Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Posted on http://www.allbest.ru/
Machines and mechanisms used in landscape construction
Grabenko Evgeny Aleksandrovich
Lecture number 1. Energy
Engine - Mechanism transforming energy into mechanical work. The electric motor converts electricity into mechanical work. The internal combustion engine converts thermal energy into mechanical work.
Engines are on gasoline and diesel. The engine on gasoline is called a carburetor. Carburetors are two-stroke and four-stroke. In the diesel engine there is no ignition system, as under pressure, diesel fuel is self-proposal. In the diesel engine there is a high pressure pump (up to 80 atmospheres). Most forestry mechanisms operate on an internal combustion engine.
Machines and mechanisms are two species: with active working bodies (bush scissors, milling machines, wooded machines, combines, etc.) or with passive working bodies.
plow landscape construction screw
Lecture number 2. Tractor
Tractor classification:
1. By engine type: gasoline and diesel;
2. By type of chassis: Wheel and tracked;
3. According to the presence of a frame: frame, semi-text and frameless;
4. For its intended purpose: Special (grape reservoirs, forestry, cotton harvesting, rigs), general purpose (meet the various fields of national economy) and industrial (high-power tractors, which are used on careers, road construction, etc.);
5. In the class of thrust (traction force - the ability of the tractor to move the maximum load on the first reduced transmission along the horizontal plane):
1) 0.6 (6 kN - traction): T25, T30. Used for gardening and park economy;
2) 1.4 (14 kN): T50, MTZ80, MTZ82;
3) 3 (30 kN): DT75, TDT75, LCT75, T150K;
4) 4 (40 kN): LCT100, TT4, T150);
5) 10 (100 kN): T100, T130, T170. Used to move the soil, etc.
All tracked tractors - frame; All wheeled - semi-grades; Motor blocks (minitractor) - frameless.
Lecture number 3. Machines and mechanisms for applying fertilizers
Fertilizers - Chemicals intended for making in the soil and improving its soil-plant properties.
Fertilizers are mineral and organic.
Mineralfertilizers - Product that is obtained on specialized chemical plants. Mainly mineral fertilizers contain the main set of substances (AFC): nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium.
Organicfertilizers - Product of overloading organic matter of natural origin.
There are 3 ways to make fertilizers:
1. Presense. Fertilizers are made before sowing;
2. Sy Supid. Fertilizers are entered during sowing;
3. feeding. When there are already shoots or plants themselves.
All types of introduction require various machines.
Agrotechnical requirements for machines:
they should equally well must soze mineral fertilizers as in the form of granules and powder;
should close fertilizers for a certain depth.
It is necessary to take into account the physico-mechanical properties of soils:
hygroscopicity - the ability of the substance to choose moisture from the ambient air;
the angle of natural slope is an angle formed by a loose substance, ate of it pour on a flat surface;
the friction coefficient - reduces or increase efforts when delivering fertilizers;
the density on which the bulk mass depends.
Classification of machines for making fertilizers:
1. By way of making. Pre-sowing, soldered, subcortical;
2. In terms of fertilizers. For bulk (mineral), liquid (organic), bound organic fertilizers (peat, manure, compost);
3. According to the type of energy tool. Tractor, car, aviation;
4. According to the method of connecting the machine with an energy facility. Trailed (weight on their chassis), mounted (all weight on the power chassis), mounted, self-propelled.
Circuit diagram for applying fertilizers:
The machine for making fertilizers consists of:
1. The bunker (inside there are violations (agile) - do not allow fertilizers);
2. The feeder (delivers fertilizer from the bunker to the next device). The feeding device can be in the form of chain-plate, tape and screw conveyors. There is also a vibratory nutrient device;
3. Scattering device - delivers fertilizer to the place of its introduction. There are three types: disk) horizontal - for pre-sowing application), barbed (located vertically and partially inside the hopper - for pre-sowing and can be used for feeding), drum (horizontally located - for related organic fertilizers).
For liquid fertilizers - the dung fluid (humic acid) uses special mechanisms.
Lecture number 4. Machines and tools for soil treatment
Soil processing is two types: the main and additional. Plows are used for the main. For additional harrows, cultivators, etc. Cutters are used both for the main and for additional processing.
In garden and park landscapes, soil damage is less than in forestry. Machines for gardening and park economy must be more maneuverable, less dimensional, aggregated on energy facilities with a wheelchair.
Additional processing is made after the main one. Task: improve soil-plant properties and reduce further cultivation costs. It includes: breakdown stakes after the main, rolling, groing formation, cultivation, harrowing.
