-3205
Several years ago we were “lucky” to get to know closely two PAZs - gasoline and diesel. Both cars recently rolled off the assembly line, and their mileage was almost zero. But they brought us so many problems that our head was spinning.
What is it worth just tossing the side glass out of the window opening while performing maneuvers on the landfill? On the second bus, the gearbox was junk, we didn’t manage to switch one of the gears. Outside rearview mirrors were constantly falling off from vibration. In a word, then, six years ago, the "grooves" left a far from the best impression, and it would be interesting to see what has changed over the past years and whether the "people's" buses have become better?
 Three models were chosen for the test drive: PAZ-32053, equipped with a ZMZ-5234.10 gasoline power unit with a mileage of 27000 km; a diesel PAZ-32053-07 with an MMZ-245.7 engine with a mileage of 28000 km and a PAZ-4234 with an extended chassis base and an increased-capacity cabin equipped with a more powerful MMZ-245.9E2 diesel engine with a mileage of 15400 km.
Three models were chosen for the test drive: PAZ-32053, equipped with a ZMZ-5234.10 gasoline power unit with a mileage of 27000 km; a diesel PAZ-32053-07 with an MMZ-245.7 engine with a mileage of 28000 km and a PAZ-4234 with an extended chassis base and an increased-capacity cabin equipped with a more powerful MMZ-245.9E2 diesel engine with a mileage of 15400 km.
First of all, I was struck by the significantly higher quality of the bodies. On the buses we tested six years ago, rust on the rough, messy welds was visible even in the passenger compartment. Now everything has changed - the seams are carefully welded, covered with a layer of primer and paint.
In contrast to the previous ones, the rubber-sealed ventilation hatches on the bus roof are now tightly closed and do not allow moisture to pass through, even in heavy rain. Now, unlike in the past, the side windows do not fall out either. In general, after the first acquaintance, the impression was that the build quality, anti-corrosion treatment and body painting improved by several orders of magnitude.
Among other things, now in the assembly of buses, a new technology of anti-corrosion treatment is used, which includes filling the empty cavities, which are most susceptible to corrosion, with a special composition "Dinitrol", which is guaranteed to protect the treated surface for six years.
 Models 32053 and 32053-07 with gasoline and diesel engines are built on a standard chassis with a body, complete with a double-leaf door, pneumatically opened.
Models 32053 and 32053-07 with gasoline and diesel engines are built on a standard chassis with a body, complete with a double-leaf door, pneumatically opened.
An emergency exit door is installed in the rear of the passenger compartment.
In both models, the layout of the cabin is practically the same, although there are certain differences in the number of passenger seats and the total passenger capacity. In the PAZ-32053 cabin, 25 passenger seats are installed, and in the PAZ-32053-07 cabin there are 22 such seats.
The PAZ-32053 and 32053-07 models are small-class buses, while the PAZ-4234 is already a middle-class model equipped with two passenger doors. Of course, in the extended version of the bus, the configuration of the body and the layout of the cabin have changed, in which a second storage area has appeared. In the extended version, the passenger capacity of the bus has been increased to 50 people, 30 of whom can ride in a sitting position.

The bodies of all tested models are made in a wagon configuration, without a partition separating the driver's compartment. It is worth noting that not all drivers are happy with the absence of a partition, but it just so happened that the driver's workplace was never fenced in on the PAZs.
The driver's seats installed on buses are quite high quality. The presence of adjustments and suspension creates comfortable conditions for the driver when making long-distance flights. But the passenger seats cannot be called comfortable in any way, although they cannot be ranked as frankly bad either. But the spacing between the seats in the cabin is quite decent, the knees do not rest on the back of the front seat.
A few words about the ergonomics of the cab. PAZ is equipped with a steering wheel optimal in diameter and rim thickness. But the lack of steering column adjustment slightly reduces the level of driver comfort. Surprisingly, many car upgrades have not yet touched on the pedal set and the headlight footswitch. As with the first PAZ models, the switch is still located next to the pedals.
In subsequent modifications, it would be optimal to provide for the possibility of duplicating the headlight switch by installing it on the steering column, and, at the same time, retaining the foot button, which has become convenient and familiar for the drivers of the "people's" bus.
