Thermal expansion due to heating is insidious. For example, if the valve of the gas distribution mechanism due to the temperature expansion of the metal will lengthen so much that the end of its rod will be strengthened into the adjacent part in the kinematic timing pattern, the valve plate will not be able to close in the saddle and ensure the tightness of the combustion chamber.
As a result, the compression is lost, the engine does not develop power, and the valve plate, having lost its capabilities during the landing in the saddle, to give heat from the cylinder head and cool, overheats, and may turn around that to eliminate the malfunction will require expensive repair of the power unit.
To avoid the negative effects of thermal expansion of the valves, the gaps must be provided between the valves and their pushers. They are called thermal, which unequivocally indicates the purpose of the gaps - to protect the motor from the problems associated with the change in the size due to different expansion of different heated parts.

However, the wear, in the process of operation, besides the valve saddles in the head of the cylinders, sealing champers on plates and stubborn ends of the rods of valves are also subject to other driving parts of the drive, no less cunning than the thermal expansion.

As the clearance installed during the engine conveyor assembly in the case of temperature expansion increases. This leads, first, to reduce the period when the valve is open. The valve opens later and closes earlier, which, depending on whether the inlet or exhaust valve occurs, adversely affects the filling of cylinders with fresh charge and their cleaning from the exhaust gases. Such a distortion of phases of gas distribution causes a decrease in engine power and increase fuel consumption.

Secondly, due to the fact that with an increase in the gap, the camshaft camshaft prematurely breaks away from the pusher, the valve plate begins to return to the saddle not smoothly, as it should, but with a blow. And camshaft camshaft, instead of smoothly press the pusher, also begins to beat it. Impact work diminishing wear and can contribute to the appearance of microcracks on contact surfaces, the further development of which, apparently, explains many well-known cases of rash valve saddle from the cylinder head. It indicates that the GDG details are shock loads, noise appearance.
This means that one presence of a heat gap is not enough. It is also necessary to provide for the possibility of adjusting it during the operation of the engine and register this procedure as mandatory for maintenance.

But there is another way out. To get rid of troubles related to the temperature expansion and wear, a special device was developed, which automatically selects the thermal gap in the valves and compensates for the effects of mechanical wear.

For users, the most obvious advantage of the use of hydraulic compensators in the gas distribution mechanism is the lack of the need to periodically check and regulate the gaps in the valves.

However, the above illustrates that much more importantly, due to the work of the hydrocomathers, the optimal phases of gas distribution and with them are the dynamic and economic characteristics of the engine, as well as the component composition of the exhaust gases. In addition, the use of hydrocompensators reduces the noise level from the engine, and since this indicates a decrease in dynamic loads, we can talk about increasing the durability of the timelines.

Another name of heat gap hydrocompators - hydrotroters, but it truly true only for nodes located directly in front of the valves. However, depending on the kinematic diagram of the valve drive and design considerations, the hydrocompensators can be placed at other drive points.

In particular, in the presence of a rumor valve valves, which are a biscuit lever, the hydrocompensator is often performed as a support for the shoulder opposite, which affects the valve.

Such nuances make hydrocomathers visually unlike each other, but their constructive essence does not change from this.

The hydrocompensator of the housing, the piston placed between the springs and the shut-off valve. The spring squeezes the body and the piston in different directions, as a result of which the valve clearance is selected. In the cavity formed in the internal volume above the piston, oil comes from the engine lubrication system under pressure and creates a sub-injector, providing an unosland kinematic connection between the valve and the parts of its drive during the motor operation.

At the moments of pressure on the hydraulic chipset with a cam or rocker, the valve locks the oil cavity over the piston from the inside. This prevents the inverse outlet of the oil from the cavity through the inlet. Losses of oil through the gap between the case and the piston are replenished during the "rest" period when the cam or rocker ceases to put pressure on the hydrocompensator.

In total there is a service life, and in the hydrocompensator it also has. The hydrocompensator works normally until the leakage of oil from the cavity over the piston is performed during the "rest". But when the balance is broken towards leaks, the drive begins to work with shocks that will be claimed by characteristic knocks.

Oil may be too quickly squeezed out of the hydrocompensator for two reasons. First, the gap between the piston and the inner surface of the case excessively increased due to the natural wear, which accompanies the movements of any details of each other.
The second reason is a valve fault that locks the internal cavity of the hydraulic components. The valve is critical not only wear, but also depositing oil aging products.