Plows are classified by:
1. Appointment. There are general purposes (in all kinds of farms), special plows (specialized in certain areas (forest, plantal, dull);
2. By type of working bodies. Lineshny, disk, auger;
3. By type of thrust. Equestrian, tractor;
4. According to the method of compounding with the tractor. Trailed, hinged, semi-mounted;
5. In terms of the number of cases (concerns lameshine plows). Single-circuit and multi-circuit;
6. By the speed of soil processing. Conventional (1.4 m / s) and high-speed (above 2.2 m / s).
Plows for garden and park economy must be a bitten, compact, maneuverable, process the soil to a given depth, etc.
Technological properties of soils are those properties that envy its workability.
Soils with large particles - sandy (lungs) - do not act on the mechanisms, gradually becoming accommodating them (the constant replacement of the main working bodies) is necessary.
Soils with small particles - clay (heavy) - well absorb moisture, which is why there is a sticking on the main working bodies, when dried, crack and harden. Well processed with normal moisture condition.
Types of main processing of soils:
1. Cultural. It is carried out with a lameshine plow with a prejudient in the fall.
2. Walk. It is carried out with a lameshine plow without a prepayment in the fall.
3. Brushing. It is carried out on a small depth (10-12 cm) in summer or autumn.
4. Plowing with soil hug. It is carried out with a lameshine plow with an additional loose paw behind the main plow housing (below 15-20 cm).
5. Unanswed. It is carried out on soils subject to erosion processes without turning the reservoir.
6. Lial. Moves layers by changing them in places.
7. Plantable. Plowing for greater depth (up to 1m). In the garden and park economy, when the soil is heavy and need to improve aeration and plant durable cultures.
8. Plowing with a turnover of the formation. It is carried out on well-drained soils.
Lecture number 5. Plugs
Plows are laminated, disc and screw.
Lineish plows.
They have the opportunity to plow for a certain depth due to its specific design features.
Mixed plows consist of: frame, energy remedy (combined with a frame by means of a universal suspension), a disk or cutlery knife, a preylder, the main body of the plow, the soil hydrogen paw, the field wheel with a screw mechanism. Plow clutch system with an energy facility and field wheel - additional organs of a limestal plow.
Disk or pork knife. Task - smoothly cut off the soil reservoir (on the hidden soils). The pile knife - can be installed at a different angle of entry into the soil (stupid or sharp). Acute is used on pure soils. Stupid swallows the soil. The disk knife rotates. Not terrible obstacles. Located on the shaft on which the bearing is fixed. Due to the complex design, the cost of the plow itself increases.
The Certifier is a reduced copy of the plow. Used in cultural plowing.
The main body is fried the arable layer of the soil. Connects with a frame by rack. It consists of a lemhery (the knife is the main working part of the main plow housing). The lemohs are of different shapes: bit-shaped (used on pure soils), trapezoidal (used on stony soils) and swears (plow with two dumps).
A soil degenerate paw is installed on the main body of the plow and produces plowing with soil hydration. Looks like a unrestituted plow.
Wheel wheel with a screw mechanism - allows you to create the necessary plowing depth. The wheel, rolling on the surface of the soil, does not give a plow. Screw mechanism allows you to vary or lower the field wheel. If the field wheel is lowered, the depth of the plowing decreases, and if rises, the depth of plowing increases.
The design of lameshine plows is universal and special.
Garden plows allow you to shift the plow axis relative to the axis of the tractor movement.
Disk plows.
Consists of: Knife, Assault (common with a mesh plow), frame, working body - disk (spherical - in this account increases the area of \u200b\u200bcontact). It is installed at an angle to the surface and at the angle of attack (stupid (sprayed) or acute (raised)).
It is intended for work on clogged soils. Each disk is fixed on an independent suspension with a spring.
Circular or dull machines (belong to laminated plows). Produce trim roots or sample of material. They have a horizontal lemeh. It produces a field wheel the desired desired root part of the plant.
Soil cutters.
Classified by:
1. Appointment. Garden, forest (in clogged territories), swamp (to work on peatlands), wet (on C / x land);
2. The principle of action. Longitudinal milling (swamp), transverse action (forest and disappearing), vertical milling (slicing of landing holes);
3. Type of working bodies. Knife (simple (used for hidden soils on forest mills), spiral and hooks (used on pure soils on the wet cutters)) and auger;
4. According to the method of compounding with a traction. Hinged, semi-mounted, trailed.
Principle of operation: These are tools with active working bodies. The cutter is connected to the energy agent due to the cardan shaft, which is attached to the power selection shaft. Reducer - a set of gears, each of which increases torque. Change the plane of the rotation of the shafts and the difference in the speed of rotation.