Most drivers and technicians like the inboard layout of the bus. It just so happened that domestic vehicles are not highly reliable, and malfunctions of various components and assemblies quite often find the driver on the road. So let's imagine that there was a similar breakdown, and there was snow, slush, frost outside the car. As a rule, in such a situation, the driver has to dress warmly, pull on gloves and fiddle in the cold, sometimes for a long time, with a faulty mechanism. But the drivers of PAZs are lucky - they do not need to leave the cozy, warm interior. It is enough to open the hood of the engine compartment, located right there, and calmly engage in repairs.
PAZ-32053 with a gasoline engine ZMZ-5234.10
We will not draw analogies between the power units of the tested sample and the car that gave us a lot of trouble six years ago. Then we were dealing with a non-rolled unit that had just rolled off the assembly line. Now we have come across a copy, "childhood diseases" of which have long been eliminated by drivers and technicians operating the car.
At idle, the engine noise is almost inaudible, but a characteristic sound similar to the screeching of a black grouse emanates from the pneumatic compressor. At high revs, the engine makes itself felt, drowning out the pneumatic compressor, recalling the good old GAZ-53 truck.
The engine power of 130 horses provides the bus with a rather high-spirited start. In the first four gears, the gearbox worked flawlessly, but when turning on the fifth and reverse, some difficulties arose. When the fifth gear was turned on, there was always a slight grinding noise, and the rear one was hard to engage due to the limited travel of the lever.
The PAZ also showed good dynamics on the road; the accelerator pedal operation pleased with its smoothness and responsiveness.
Until 2003, buses were equipped with a dual-circuit braking system with hydraulic and pneumatic brakes. After modernization, only pneumatic brakes were installed on PAZs, which made it possible to use the anti-lock braking system ABS manufactured by the German company Knorr-Bremse. But the brake pedal, as before, is located poorly, as it is at different levels with the accelerator pedal.
Not very convenient and too high position of the hydraulic clutch pedal. In city driving conditions, the driver is forced to constantly keep his foot on the clutch, which, with such a pedal position, creates a feeling of discomfort. Drivers working on suburban routes do not have such problems, because on a free road, you do not need to keep your foot on the grip all the time.
As for maneuverability, this characteristic was and is one of the main advantages of Pavlovsk buses. Suffice it to note that with a turning radius of 8.5 meters, the PAZ makes a U-turn in two steps on a road 6 meters wide. It should be noted also the impeccable operation of the power steering, which operates easily and silently.
During the test drive, the chassis did not cause any complaints either. The buses are equipped with bridges manufactured by the Ryazan and Kanash auto-aggregate plants. The test unit was equipped with a Ryazan bridge, and, possibly, therefore, did not emit the typical howling sound characteristic of GAZ trucks.
PAZ-32053-07 with Minsk diesel engine
All the advantages and disadvantages that we noted when talking about a car with a gasoline engine are also inherent in a bus with a diesel power unit.
Being next to a bus with a running engine, it is difficult not to pay attention to the characteristic noise of the Minsk diesel engine MMZ D-245.7. If you don't see that there is a bus nearby, you might think that a Belarus tractor is working nearby. The designers of the Pavlovsk Automobile Plant worked a lot to reduce the engine noise level, bringing it to the certification standards, but it was not possible to completely get rid of the "tractor motives".
In the cabin, the noise of the engine is not so noticeable, especially compared to a similar car six years ago, in which it was problematic to hear the interlocutor.
The dynamic characteristics of gasoline and diesel engines are almost identical, but in terms of fuel consumption, diesel is much more economical, which increases the profitability of its operation.
It should be noted that PAZ-32053-07 and PAZ-4234, corresponding to the middle class and equipped with a more powerful diesel unit, have almost similar fuel consumption indicators.

The extended version of the PAZ-4234 bus is equipped with a reinforced Ryazan-made bridge and a five-speed manual transmission, familiar to us from ZIL trucks.
The expected somewhat sluggish dynamics of the elongated PAZik is compensated by the larger capacity, the bus can carry up to 50 passengers, which is 10-12 more people than the small class brothers can take on board. The successful layout of the passenger compartment made it possible to organize two fairly spacious storage areas.
Naturally, on this model, it is impossible to make a U-turn in two steps on a 6-meter wide road due to its dimensions. With a length of 8.2 m and a turning radius of 8.7 m, you cannot maneuver in urban conditions, but for suburban and rural roads, the bus is ideal.