In addition to the problems associated with oil leakage, there is another trouble that can occur with the hydrocommoverster - the piston jamming in the case. As indicated by manufacturers, this is the main reason for the return of hydrocompensators during the warranty period. However, by its expiration, foreign particles that have fallen into the hydrocommoventrator along with oil and penetrated into the gap between the plunger and the sleeve, can also cause the jam.

In any case, the lifespans are determined by the quality of lubrication. Hence the demandingness to the characteristics of motor oil and strict observance of the periodicity of oil replacement and oil filter.

But what is still a resource of hydrocomponentials? If you ship out the information of these devices manufacturers, it turns out that it is possible to count on trouble-free operation only before the range of 120 thousand km. Next - as cards will be shaved.

Undoubtedly, the voiced figure will slide oil into the fire of disputes, which is better - hydrocomathers or their absence and adjustment of thermal gaps by hand, because, as practice shows, it can also be needed only to the specified mileage. And maybe they do not need - such a practice is also known. If we take into account all the advantages and disadvantages of using hydrocomathers, truth, as usual, somewhere in the middle.
The most common fault of modern engines is a knock of hydraulic components. The reasons are many, in their most people they are associated with the quality of oil. What to do with this malfunction and how to deal with it will tell this material.
What is the hydrocompensator and how the hydrocompensator works
Hydrocompensator is a simple device for automatic adjustment of the gap in the valve drive, eliminating the need to disassemble the engine during its maintenance. The hydrocompensator, in the surrounding "hydrika" is a miniature hydraulic cylinder, changing its length when the engine oil is injected.

Oil volume compensates for the gap between the valve stem and the camshaft camshaft. The oil in the cavity of the hydraulic components is hung through the valve with a very small hole, and it turns out through the natural gaps of the valve pair. How well works "hydrik" depends on the oil flow and on the state of the plunger pair, the lack of wear or jamming.
How to understand that the hydrocompensator is knocking
The faulty hydrocompensator makes a sharp knock, shock, with a frequency of twice the speed of the engine.
The hydrocompensator is considered to be faulty, which knocks more pairs of minutes after starting the engine or knocks after full engine warming up. A knock is listening on top of the engine and can be silent from the car's interior.

Why the hydrocommovensector is knocking
The reasons for the cooke of the hydrocomponancetor "on the cold" (with an immentable motor):
- Too thick butter, on an immentable engine, poorly enters the cavity of the hydrocommovensector. It takes time so that the cavity is filled with oil
- Clogged with pollution oil highway or valve hydraulic components. Pollution appears with low quality or under protracted shifts of motor oil, and can also be the wear products of some engine parts.
- Wear or jamming the plunger of the hydraulic components. It happens from natural wear or from the ingress of abrasive contaminants in engine oil.
The reasons for the cooke of the hydrocomponancetor "on the hot" (on a heated motor):
- Enclosing a plunger pair of the hydraulic compartmentdue to natural wear or pollution. The plunger's jackets block its movement and the hydrocompensator completely loses its performance. The clearance is not selected and the hydrocompensator is knocking.
- Too low viscosity of the heated oilThe oil flows through the plunger gaps faster than the pump is supplied. Elected-quality oil or too liquid oil for this engine is strongly diluted when heating and easily flows through technological gaps.
3. Increased oil in the engine, foaming of the oil due to the mixing of the crankshaft or due to the injection of water into the engine. You should check the oil level in the engine, as well as use only high-quality engine oils.
The easiest way to eliminate the knock of the hydraulic components
The easiest and most effective way to help in most cases, additive to the oil additive LIQUI MOLY oil. The additive is washed with oil channels, removes pollution and restores oil supply to hydrocomathers. In addition, the additive slightly thickens the oil, thereby compensating for their natural wear. The additive is added to the heated engine oil, the total action occurs after about 500 km of run.