Installations for chemical protection of plants
The chemical method is to destroy pests using chemicals. This method is used very widely and is considered the most efficient. The chemical method in the complex with a system of agrotechnical and organizational and economic events allows to significantly protect forest plantings from pests and diseases. Pesticides for the chemical method of struggle are used as follows:
spraying fluids - solutions, suspensions, emulsions, extracts;
powders for pollination;
gases for fumigation.
The solution is a liquid in which the solid is completely dissolved, for example, an aqueous solution of copper sulfate, salts, and the like.
Suspension is a mechanical mixture of dry powder and a liquid substance in which the powder does not dissolve, but is in suspended state, for example, a mixture of chalk powder or lime in water.
Emulsion is a mechanical mixture of liquids of various density (specific gravity) and viscosity, for example, a mixture of oil and water, kerosene and water, soap and water, etc.
The extract is a hood from poisonous plants and animal organisms. Anabazine and Nicotine are extracts of poisonous plants (chamomile, tobacco).
The working fluid is a mixture of pesticides with water at a certain concentration. When spraying a pesticide on infected objects are applied in the form of a working fluid, and during pollinating pesticides, the structural plants are applied as a dry powder.
When the soil fumigation is introduced into it easily evapoable pesticide, which evaporating, saturates pairs the top horizon of the soil or enters the root system of plants and destroys the pests in them.
Classification of machines and devices. Machines and apparatuses to combat pests of plantations are classified into the following types and methods of their aggregation: sprayers - are used to combat pests and diseases with the help of a poisonous liquid. They are a rapid capacity of up to 20 liters; Tractor (trailed and mounted) and aviation. Trailed sprayers work in connection with tractors, mounted can be hung on a tractor attachment or mounted on it.
Sprayers installed on an airplane or helicopter are called aero-plants;
fanghers are used to combat pests and diseases with a dry poisonous powder or dust. They are knitted, tractor (trailed attached) and aviation;
aerosol generators are used to combat pests and diseases with the help of a poison fog generated by thermomechanical or mechanical methods.
They are rite, automotive and aviation;
combined - can be used both as sprayers, and as freings.
They are tractor (mounted, trailed);
fumigators are used to supply a poisonous easily evaporated liquid into the soil.
They are hand and mechanical (tractor). Mechanical fumigators are usually installed on the working bodies of tillage machines (plows, cultivators);
Posted on Allbest.ru.
...Similar documents
Machines used for main soil processing, meadows and pastures. Tillage-sowing units, seeders. Machines for making mineral and organic fertilizers, chemical protection of plants. Shooting, adjustment and rolling in the cultivator.
thesis, added 24.02.2015
Tasks and types of additional soil processing. Classification of machines and guns. Teeth and disk harrows. Sealing the top layer of soil rollers. Inter-row processing of soil in sowing for the purposes of soil looser, making fertilizers, the destruction of weeds.
presentation, added 08/22/2013
Classification of tractors and cars. Main mechanisms and engine systems, basic and accessories. Agricultural and tillage machines, their classification and marking. Plows, harrows, leuffers, rollers, cultivators.
cheat Sheet, added 07.06.2011
The overall characteristics of floral design in landscape design, its main elements. Classifications, distinctive features and a flower bed device. The history and typology of flower plants, the specifics of their selection conditions. Features of carbons care.
course work, added 11/14/2010
Assessment of fertilizer values \u200b\u200bin the development of thrust agricultural land. Determination of agrotechnical requirements for mineral and organic fertilizers and machines for their introduction into the soil. Technical parameters of cultivators and fertilizer spreaders.
presentation, added 08/22/2013
Technological processes in landscape construction. List of basic operations for creating wood plantings in the suburban forest park. Compilation of machineryractor aggregates and a selection of motorized equipment. Traction calculation of tractors.
coursework, added 12/12/2015
Methods for making fertilizers, agrotechnical requirements. AIR-20 Aggregate: device features, work process and adjustment. The principle of operation of the RT-4,2A seeder. The device of the mounted spreader of NRU-0,5, the uniaxial spreader of 1-RMG-4A and body row-6.
abstract, added 02.02.2011
The chemical method of protection of plants, its assessment as a means of regulating the number of harmful organisms holding their number on an excessive level. Brief characteristic of pesticides, loss analysis. Classification of spraying methods.
abstract, added 06/29/2015
Device and technological adjustment of the disk radical, seeders, sprayer. Machines for the preparation of lands for development and cultural work. Improving productivity and quality of the forage harvester. Plant protection machines.
examination, added 04.12.2013
Chemical protection of plants from pests: Nematocides, Mollocides, Rativeycides. Stability of harmful organisms to peatecids. Methods and means of chemical protection of plants from diseases. Fungicides for processing recreation material and putting into the soil.