Concluding the test drive, we can summarize that Pavlovsk car manufacturers have managed to step far ahead in recent years.
New models of PAZ-4320 "Aurora" with a rear engine are already rolling off the assembly line of the plant, low-floor city buses PAZ-3327 can often be found on the streets of Moscow, new models of a small class with a front-mounted PAZ-3203 power unit are being tested and gradually go into production and PAZ-3204.

In short, the plant is trying to keep pace with the times, constantly improving the existing models and developing new ones that correspond to the trends of the modern bus market in the country.
With all this, it should be noted that old models are still in demand on the market. Long-familiar and well-proven machines attract many with their accessibility, ease of maintenance, and unpretentiousness. Perhaps foreigners who meet the "people's" bus on our roads may be confused by its outdated design, but it is produced not for Sweden and Germany, but for our people, and people like it.
What's the bottom line?
The streets of Moscow and other Russian megalopolises, crowded with car novelties from the world's leading manufacturers, have acquired the features of European cities in recent years. However, they are not a reflection of the situation on the roads of a huge country. And the situation is such that cars and buses, whose roots go back to the Soviet auto industry, will run on 1/6 of the land for a very long time.
In Soviet times, the lion's share of passenger traffic in rural areas and on short suburban routes was carried out using Pavlovsk and Kurgan buses. The agile, nimble PAZik has practically not changed in appearance since those times, but, at the same time, has not lost its relevance and popularity. It is noteworthy that the Pavlovsk Bus Plant was one of the few enterprises in the industry that managed not only to survive, but also to develop during the years of destructive restructuring, and in the dashing 90s, and in the stable zero.
It would not be an exaggeration to call PAZ buses one of the symbols of the country, which has rallied several generations of drivers and passengers around itself. If in other countries young people can see the buses that their fathers and grandfathers used only to the movies, our young people can not only see them on the streets, but also ride them.
However, the high demand for PAZs cannot be attributed only to the continuity of generations. The popularity of Pavlovsk buses is largely due to the effective marketing and technical policy pursued by the Russian Buses company, which, in addition to the Pavlovsk Automobile Plant, also includes the Likinsky, Kurgan and Golitsinsky Bus Plants.
To date, in addition to cars with traditional gasoline power units, PAZ has launched the production of buses equipped with various modifications of the MMZ-245 diesel engine. The installation of a diesel engine has significantly increased the profitability of the operation of the machines. Suffice it to say that the fuel consumption of diesel buses is on average 10 liters less than that of gasoline counterparts. In addition to reducing fuel consumption, the diesel unit also made it possible, to a certain extent, to solve the problem of the buses' compliance with modern environmental requirements.
The decision to enter serial production of the middle-class model PAZ-4234 with a passenger capacity increased to 50 people turned out to be no less successful.
Russian Buses is implementing a production modernization program aimed at increasing its efficiency and reducing costs. This approach was evidenced by the rejection of the technology of energy-intensive stamping production in favor of a tubular body frame with the use of polymer outer panels.
For the first time, the new technology was implemented in the serial production of the PAZ-4230 "Aurora" family of buses, which are already supplied to the market in sufficient quantities.
Of course, "Aurora" is a fairly comfortable, modern bus. But it should be noted that its cost is almost twice the price of the "people's" PAZ-3205, even in its most expensive diesel version. Thus, it can be argued that the bus, which "came from the people", still has a long working history.