How else can you eliminate the knock of the hydrocompensators
- Replacing hydrocompensators Advantages: Guaranteed Result. Disadvantages: expensive and long). It must be borne in mind that on some foreign cars, you first need to order details, wait until they come, and make an appointment in the service. On most engines, the replacement of hydrocompensators will require additional costs of disposable parts, such as laying or sealant.
- Careful washing of oil system with special flushing, for example: Liqui Moly. Advantages: relatively inexpensive. Disadvantages: The result is not guaranteed.
3. Perhaps in running cases, it will be necessary replacing the oil pump or cleaning of oil highwaysengine with its partial or complete disassembly.
What will happen if you do not fix the knock of the hydraulic components
If you do not engage in the removal of the vocabulary knock, then you can drive for quite a long time without any problems, but, with time, the engine will work louder, with vibrations, power will fall and the fuel consumption will increase.and then happen wear of the entire valve mechanism, It is part of the engine camshaft. His replacement is a very expensive event.
Outcome
If the knock of the hydrocompensators repeatedly arises, it makes no sense to wait down the situation. Additive additive will solve the problem and prevents the development of wear for a long time.
VIDEO
;
The gas distribution mechanism of motors over time was significantly upgraded. Development did not bypassed the body and the valve device of the DVS. At first, the arising clearances between the valves and the distribution shaft were adjusted manually, then mechanical regulators appeared, but hydraulic compensators began to adjust the vertex. Do you know little about similar details? Then be sure to familiarize yourself with the article below, which will help everyone to understand why the hydrocompensators are knocking, which they represent and can be repaired.
Device and principle of hydrocompensators
Any more or less experienced motorist knows that the valve mechanism of the engine regulates the inlet of the fuel mixture into cylinders and the release of exhaust gases. In the process of its operation, the motor valves in pairs are open and, naturally, work under conditions of colossal load, which is associated with a high fuel combustion temperature. To minimize the negative properties of the temperature expansion between the nodes of all timing, heat gaps are provided, the regulation of which and the standard hydrocompensator is engaged.
The difference between hydraulic compensators from other valve clearance regulators is that the first work is fully automatically working, while other mechanisms require one or another motorist participation in their lives. What does it mean? So this is that in the absence of hydrocompensers, the owner of the car with some periodicity should personally put the thermal gap of the valves and closely monitor them during the operation of the unit.
Speaking with simple words, the hydraulic components device is a bunch mechanism set between the motor camshaft and each valve. The part works on the principle of the plunger pair and circulation of oil, speaking at the same time with the "gasket" between the previously marked elements of the timing. As a result, it turns out that, depending on the temperature mode of the engine, there is always an interaction between the camshaft and the work valve, and the most important thing is a properly tuned heat gap.

Why appears a knock of hydrocompensators
From many motorists it is often possible to hear phrases by type:
- "Why is the hydrocomathers on the cold? What to do?";
- "What are the hydrocompensators on the hot? Where to regulate? ";
- "Hydrocompensators were careisred. How to fix them now? "
Immediately we note: the formulation of the problem is in a similar way initially incorrect. It is important to understand one simple thing - valve hydraulic components can not knock, knocks the valve mechanism itself due to improper functioning. But the latter already often provoke precipitation of hydrocompensators. But first things first.
Above it was noted that any type of hydraulic compensator is hydromechanism, working at the expense of a plunger pair and oil entering it from the motor. That is, the cause of the knocking of hydraulic components or valves, as it will be correct, lies either in the incorrect operation of plungers, or in problems with the oilsecurity of this mechanism. To be more accurate, the unpleasant sound may appear for several reasons:
- Oils that reach the hydrocompensators is not enough or it has very poor quality. As a result, the plunger pair does not receive due lubrication, the pressure in the system does not appear and the regulation of the clearance does not occur. Naturally, the knuckle of valves begins, provoked by the wrong thermal gap;
- Channels of the GBC or the hydraulic mechanism have been worked out. Such a phenomenon occurs due to improper use of oil. That is, the absence of timely oil replacement or its excessive burnout is capable of scoring the oil channels and make a completely defective hydrocompatator from the working unit;
- The hydraulic mechanism itself has failed. There are two main breakdowns: a plunger wedge or incorrect operation of a ball valve acting directly on the thermal valve of the motor. A similar one can happen either because of a nagar that appears due to the use of bad oil, or due to the marriage made by assembling the mechanism. The physical wear of the node is almost excluded, because it is actually eternal. In any case, only a thorough check of the hydrocomathers and a professional look at their condition will help determine the exact cause of the malfunction.
Make on the wrong work of the hydromechanisms in the design design, it makes sense only if the presence of other breakdowns in the system is excluded (especially damage valves). With the other circumstances, the repair of hydrocomathers will look something unnecessary and meaningless.