The successful development of green construction is possible only on the basis of broad implementation in the production of mechanization.
The maximum use of mechanization when landscaping, in particular when booking new plantations, repair and operation, they significantly reduce the cost of work and allows the use of the most advanced techniques of agrotechnics.
Mechanization of labor-intensive processes reduces labor costs and facilitates it, which is also important in green construction, the operation of green plantings and the cultivation of planting material.
Most of the machines used in the green construction of machines and tools manufactured by the industry for agriculture and forestry does not require special major devices, and some of them can be used by adding minor devices. For the mechanization of labor-intensive work, it is necessary to select machines and tools, taking into account soil-ground conditions, high-quality performance of machines and guns, and the economic feasibility of using them (performance, etc.). The choice of cars and guns depends on the scope of work and the conditions of the economy.
In green building, the correct use of machines is of great importance. It is important that the machines work well-trained people who know their device and adjustment.
All machines and tools daily to work must be carefully checked, whether the mechanisms are working and the fasteners are reliable. It is necessary to check whether the car is refilled with combustible, and in trailed and mounted guns whether the working bodies are installed. After that, you should check the unit in action.
During the work, it is necessary to strictly comply with the rules for technical care for machines - to carry out lubricant timely, check the fastening of parts, the deposit of the working bodies, etc. It is especially important to comply with the safety rules during the operation of the aggregates, as well as during the winter of their maintenance and storage. If machines and guns are fixed behind the brigade, then the technician or brigadier (forehead) must be responsible for their storage.
When landscaping and care for plantings in some cases, it is necessary to use manual labor. Therefore, farms should be provided with the relevant inventory that meets one or another work technology.
In the farm, first of all, it is necessary to have garden shovels. Different types. Universal garden shovels SELL with a small oval rounding of the cutting part are designed to resist soils and squeezing landing holes. The spacing shovels of the WL with a flat cutting part are less damaged roots of planting material and in works on planting plants provide greater productivity than other shovels.
Moth and looseners are needed to work, which are different in form and appointment. Thus, grained moths of a lightweight type are used for loosening of medium-heavy soils to a depth of 3-5 cm. Universal heavy and middle hoes are designed to work on heavy soils and provide loosening to a depth of 5-7 cm. For loosening of highly compacted soils to a depth to 10 cm, use Moth kirk. On loose soils for the destruction of peeling, special 3-5-toothed rippers are used.
The choice of machines, guns and inventory in each particular case is solved on the basis of the alleged volume and work conditions.
In order to intensify works on the creation and content of garden-parking facilities in the gardening and park economy, a number of machines and mechanisms are used that significantly increasing productivity and reduce labor-intensiveness of production processes. To date, the park of machines and mechanisms is constantly increasing and improved in the direction of the specialization of garden and park economy. In the garden and park economy, small-sized equipment, along with machines used in road construction and agriculture, are becoming more and more applied. Machines are widely applicable for the preparation of territories for landscaping and maintenance of objects. Earthworks use bulldozers, automotive drivers, excavators. In the production of work, large trees transplanting machines are introduced, aggregates for sowing the lawn seeds, fertilizer making, irrigation of plantations.
Means of mechanization are applicable to fulfill labor-intensive main works. The final "finish" and the design of garden-park objects is conducted by the hands of qualified workers using manual mechanisms.
- Tractors and energy products
Tractors are the main basic machines used in the creation of garden-park objects. The tractors are aggregated (hanging out or trailers) interchangeable mechanisms, machines and guns for performing all types of gardening works.
When creating garden and park objects apply:
Wheel tractors of medium and low power;
Crawler tractors used as roadbuilding machines when creating new facilities, as well as in wood and ornamental nurseries, aggravation of decorative gardening.
When the content of green plantings on objects, small in size, complex configuration, especially in residential building, there is a variety and specificity of the technological operations performed. This determines the special requirements for the selection of machines. In difficult conditions of the urban environment, you can use mainly small-sized machines and mechanized tools.