Specifications PAZ-3205
| Bus model PAZ-32053-07 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Bus class | Small | |
| Appointment | Urban / Suburban | Basic parameters of modifications |
| Wheel formula | 4x2 | |
| Body type | Load bearing, wagon layout | |
| Overall dimensions, mm | Length | 7000 |
| Width | 2530 | |
| Height | 2880 | |
| Base, mm | 3600 | |
| Interior ceiling height, mm | 1965 | |
| Number / width of doors, mm | One door is pneumatic (726 mm), the other is an emergency exit | |
| Entry angle lane / exit angle rear hail. | 24 / 15 | |
| Min. turning radius, m | 7,6 | |
| Steering gear | MAZ-64229 with power steering | |
| Brake system | Working | pneumatic double-circuit with division into contours along the axes, brakes of all wheels - drum, ABS. |
| Spare | one of the circuits of the service brake system | |
| Parking | the drive from the spring brake accumulators to the rear wheel brakes. | |
| Ventilation | 3 sunroofs, vents on the side windows | |
| Fuel tank capacity, l | 105 | |
| Bridge | RZAA ZIL CJSC or KAAZ OJSC, rear driving axle, main gear - bevel, hypoid, gear ratio 5.86 / 5.29 | |
| Weight, kg | Curb | 5610 |
| Full | 8390 | |
| Number of places | General | 38 |
| Landing | 23 | |
| Clutch | Single disc, dry, with a torsional vibration damper and hydraulic drive. | Power unit (Diesel) |
| Engine (type) | MMZ 245.7 (Diesel) | |
| Location | Front, longitudinal | |
| Number and arrangement of cylinders | 4R | |
| Environmental safety standards | Euro-3 | |
| Engine displacement, l | 4,75 | |
| Engine power, kW (hp). | 86.2 (117) - 2400 min-1 | |
| Max torque, Nm | 413Nm at 1500min-1 | |
| Control fuel consumption at 60 km / h, l / 100 km | 16 | |
| Maximum speed, km / h | 85…96 | |
| Checkpoint | PAZ-3206-70 mechanical, synchronized, 5 st. | Other characteristics: |
| Body painting | The base color is white. On request when choosing from the color catalog. | |
| Doors |
One door is pneumatic, two-leaf, electrically controlled, equipped with an emergency button for the exit of passengers |
|
| Second door - emergency exit opens manually | ||
| Window | Single glasses, installed in rubber seals | |
| Seats for passengers | Double, soft, material - leatherette. | |
| Driver's seat | Sprung | |
| Seat belts | Installed in the driver's seat | |
| Heating system | Ventilation and heating systems. Autonomous heater "Webasto", liquid ovens in the cabin, individual heating of the driver | |
| Rear view mirrors | 3 pieces | |
| Lighting | Combined headlights, horizontal taillights, rear fog lamp. | |
| Interior | Partition with a handrail on the rear of the driver, a sun blind for the driver, hammers for emergency breaking of windows, emergency opening of the interior doors is possible | |
| Equipment | Jack, spare wheel, tool kit. | |
The buses of the Pavlovsk bus plant (currently PJSC Pavlovskiy bus) are long-livers of the domestic auto industry. The first PAZ-651 bus left the factory gates in 1952 and since then buses of this brand have been successfully operated in almost all regions of the country. They have been modernized several times and now on the roads of Russia and many CIS countries you can find more than 50 different modifications created on the basis of PAZ 3205 (1984), PAZ 3206 (1995) and PAZ 3204 (2007) buses. At different times, various motors of both domestic (ZMZ, YaMZ, MMZ) and foreign production (Cummins) were used as power units for these buses. At the same time, any PAZ engine with which the bus is aggregated is highly reliable and can operate when using low quality fuels and lubricants.
Specifications
For a long time, the ZMZ 5234 engine produced by the Zavolzhsky Motor Plant was considered the base engine of PAZ buses.
| OPTIONS | MEANING |
|---|---|
| Working volume of cylinders, l | 4.67 |
| Rated power (at a crankshaft rotation speed of 3200 ... 3400 rpm), hp with. | 130 |
| Maximum torque (at a crankshaft speed of 2000 ... 2500 rpm), Nm | 314 |
| Number of cylinders | 8 |
| Valves | 16 |
| Cylinder diameter, mm | 92 |
| Piston stroke, mm | 88 |
| Compression ratio | 6.5 |
| Gas distribution mechanism type | OHV |
| Cylinder sequence | 1-5-4-2-6-3-7-8 |
| Power system / carburetor type | Carburetor / K-135 |
| Valve mechanism | OHV |
| Fuel type / brand | gasoline / A-76 |
| Fuel consumption (mixed), l / 100 km | 32 |
| Lubrication system | Combined (under pressure + spraying) |
| Butter | Mineral: 10W-40, 15W-40, 20W-50 |
| Cooling system | Liquid, closed type, with forced ventilation |
| Weight, kg | 257 |
The engine was installed on buses of the PAZ-3204, PAZ-3205 and PAZ-3206 series.