Repair of hydrocompensators
Replacing the hydrocompathers or repair of these timing elements with their own hands is required, just say, very rarely. This is due to the fact that the design of the mechanisms is thought out to the smallest detail and their real breakdown is often not the conditions of work, but the carelessness of the owner of the machine. The latter, of course, is not all motorists, therefore the repair of hydrocompensators is not required to many.
In any case, knowledge is power, so information on symptoms and general principles of the repair of hydraulic gap regulators will be worth it. First, pay attention to the signs of damage to hydrocomathers. Often they are more than transparent and presented to the next list:
- motor began to work unstable;
- violated the movement dynamics;
- appeared "knocking" noises in the work of the engine;
- burned valve;
- rose fuel consumption.
Naturally, the greater the number of symptoms appears - the larger bases are available in order to think about the repair of hydrocompensators with their own hands. Why it is own, and not a hundred? Everything is simple. There are no special difficulties in repairing parts, so give a lot of money to other people, probably meaningless.
Returning to the question of how to check the hydrocomathers on the correctness of work, it is necessary to state the thing unpleasant for many cars - without removing elements from the engine, the diagnostics cannot be implemented. Given this feature of the repair, replacement and inspection of hydromechanisms, consider jointly. In general, the process of repairing hydrocompensators looks like this:
- First of all, we fully change the oil in the engine and the oil filter. If after that, the knock or other symptoms have not passed the breakdown, proceed to the next step. At the same time, do not forget that after changing the oil, the hydrocomponents are required. How to pump the hydrocomathers? In no way, the system will do everything after starting the motor. To speak more precisely, the new oil pump lubricant is pumped into each hydraulic mechanism and only after that they will stop knocking, which will allow them to evaluate their new job. Often it takes 5-15 minutes, no more;
- So, apparently - no effect? Then partially disassemble the motor to access the valve mechanism. On many models, the car is enough to remove the GBC and dismantle other motor nodes that interfer access to the valves;
- After that, there are two options:
- The first is the search for a faulty hydraulic components. The procedure is not complicated and is carried out as follows: We assign the rocker and the rod of the pusher of each valve as much as possible from the hydromechanism and are trying to press on the last. If the compensator goes down under considerable pressure, then it is working, otherwise it should be removed the item for a better check;
- The second is the removal of all hydrocompensators to check each. When this option is selected, the standard disassembly of the valve mechanism and the elements of interest to us are respectively.
- By performing the operation described above, it remains only to replace the faulty GDM element and return the car to the original state. If there was a disassembly of the mechanisms, it is required to check their internal state and clean from Nagara. In the case when everything is normal with the regulator, then install the hydrocompensator follows to the design of the motor and then check it on working capacity. During other circumstances, the node is required to be completely replaced. In more detail, we will not talk about how to disassemble the hydrocompensator, since this procedure is not so complex and under the power of any motorist. The main thing is to act gently and slowly.
Perhaps more information on how to replace the hydrocompensators, it is meaningless. The practice is more important here, so reserve the basic set of auto repair and head to the garage, of course, if you have the need for this.

Prevention breakdown
As it became clear, checking, repairing and installing hydrocompensators - simple procedures, and the adjustment of the node is not required at all. Despite this, the vehicle breakdowns does not want to allow a completely any motorist, so it would be advisable to talk about preventing faults and compensators.
The main thing in the prevention is to remove the car from the "ration" of the car cheap and poor-quality lubricant. Ask how to determine a good oil producer? The answer is very simple - according to the reviews of motorists. According to the research of our resource, the best oils for the following companies:
- Liqui Moly (Liquim Moli) is a German organization, famous for a huge amount of lubricating goods for cars. Immediately note that the additives for hydrocomathers from Liqui Moly is not needed to buy (such means completely from any manufacturer only clog the cavity of the motor), but the engine oil is necessarily;
- Motul (Motul) - the British manufacturer of the same lubricants for cars. Perhaps the most important competitor in its field of activity for Liqui Moly, which is best for you - decide for yourself. Unambiguously, we can say that both manufacturers are worthy of attention and respect;
- Castrol (Castrol) - as well as Motul, manufacturer from foggy albion. According to the status and reviews, this company, of course, is inferior to those discussed above. However, compared to the rest of the market representatives, it is Castrol who has the best reviews about their products, so our resource can only recommend its oil to buy.