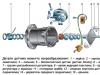
Fig. 8.2. General Type of Motoblock: 1- control handle; 2- clutch control lever;
3 - gas lever; four- reverse lever; five- gear lever; 6, - steering rod;
7-inclusion lever Vom-A; 8 - gas tank; 9 - air filter; 10- engine;
11 - wheels; 12 - Coupling Vom-A; 13- rack; fourteen-trailer
Depending on the mass and power of the engine, small-sized tractors and motoblocks are divided into three types: easy, medium, heavy.By the design of the chassis, small-sized tractors are divided into :, wheel, to forest-trapand crawler.A variety of these tractors can be considered self-propelled trolleys (microssed). Motoroblocks and Motorudia have a union wheel drive and are used for soil processing, making herbs and other works.
Most small-sized tractors have a traditional layout scheme similar to the "large" tractors with the rear-wheel drive wheels and the front (leading and leading) wheels of smaller size, as well as the articulated design with all the leading wheels of the same size. A distinctive feature of the layouts of motoroblocks and motor customs is the location of the engine.
The following schemes are allocated:
The engine is installed console. The engine crankshaft is coaxial to the leading shaft of the transmission and perpendicular to the axis of the leading wheels. Transmission is rigidly connected and is a single unit. Regarding the move wheels, the engine is transferred forward or backward - the European layout scheme;
The engine is installed on a special bracket. Located with a transmission of a clinoremable transmission that simultaneously performs the role of the clutch clutch, the Japanese layout scheme;
The engine is an easy-sensitive energy module. The crankshaft is located vertically. The module is connected to various technological modules - traction, mowing, pumpingand etc.
In tab. 8.1 shows the type of small-sized tractors and motoblocks.
disciplines
« Machines and mechanisms in garden and parking and landscape construction»
for specialty250203 "Garden and park and
landscape construction »
Developed:
Mikhaylenko N.A.
Krasnodar2010
|
Introduction | ||
|
Machines and mechanisms for the mechanization of soil processing and plant care works | ||
|
Machines and mechanisms for the mechanization of sowing and landing work. | ||
|
Machines and mechanisms for mechanization of fertilizer work. | ||
|
Machines and mechanisms for irrigation mechanization | ||
|
Machines and mechanisms for stripping lawns and mowing grass | ||
|
Machines and mechanisms for forming and trimming crowns of trees and shrubs | ||
|
Minite equipment for the mechanization of the nursery | ||
|
Topic 8. Machines for preparatory earthworks and soil preparation | ||
|
Machines and mechanisms for mechanization of work to combat pests and diseases |
Introduction
Plan lectures
Means of mechanization in gardening and park economy
Tractors and energy products
Means of mechanization in gardening and park economy
In order to intensify works on the creation and content of garden-parking facilities in the gardening and park economy, a number of machines and mechanisms are used that significantly increasing productivity and reduce labor-intensiveness of production processes. To date, the park of machines and mechanisms is constantly increasing and improved in the direction of the specialization of garden and park economy. In the garden and park economy, small-sized equipment, along with machines used in road construction and agriculture, are becoming more and more applied. Machines are widely applicable for the preparation of territories for landscaping and maintenance of objects. Earthworks use bulldozers, automotive drivers, excavators. In the production of work, large trees transplanting machines are introduced, aggregates for sowing the lawn seeds, fertilizer making, irrigation of plantations.
Means of mechanization are applicable to fulfill labor-intensive main works. The final "finish" and the design of garden-park objects is conducted by the hands of qualified workers using manual mechanisms.
Tractors and energy products
Tractors are the main basic machines used in the creation of garden-park objects. The tractors are aggregated (hanging out or trailers) interchangeable mechanisms, machines and guns for performing all types of gardening works.
When creating garden and park objects apply:
Wheel tractors of medium and low power;
Crawler tractors used as roadbuilding machines when creating new facilities, as well as in wood and ornamental nurseries, aggravation of decorative gardening.
When the content of green plantings on objects, small in size, complex configuration, especially in residential building, there is a variety and specificity of the technological operations performed. This determines the special requirements for the selection of machines. In difficult conditions of the urban environment, you can use mainly small-sized machines and mechanized tools.
These funds include small-sized tractors (Fig. 8.1), motoblocks (Fig. 8.2), power units, Motoruda (Motorokultivators, Engineers, Motorofrus, Motocos, etc.).