Description
 The ZMZ 5234 engine is a 4-stroke 8-cylinder carburetor power unit with an overhead valve arrangement and is a further development of the well-known ZMZ 511 and ZMZ 513 engines. The camshaft is located at the bottom of the V-block with a 90-degree camber angle.
The ZMZ 5234 engine is a 4-stroke 8-cylinder carburetor power unit with an overhead valve arrangement and is a further development of the well-known ZMZ 511 and ZMZ 513 engines. The camshaft is located at the bottom of the V-block with a 90-degree camber angle.
The cylinder block is made of an aluminum alloy, in which the cylinder liners are installed. The latter are sealed from below with copper rings, and from above are pressed by the head. Additional rigidity of the block is provided by the fact that its lower part is located 75 mm below the crankshaft axis. The cylinder heads have highly turbulent combustion chambers and screw-type intake ports.
The crankshaft is cast from ductile iron and the use of forged connecting rods helps reduce engine weight. Due to the piston stroke increased by 8 mm, the designers managed to increase the volume of the engine cylinders.
The compression ratio is compensated by special grooves in the piston crowns.
The engine is equipped with an exhaust gas recirculation system, which reduces the toxicity of the exhaust.
Maintenance
The ZMZ 5234 engine is distinguished by its unpretentiousness to the quality of consumables, which is essential when operating in rural areas. In addition, it is easy to maintain and does not require professional training of the operating personnel.
In order to ensure trouble-free operation of the engine, it is necessary to regularly carry out regulated maintenance (MOT), which includes:
- Daily maintenance;
- THEN when running in the motor
- Periodic maintenance every 10 (TO-1) and 20 (TO-2) thousand kilometers traveled by the car.
- Seasonal maintenance carried out twice a year.
The frequency of maintenance is set depending on the operating conditions. In this case, the deviation from the mileage is allowed within 500 km.
Daily maintenance is carried out before each start of the power unit and includes checking:
- engine oil level in the crankcase;
- the presence of coolant in the expansion tank;
- tightness of lubrication, power supply, cooling and ventilation systems of the power unit.
All other types of maintenance must be carried out in accordance with the list of works given in the accompanying documentation of the power unit.
Malfunctions
ZMZ 5234 is quite simple to repair, but it is characterized by a number of typical malfunctions:
| FAILURE | CAUSE |
|---|---|
| The motor does not start. | The installation of the valve timing is violated; malfunction of the drive of the gas distribution mechanism; malfunction of the power supply system. |
| Unstable motor operation. | The presence of water in the fuel tank; failure of one of the cylinders. |
| The power unit does not develop the declared power. | Carbon deposits on the intake valves; the phase adjustment in the gas distribution mechanism is broken; wear of the camshaft cams; excessive carbon deposits in the combustion chambers; malfunction of one or more spark plugs; insufficient compression. |
| Overheating of the power unit. | Lack of coolant; the thermostat is out of order; the cylinder head gasket is burnt out; faulty water pump (pump); malfunction of the fan or its power supply circuit. |
| Increased consumption of engine oil. | Leakage of engine oil through stuffing box seals and gaskets; the oil separator caps are out of order; worn out pistons, cylinders, valve guides, etc.; the integrity of the cylinder head gasket is broken. |
| Extraneous knocks in the engine. | Wear of the crankshaft liners; wear of parts of the connecting rod and piston group; wear of cylinders; the pump bearing (water pump) is out of order; the generator bearing is faulty. |
Tuning
Carburetor engines of commercial vehicles of the past years of production are rarely subjected to tuning associated with an increase in power. It is easier and cheaper to replace such a motor with a more modern one. However, there are several simple ways to slightly increase the power of such a motor without significant financial investments:
- Thermal insulation of the exhaust system
It is known that the higher the temperature of the exhaust gases, the higher the speed of their movement through the exhaust system. An increase in the speed of their movement contributes to a more complete release of combustion chambers from combustion products and the more new air-fuel mixture enters the cylinders. Having well insulated the exhaust manifold, it is possible to achieve an increase in power by 1 ... 3%.
- Increasing the compression ratio
It is possible to increase the compression ratio of the air-fuel mixture in the engine cylinders by installing a thinner cylinder head gasket; by sawing down the lower part of the cylinder head; having bored the cylinders under the piston of a larger diameter.