In addition to the selection of lubricants, it is desirable to remove the hydrocompensators at least once in 80-100,000 kilometers for cleaning and high-quality verification. For the rest of the same data, the Merry Timing Elements do not require and when it is properly opened, the full operational term of the engine of any car is debugged.
In general, there is nothing more to say on today's theme. We hope the above material was useful for you and gave answers to the answers. Good luck on the roads and car maintenance!
If you have any questions - leave them in the comments under the article. We or our visitors will gladly respond to them
The first engine with the hydraulic components was installed on Cadillac in 1930. At that time, no one thought about servicing the power aggregates, so in real sought-after "hydrics", as they are now called in the people, they received only in the 80 years. Then the Japanese car industry entered the world market, and then won it.
But the use of these elements led to the complication of the engine design and increased the cost of machines, so they began to put them less frequently. The reliability of engines for economic reasons has slightly lost its importance, but still owners of machines with hydrocompensators can consider themselves wearing.
Hydrocompensator - What is it in the engine?
In motors created during the development of the automotive industry, thermal gaps were regulated by special mechanisms. The gap appears as a result of valve wear. The valve system setting was recommended to produce every 15,000 km. I had to open the GBC, and only a qualified master could do it.
But the auto industry continued to develop, and experts developed a device that supports the valve clearance without adjustment. With its work, the timing is taken into account. The device performs the role of the pusher, the design of which includes springs. They are in constant movement and change in the amount in proportion to gaps. This mechanism is called a hydraulic compensator.

What do the hydrocomponents look like?
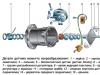
There are compensators for engines made according to SOHC and DOHC schemes. According to the design, they differ, but slightly. Any hydrotherapler is installed in a metal housing that is not disassembled. In SOHC engines, it is put in the jacks of the valve rockers, in the DOHC engines - in the GBC nests. The device consists of:
- plunger;
- his sleeves;
- valve spring;
- ball-shaped valve;
- plunger springs.
Why do we need hydrocompensators?
With the heating of the engine to its operating temperature, parallel heating of other power units devices occurs. Details are expanding, due to which the gaps are reduced between elements of the design.
If we talk about the timing, the accuracy of the gaps is very important - the clarity of the work of the engine depends on it. Valve mechanisms can be adjusted both manually and using special devices. Valves are under constant thermal and shock loads. By the way, all the MRM items are warmed unevenly, and natural wear is the main "disease" of the valve mechanism.

The thermal gap provides normal valve system operation. Exhaust valves due to contact with hot gases heated much stronger inlet, so the gaps here are more. Adjected gaps are constantly changing due to the wear of the mechanism and for other reasons. Their changes lead to premature GDM wear. Valves begin to knock, fuel is spent rapidly, the motor power drops.
Exhaust valves suffer much more intake. Hot gas, passing through disturbed seals, can destroy the valve seat and its plate. And even the formation of the gap leads to an increase in shock loads and to power loss by the power unit.
The adjustment of the gaps can be carried out manually - but only in the presence of experience and appropriate skills. The adjustment should be carried out every 15,000 km. It is necessary to carry out the procedure with the temperature oscillations - the average value here is not taken into account. With hydraulic components, regulating the clearance automatically, there are much less problems.

How do valve hydraulic components work?
The principle of operation of hydrocompensers is a rational change in the gap between valves and parallel axes. All changes are made automatically. Displacement parts occur due to oil supply and springs. With this mechanism, there is no need to adjust the valve system - the opening and closing of the valves occurs without external intervention. When the gap changes, the pusher "waivers" the valve to the required position.
The device of the hydraulic compressor includes a plunger pair and an oil conductive valve. For compensator, the oil is extremely important. The compression rate is low, so oil pressure is the main power of the work of "Hydrika".
Where is the hydrocomponator?
At the very top of the power unit there is a head block of the cylinder. Inside it there is a rotation of the camshafts. In its type, camshaft resembles the usual axis with cams, under which compensators are located. Oil easily fills them when they are in a relaxed state, but its output occurs within a few hours. The supply of a working fluid is carried out from the channel located in the bearing case, through a special hole.

The main elements of the device are plunger pairs installed in the GBC instead of ordinary bushings and bolts. Plunger all the time presses on the valve lever, pressing it to the camshaft camshaft.
Types of hydrocompensators
There are 4 types of devices:
- Hydraulicator. It is located on modern models of cars. Adjusts the gaps between the camshaft and the valve.
- Hydropar.
- Hydraulic support for working in rocker and levers. Now this device is almost not used. It was actively used in the former models of gas distribution mechanisms.
- The hydrotrodeter on a roller-based basis.
Today, the hydrotrifers are increasingly used, and the hydraulic rods gradually go into the past. There are all 4 designs.
Pros and Cons Applications
The direct appointment of the compensator is the adjustment of the gap, which is formed between the valve and the shaft. Without this normal, the power unit will not be able to work. It happens automatically by oil pressure. The advantages of applying the mechanism are:
- fuel consumes slower;
- the dynamics improves;
- the motor works softly and silently;
- the term of the MRM is increasing, the accuracy of its phases increases;
- power and resource of the engine work increases.
Does not do without minuses. As already mentioned, the main scene power of the system is oil. Only high-quality, and therefore expensive oils. Synthetic working fluid is preferred. In addition, oil has to be changed, and this also "smells" with impressive expenses.