Fig. 8.1. General view of a small-sized tractor: 1- engine; 2.- clutch;
3 - gearbox; 4 - gear shift handle; 5 - reverse lever;
6 - steering;7- seat; 8 - connecting shaft; nine- main gear
Rear axle; 10- Differential; 11 - Power takeoff shaft; 12- rear wheel drive switching lever; 13 - rear wheel; 14 - final gear; fifteen- front wheel

Fig. 8.2. General Type of Motoblock: 1- control handle; 2- clutch control lever;
3 - gas lever; four- reverse lever; five- gear lever; 6, - steering rod;
7-inclusion lever Vom-A; 8 - gas tank; 9 - air filter; 10- engine;
11 - wheels; 12 - Coupling Vom-A; 13- rack; fourteen-trailer
Depending on the mass and power of the engine, small-sized tractors and motoblocks are divided into three types: easy, medium, heavy.By the design of the chassis, small-sized tractors are divided into :, wheel, to forest-trapand crawler.A variety of these tractors can be considered self-propelled trolleys (microssed). Motoroblocks and Motorudia have a union wheel drive and are used for soil processing, making herbs and other works.
Most small-sized tractors have a traditional layout scheme similar to the "large" tractors with the rear-wheel drive wheels and the front (leading and leading) wheels of smaller size, as well as the articulated design with all the leading wheels of the same size. A distinctive feature of the layouts of motoroblocks and motor customs is the location of the engine.
The following schemes are allocated:
The engine is installed console. The engine crankshaft is coaxial to the leading shaft of the transmission and perpendicular to the axis of the leading wheels. Transmission is rigidly connected and is a single unit. Regarding the move wheels, the engine is transferred forward or backward - the European layout scheme;
The engine is installed on a special bracket. Located with a transmission of a clinoremable transmission that simultaneously performs the role of the clutch clutch, the Japanese layout scheme;
The engine is an easy-sensitive energy module. The crankshaft is located vertically. The module is connected to various technological modules - traction, mowing, pumpingand etc.
In tab. 8.1 shows the type of small-sized tractors and motoblocks.
To narrow the results of the search results, you can specify the request, specifying the fields for which search. List of fields is presented above. For example:
You can search for several fields at the same time:
Logically operators
The default operator uses And..
Operator And. means that the document must comply with all elements in the group:
study Development
Operator Or. This means that the document must correspond to one of the values \u200b\u200bin the group:
study Or. Development
Operator Not. Excludes documents containing this item:
study Not. Development
Search type
When writing a query, you can specify the method for which the phrase will be sought. Four methods are supported: Search for morphology, without morphology, search for prefix, search phrase.
By default, the search is made taking into account morphology.
To search without morphology, in front of words in the phrase, it is enough to put a dollar sign:
$ study $ development
To search for the prefix you need to put an asterisk after the request:
study *
To search the phrase you need to enter into double quotes:
" research and development "
Search for synonyms
To include in the search results, the words need to put a lattice " #
"Before the word or before expressing in brackets.
In applied to one word for it will be found to three synonyms.
In applied to expression in brackets, it will be added synonym for each word if it was found.
Not combined with search without morphology, search for prefix or search by phrase.
# study
Grouping
In order to group search phrases you need to use brackets. This allows you to manage the milk logic of the query.
For example, you need to make a request: to find documents from which the author of Ivanov or Petrov, and the title contains words research or development:
Approximate word search
For approximate search you need to put a tilda " ~ "In the end of the word from the phrase. For example:
bromine ~
When searching, words as "brom", "rum", "prom", etc. will be found.
You can additionally specify the maximum number of possible revows: 0, 1 or 2. For example:
bromine ~1
By default, 2 edits are allowed.
Criterion intimacy
To search by the criterion of proximity, you need to put a tilda " ~ "At the end of the phrase. For example, in order to find documents with the words research and development within 2 words, use the following query:
" study Development "~2
Relevance of expressions
To change the relevance of individual expressions in the search, use the sign " ^
"At the end of the expression, after which, indicate the level of relevance of this expression in relation to the rest.
The higher the level, the more relevant this expression.
For example, in this expression, the word "study" is four times relevant to the word "development":
study ^4 Development
By default, the level is 1. Valid values \u200b\u200bare a positive real number.
Search in the interval
To specify the interval in which the value of some field should be, the boundary values \u200b\u200bseparated by the operator should be specified in brackets To..
A lexicographic sorting will be made.
Such a request will return results with the author, ranging from Ivanov and ending with Petrov, but Ivanov and Petrov will not be included in the result.
In order to enable the value to the interval, use square brackets. To exclude the value, use curly brackets.