By increasing the compression ratio of the combustible mixture to 9: 1, a power increase of about 2% can be obtained.
IMPORTANT! Mechanical modification of engine parts leads to a change in the kinematics of the engine and requires careful tuning and adjustment of a number of interdependent parts and assemblies. Therefore, it is better to entrust such work to highly qualified specialists who have experience in carrying out such work.
Introduction
1.General characteristics
1.1 Engine
1.2 Transmission
1.3 Wheels and tires
1.4 Suspension
1.5 Brakes
1.6 Steering
1.7 Electrical equipment
1.8 Weight of units
1.9 Other
2. Transmission
2.1 Clutch
2.2 Gearbox
2.3 Cardan drive
2.4 Main gear
2.4.1 Single hypoid final drive
2.5 Differential
2.5.1 Gear symmetrical differential
2.6 Half shafts
Conclusion
Bibliography
INTRODUCTION
History of the Pavlovsk Bus Plant
The history of PAZ began to be laid back at the beginning of the 20th century. The construction of the Pavlovsk Bus Plant began in early August 1930. At that time, it was known as the Automotive Tool Factory. But by the beginning of 1932 the construction was completed and on December 5, 1932 the plant was declared operational. This kind of instrument was the main production focus of the Pavlovsk Bus Plant until 1952, with a break for 1941-1945. (during the war years, the enterprise was directed to the production of ammunition).
Establishment of the PAZ automobile plant
By a decree of the Government of the USSR in 1952, the Automotive Tool Plant became the Pavlovsk Bus Plant due to the lack of public transport (negative consequences of the war). A plan for the reconstruction of the plant and a program for the production of 10,000 buses were also approved. The first batch, which consists of five PAZ-651 model bonnet buses, begins to be produced.
In 1989, the PAZ-672 model was released from the factory for the last time. At the end of the same year, without stopping the production process, the serial production of the current basic model of the PAZ-3205 bus was started. This bus model has become the face of the PAZ automobile plant. Also, about thirty modifications of this bus were developed by the engineers of the plant, which were intended for operation in various climatic conditions. Serially, only about 10 modifications were produced. This model of the PAZ bus has perfectly proven itself on the roads of our country, which was noted directly by the passengers.
In 2000, the production was directed to the manufacture of buses of large (PAZ-5272) and middle class (PAZ-4230 "Aurora"). In the same year, the PAZ car plant was merged with the management company RusPromAvto. Pavlovsk Bus Plant has repeatedly confirmed its reputation as the largest and leading Russian bus manufacturer.
In 2000, the restructuring and optimization of production processes was also started, and already in 2003 it covered all divisions of the Pavlovsk Bus Plant, which led to excellent results. This can be seen in the combination of workshops into one building:
Welding and painting;
Press;
Metal procurement.
Close attention was paid to optimizing the production of the PAZ plant, and therefore work was started in the assembly shop according to the methods of the Toyota company. The result was obvious.
1.GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
Small class bus for rural communication PAZ-3205.
Body - wagon type, supporting structure, 3-door (one door for the driver, one for passengers and one emergency). The seating arrangement is 4 rows. Units - respectively, GAZ-3307 and GAZ-66-11 vehicles. The location of the engine is forward. The driver's seat is adjustable for length, cushion tilt and weight. Heating system - air, using heat from the engine cooling system.
1.1 Engine
Maud. ZMZ-672-11, gasoline, V-mod. (900), 8 cyl., 92.х80 mm, 4.25 liters, compression ratio 7.6, operating procedure 1-5-4-2-6-3-7-8; power 88.3 kW (120 hp) at 3200-3400 rpm; torque 284.5 Nm (29 kgf-m) at 2000-2500 rpm; carburetor K-135; oil inertial air filter.
1.2 Transmission
The clutch is single-disc, the shutdown drive is hydraulic. Gearbox 4-speed, gear numbers: I-6.65; II 3.09; III 1.71; IV-1.00; ZX-7.77; synchronizers - in III and IV gears. Transfer case (for PAZ-3206) 2-speed will transmit. numbers: 1-1.963; 11-1.00. Cardan drive: for PAZ-3205 it consists of two shafts with an intermediate support; PAZ-3206 has three cardan drives: from the engine to the transfer case and from the transfer case to the axles. The main gear is single, hypoid, gear. number 6.83.