Compensators are often clogged - this is another minus mechanism. The timing of the timing begins to make a strong noise, and the operation of the power unit deteriorates.

Design is difficult to repair - it is better to entrust this business to specialists. In order not to constantly visit the car service and change the hydraulic compensators, you need to ensure that the motor is clean. With the earliest need to change the oil in the system, rinse the motor thoroughly. Malfunctions need to be eliminated immediately after they are detected.
Remember: the failure of the compensator may cause serious problems with DVS. So why not observe the rules of operation?
As follows from the name, the hydraulic component is a hydraulic mechanism in the car engine.
It is responsible for maintaining a permanent working gap in the valve mechanism of the DVS, since with increasing engine temperature, the size of its parts and gaps between them occurs.
The health of the hydraulic components guarantees the trouble-free functioning of the car's power unit, including at considerable temperature surges.
It supports the gap of intake or exhaust valves in the same level, including in the occurrence of GDM and the valve mechanism as a whole.
Ideally, when working, the hydrocompensator should not make any extraneous noise - silk, grincping or knock.
Any such sounds indicate its malfunction and the need to diagnose the mechanism.
Ignoring the problem in the future can lead to incorrect operation of the power unit, increased gasoline consumption, rapid wear of the valve mechanism and the critical drop of engine power.
With proper caringness and careful operation of the car, the hydrocomathers serve for a long time and do not require any special attention.
However, sometimes problems with this node are still happening.
For example, if the car already has a solid mileage, when natural wear of the hydraulic pairs of the hydrocomponnet occurs, error in service or a significant break in the operation of the vehicle, the system, and its partial delighting can occur.
It is manifested by such a defect on the heated engine with a small knock in the GRM drive.
Solve such a problem can be tried independently by pumping the hydrocomathers.
Since the engine oil of the engine oil is the working fluid of hydrocommovers, then you need to trace so that the oil is fresh and its level is sufficient.
If everything is in order, then the car needs to start and raising turns up to 2 thousand. Give it to work for 2 minutes.
Then give the engine to work for about 3 minutes by changing the revolutions in the range from 1.5 to 3 thousand. After that, let go of the gas pedal and give the engine to work at idle speeds about 1 minute.
For the disappearance of the defect, one cycle of pumping is most often most often, but may also be repetition.
If after 2-3 pumping noise in the GDM drive is preserved, then it is necessary to look for a malfunction of the hydrocomathers by diagnosing and parsing the mechanism.
It should be noted that the knock is the most important external manifestation of the malfunction of the hydrocomathers.
It may arise for various reasons, the following are:
- . significant depreciation of the mechanism or the defect in the process of operation, up to jamming, hydrocomathers;
- . low-quality, unreasonable or lost factory properties engine oil;
- . Mud deposits in the inner parts of hydrocomathers or violations in the DVS lubrication system.
The ingress of dirt and deposits into the internal cavities of the hydrocomathers are associated, as a rule, with a poorly functioning oil filtration system in the engine, clogged with an oil filter, a long period of operation of the engine in an old oil.
Therefore, it is very important to strictly follow the requirements of the automaker and timely replacing the oil and oil filter in a timely manner, pour oil with an appropriate engine marking engine and viscosity.
Also, it should be replaced by oil and filter after all DVS faults, for example, after its overheating, since such problems may result in changing the chemical properties of engine oil.
With significant contamination of the hydrocompensators, a characteristic knock may appear both when the engine is cold started and after it is heated to normal temperatures.
Experts believe that the wall of the hydrocomathers arising on the cold engine, immediately after launch, is not a sign of their malfunction.
If, after warming up the engine, the knock disappears, then this can be attributed to the normal operation of the mechanism.
At the time of starting the engine, the oil in it does not have the desired viscosity hydraulic components, which leads to the appearance of the knock, then the oil is heated, the knock disappears.