1.3 Wheels and tires
Wheels - disc wheels, rims 6.0B-20 with side rings, fastening on 6 studs. Tires 8.25R20 (240R508), on PAZ-3205 - models K-84 or KI-63, NS - 10, tread pattern - universal, pressure, kgf / cm. sq. : mod. K-84 - front 6.0, rear 5.0; Maud. KI-63 - front 6.1, rear 5.0. On PAZ-3206 - tires mod. K-55A; НС - 10, tread pattern - universal, pressure, kgf / cm. sq .: front 6.0, rear 4.3. The number of wheels is 6 + 1.
1.4 Suspension
Dependent, front - on semi-elliptical springs, two shock absorbers. Rear - the same, with adjusting springs, the bottom of the shock absorber. On PAZ-3206, the front and rear suspensions are equipped with an anti-roll bar.
1.5 Brakes
The working brake system is double-circuit, with a pneumohydraulic drive, drum mechanisms (diameter 380 mm, lining width 100 mm), cam release. Parking brake - transmission - drum, drive - mechanical. The spare brake is one of the circuits of the service brake system. The pressure in the pneumatic drive of the brakes is 5.2-5.5 kgf / cm. There is a fuse against condensation freezing.
1.6 Steering
Maud. MAZ-5336-34000 10-60, steering gear - screw with ball nut and sector, hydraulic booster. will transmit. number 23.55, nom, pressure in the amplifier 65-70 kg / cm. sq. Steering wheel play when the amplifier is working up to 150.
1.7 Electrical equipment
Voltage 12 V, storage battery 6ST-105EMS, generator G287 with built-in rectifier and voltage regulator PP132, starter ST230-A, distributor R133-B, transistor switch TK1 02, ignition coil B116, candles A11-3.
1.8 Weight of units
Engine with equipment and clutch - 304 kg
Cardan shaft - 27 kg
· Transmission - 56 kg
Transfer case - 48.5 kg
Front axle - 195 kg
Rear axle - 270 kg
Body - 2100 kg
Complete wheel with tire - 80 kg
Radiator - 18.5 kg
1.9 Other
Fuel tank - 105 liters
· Cooling system - 25l, water or antifreeze A-40;
· Engine lubrication system - 10 l, all-season M-8B, or M6 / 10V, in winter ASZp-6;
· Steering gear housing 1.5 l, TAP-15V;
· Power steering system - 3.2 l, all-weather grade P oil, substitutes: turbine grade T in summer, spindle AU in winter;
· Transmission - Zl, TAP-15V or TSp-15K;
· Transfer case - 1.5 l, TAP-15V or TSp-15K;
· Rear axle housing - 8.2 l, TSp-14gip;
· Front axle housing - 7.7 l, TSp-14GIP;
· Hydraulic system of drive of brakes and clutch - 1.47 l, brake fluid "Tom";
Shock absorbers - 4x0.475 l, АЖ-12Т;
· Windshield washer reservoir - 2 l, NIISS-4 fluid mixed with water;
· Safety lock for brake system - 0.2 l, industrial alcohol.
2.TRANSMISSION
The torque created on the crankshaft of the engine is transmitted to the driving wheels of the car through the units and transmission mechanisms.
In PAZ-3205, the drive wheels are rear and the power train consists of a clutch, gearbox, cardan gear, main gear, differential and semi-axles.
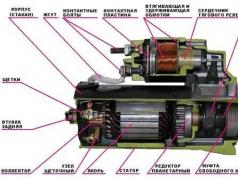
2.1 Clutch
The clutch is used for short-term separation of the engine from the transmission (when shifting gears in the gearbox) and smooth connection of the engine and transmission (when starting off).
The principle of the clutch is that torque is transmitted due to the friction that occurs between the drive and driven discs, pressed against each other by springs.
The clutch is mounted on the flywheel, which is one of its drive discs.
The PAZ - 3205 clutch is designed and operates as follows (see Fig. 1). Twelve springs (12) press the driven disc (3) through the pressure plate (4) to the ground surface of the flywheel. The driven disc is mounted by the hub on the splines of the drive shaft (9) of the gearbox. Thus, when the clutch is engaged, the torque from the flywheel is transmitted by friction to the driven disk and then through the drive shaft of the gearbox to subsequent transmission mechanisms.
The clutch drive is mechanical. To disengage the clutch, it is necessary to press the pedal (16) so that the rod (14) with the adjusting nut (13) turns the lever (18) of the fork, which will move the coupling (8) with the bearing (20) along the bushing. The clutch will rotate the inner ends of the levers (5) around its axes, and their outer ends will retrace the pressure plate, compressing the springs located between the stamped steel clutch cover (11) and the disc (4). The driven disc is released, and torque will not be transmitted to subsequent mechanisms. If you release the pedal, it will move by the springs (15 and 19) and the clutch will re-engage.
A thrust ball bearing installed in the clutch reduces friction between it and the ends of the levers when the clutch is disengaged. The fork (18) is attached to the clutch housing (2) with a ball joint.
When the clutch is engaged, its parts heat up due to friction between the drive and driven discs. Heat insulating washers located between the pressure plate and the springs reduce the transfer of heat to the springs, which lose their elastic properties when heated.
Clutch disc. Six spring wavy plates and two friction linings are riveted to the steel driven disc. The pads are made of pressed asbestos fiber impregnated with bakelite or synthetic resins and have an increased coefficient of friction.
The PAZ-3205 bus is a basic model of a small class, produced at the Pavlovsk bus plant. With its compact dimensions, this high-floor vehicle is ideal for transporting small groups of passengers over short distances. The bus, like most domestic models, does not have much comfort, but it is perfectly adapted to Russian roads and fuel, has good cross-country ability, and is simple in design. High ground clearance allows the use of equipment in off-road conditions.
History of creation
The prototype of the PAZ-3205 was the PAZ-665, created in 1966. Initially, 2 versions were developed - for urban and tourist transportation. Tourist buses were distinguished by more comfortable interior equipment. However, the initial tourist modification of the PAZ was not mass-produced. The improvement of the device of the model lasted almost 15 years, during which time 10 different versions were created.
The PAZ-3205 model in the form that we know now appeared after the choice of the Gorky Automobile Plant as the main supplier of units and assemblies. The first buses of this modification were produced in 1981. After measures to improve the design in 1986, the production of small volumes of the PAZ-3205 model began. Serial production of equipment began in 1989. In its configuration, two types of engines were used - gasoline and diesel. Doors - front automatic, rear - emergency, axle - from a GAZ car, brakes - hydropneumatic.
Modifications PAZ-3205
In 2009, after the withdrawal of the original model from production, the development of its improved modifications continued. The comprehensive modernization of PAZ-3205 consisted in replacing Ukrainian and Belarusian products with German components and assemblies, in the appearance of gray plastic trim and anti-corrosion tape at the body joints, in the development of new layouts of passenger seats and cargo compartment. The new complete set of the heating system made it possible to use cars even in severe frosts. Since 2002, all equipment has been equipped with an ABS system.
PAZ-320570-04. Equipment certified for the transport of children. Seats - separate, soft, located on the podium. There are additional handrails at the entrance and in the salon. Additional heating devices are provided.
Specifications PAZ-3205
The length of the bus is 7 m, width - 2.5 m, height - 2.9 m, weight - 4.83 tons. Other technical parameters:
- the highest speed in a lightly loaded state - 90 km / h, in a fully loaded state - 60 km / h;
- fuel consumption per 100 km - 32 liters;
- cabin capacity - 41-42 people;
- number of seats - 23-25;
- service place - 1;
- brake system - double-circuit pneumatic;
- Gearbox - 4- or 5-speed.
Advantages of PAZ-3205 and its modifications
The lack of comfort of these buses is compensated by a number of advantages, thanks to which the brainchild of the Pavlovsk Bus Plant has been widely used on the roads of Russia for several decades:
- A wide range of models allows you to choose the modification that best suits the planned purpose, load, routes, climate characteristics.
- Possibility to order an individual complete set of a car designed for emergency assistance, laboratory services, and servicing various groups of the population.
- Simplicity and ease of construction, the ability to use in difficult road conditions.
- The ability to carry out repairs by the driver. While modern imported buses, equipped with electronic components and other technically advanced devices, can be repaired only under the conditions of specialized services.
- High reliability thanks to which this machine is effectively operated on city, settlement, rural roads, for servicing industrial and agricultural enterprises.
 |
 |
 |