"Cold" knock may also arise for the following reasons:
- Fault Valve of the hydraulic components.
During the engine idle time, the oil can flow from the hydrocompensator, which leads to a systematic recent mechanism. During heating or pumping, the pressure is normalized and the knock disappears; - Significant pollution of the oil channels of the hydrocompanator.
The higher the temperature of the oil, the less dense becomes the deposition of dirt in the channels, so that the knock will disappear. Here you need to keep in mind that over time, the channels can be shuffled tightly, it will finally eliminate the hydrocomponancetor, and it will constantly knock. In some cases, the situation can correct the use of good quality engine oil purifying additives from a proven manufacturer; - Incorrect operation of the oil filter.
If its functional ability to skip the oil is broken, then at the beginning of the operation of the engine, the hydrocompensators may experience oil starvation, when it goes out to the "working viscosity" of oil, the knock will disappear, but the problem oil filter is still better replaced.
Cutting hydrocomathers in the engine with a warm engineer, experts consider the most dangerous. It can be a permanent knock on a heated motor at idle and under the load in motion.
The fault diagnostics begins with the definition of the source of the knock in the engine, because parts that can knock when the engine occurs in the engine is abuse: pistons, connecting rods, crankshaft and distribution shafts, etc.
The wall of the hydrocompanator is quite characteristic, ringing, metallic, in high tone and proceeds directly from under the valve cover.
In diagnostic purposes, car service specialists often use a stethoscope.
As a rule, if the hydrocompensator is knocking constantly, it speaks of his critical fault. It is necessary to dismantle the mechanism and determine its condition.
If the cause of the hydrocompanator's knock is in a heated motor in the pollution of the oil supply channels, it will be enough to disassemble and rinse. At the same time, it is recommended to conduct an audit of the lubricant system, replace the engine oil and an oil filter.
If the plungering pair has occurred, then such a hydrocompensator is immediately replaced.
When replacing one hydrocompensator due to its jam, it is better to replace the entire set so that in the future it did not have to open the engine to repair or defecting other hydrocomathers.
Only prepared hydrocomathers should be installed.
New "factory" hydrocompensators are filled with oil solution, it is not necessary to delete it, it will ensure the trouble-free start of the mechanism and in the future mixed with engine oil.
If the hydrocompensator is installed after disassembling and washing, it must first be filled with engine oil first to avoid bringing the mechanism and shock loads on the motor after its start.
Replacing the hydrocompensators has its technical features related to the installation of the correct working position of plunger pairs, so this work is better to entrust the professionals of the car service.
Moreover, the engine is the most expensive part of any car and experiments with its parts, as a rule, is expensive.
Look at our engine repair prices
How much does it cost? Prices for such work are quite loyal. Call us and see for yourself!
| Name | Engine | Domestic | Foreign cars | |
| Search engine malfunction rub / hour | from | 1000 | 1250 | |
| Chain shoe (replacement) | from | 1000 | regulatory | |
| Cylinder block (boring) | from | 2700 | 2700 | |
| Inserts (replacement) | from | 5000 | regulatory | |
| Hydrocompensators (replacement) 16 valves | 16 valves | from | 2500 | regulatory |
| Hydrocompensators (replacement) 8 valves | 8 valves | from | 1900 | regulatory |
| Valve hydro pulls (replacement) V-shaped | V-shaped | from | - | regulatory |
| Valve hydro pulls (replacement) single-row | single row | from | 3000 | regulatory |
| Valve hydro pulls (replacement) Opposite | Opposite | from | - | regulatory |
| Block head (repair) with s / y single-row | from | 6000 | 7000 | |
| Block head (s / y) Single row | from | 4000 | 5000 | |
| Camshaft bed cover (gluing) with / y | from | 3200 | 5000 | |
| Cylindro-piston group (replacement) | from | 5000 | regulatory | |
| Engine (s / y) | from | 4000 | 6000 | |
| Engine V-shaped (repair) Capital with C / y | V-shaped | from | - | 25000 |
| Engine single-row (repair) Capital Capital with / y | single row | from | 18000 | 24000 |
| Opposite engine (repair) Capital with C / y | Opposite | from | - | regulatory |
| Ignition (Installation) of the moment | from | 450 | 650 | |
| Engine Protection (Installation) | from | 400 | 400 | |
| Engine protection (s / y) | from | 130 | 130 | |
| Carburetor (replacement with adjustment) | from | 550 | regulatory | |
| Carburetor (repair with s / y) | from | 1000 | regulatory | |
| Valve (trigger) for 1 pc | from | 300 | 500 | |
| Valve (adjustment) of gaps 16 valves | 16 valves | from | 1800 | 2200 |
| Valves (adjustment) of gaps 8 valves | 8 valves | from | 1100 | 1200 |
| Crankshaft (grinding) | from | 1800 | 1800 | |
| Inlet collector (s / y) | from | 1800 | regulatory | |
| Caps oil slimming (replacement) 16 valves | 16 valves | from | 3500 | regulatory |
| Caps Outline (replacement) 8 valves | 8 valves | from | 2500 | regulatory |
| Compression Rings (replacement) V-shaped | V-shaped | from | - | regulatory |
| Compression rings (replacement) single-row | single row | from | 10000 | 15000 |
| Compression Rings (Replacement) Opposite | Opposite | from | - | regulatory |
| Generator bracket (replacement) | from | 650 | 850 | |
| Cover valve (s / y) | from | 550 | 600 | |
| Oil pump (C / y) V-shaped | V-shaped | from | - | regulatory |
| Oil pump (s / y) single-row | single row | from | 1100 | 1400 |
| Outlet pump (s / y) Opposite | Opposite | from | - | regulatory |
| Oil + filter in the engine without flushing (replacement) | from | 400 | 400 | |
| Oil + filter in the engine with washing (replacement) | from | 450 | 450 | |
| Masbandry (replacement) | from | 1100 | 1300 | |
| Chain tensioner (replacement) | from | 1000 | regulatory | |
| Rear engine cushion (replacement) | from | 350 | 600 | |
| LEF engine cushion (replacement) | from | 400 | 700 | |
| Front engine pillow (replacement) | from | 350 | 700 | |
| Engine Pillow Right (Replacement) | from | 400 | 700 | |
| Block head gasket (replacement) V-shaped | V-shaped | from | - | regulatory |
| Block head gasket (replacement) single-row | single row | from | 3800 | regulatory |
| Block head gasket (replacement) Opposite | Opposite | from | - | regulatory |
| Laying valve cover (replacement) with chine sealant | 650 | 800 | ||
| Laying valve cover (replacement) | from | 550 | 600 | |
| Carter Pallet Laying (Replacement) | from | 1100 | 1500 | |
| Camper. Valve adjustment shaft (s / y) V-shaped | V-shaped | from | - | regulatory |
| Camper. Valve adjustment shaft (s / y) single-row | single row | from | 1100 | 3500 |
| Camper. Valve adjustment shaft (s / y) Opposite | Opposite | from | - | regulatory |
| Generator belt (replacement) | from | 350 | 650 | |
| Generator belt (adjustment) | from | 100 | 100 | |
| Timing belt (replacement) V-shaped | V-shaped | from | - | regulatory |
| Timing belt (replacement) single-row 16 valves | single row | from | 1500 | regulatory |
| Timing belt (replacement) single-row 8 valves | single row | from | 950 | regulatory |
| Timing belt (replacement) opposite | Opposite | from | - | regulatory |
| Air conditioner belt (replacement) | from | 350 | 650 | |
| Drive belt (replacement) | from | 550 | 650 | |
| Timing belt tensioner (replacement) single-row 16 valves | from | 1500 | regulatory | |
| Timing belt tensioner (replacement) single-row 8 valves | from | 750 | regulatory | |
| Roller drive belt (replacement) | from | 650 | 650 | |
| Rear crankshaft gland (replacement) with a box | from | 200 | 250 | |
| Rear Crankshaft Oil (Replacement) With Box Removal | from | 2100 | 3700 | |
| Front crankshaft gland (replacement) when removing timing 16 valves | from | 250 | 350 | |
| Front crankshaft gland (replacement) when removing timing 8 valves | from | 250 | 350 | |
| Front crankshaft oil seal (replacement) with removal of timing of 16 valves | from | 1700 | regulatory | |
| Front crankshaft gland (replacement) with removal of timing 8 valves | from | 850 | regulatory | |
| Seal camshaft (replacement) | from | 750 | regulatory | |
| Candles (replacement) kit 4 pcs | from | 350 | 400 | |
| Glow Candles (Replacement) | from | regulatory | regulatory | |
| Valve Saddle (Replacement) | from | 550 | regulatory | |
| Turbine (repair) | from | regulatory | regulatory | |
| Turbine (s / y) | from | regulatory | regulatory | |
| Soothing chain (replacement) | from | 1000 | regulatory | |
| Oil filter (replacement) | from | 150 | 150 | |
| Timing chain (replacement) V-shaped | V-shaped | from | - | regulatory |
| GRM chain (replacement) Single row | single row | from | 1500 | 4000 |
| Timing chain (replacement) Opposite | Opposite | from | - | regulatory |
* Pricing are familiarizing, valid on 06/10/2018 and are subject to change without notice. Not a public offer.