CHAPTER 2. CHEMICAL BOND AND MUTUAL INFLUENCE OF ATOMS IN ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
The chemical properties of organic compounds are determined by the type of chemical bonds, the nature of the bonded atoms, and their mutual influence in the molecule. These factors, in turn, are determined by the electronic structure of atoms and the interaction of their atomic orbitals.
2.1. The electronic structure of the carbon atom
The part of the atomic space in which the probability of finding an electron is maximum is called the atomic orbital (AO).
In chemistry, the concept of hybrid orbitals of the carbon atom and other elements is widely used. The concept of hybridization as a way of describing the rearrangement of orbitals is necessary when the number of unpaired electrons in the ground state of an atom is less than the number of bonds formed. An example is the carbon atom, which in all compounds manifests itself as a tetravalent element, but in accordance with the rules for filling orbitals on its outer electronic level, only two unpaired electrons are in the ground state 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 (Fig. 2.1, a and Appendix 2-1). In these cases, it is postulated that different atomic orbitals, close in energy, can mix with each other, forming hybrid orbitals of the same shape and energy.
Hybrid orbitals, due to the greater overlap, form stronger bonds compared to non-hybridized orbitals.
Depending on the number of hybridized orbitals, a carbon atom can be in one of three states
Rice. 2.1.The distribution of electrons in orbitals at the carbon atom in the ground (a), excited (b) and hybridized states (c - sp 3 , g-sp2, d- sp)
hybridization (see Fig. 2.1, c-e). The type of hybridization determines the orientation of hybrid AOs in space and, consequently, the geometry of molecules, i.e., their spatial structure.
The spatial structure of molecules is the mutual arrangement of atoms and atomic groups in space.
sp 3-Hybridization.When mixing four external AOs of an excited carbon atom (see Fig. 2.1, b) - one 2s- and three 2p-orbitals - four equivalent sp 3 -hybrid orbitals arise. They have the shape of a three-dimensional "eight", one of the blades of which is much larger than the other.
Each hybrid orbital is filled with one electron. The carbon atom in the state of sp 3 hybridization has the electronic configuration 1s 2 2(sp 3) 4 (see Fig. 2.1, c). Such a state of hybridization is characteristic of carbon atoms in saturated hydrocarbons (alkanes) and, accordingly, in alkyl radicals.
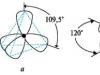
Due to mutual repulsion, sp 3 -hybrid AOs are directed in space to the vertices tetrahedron, and the angles between them are 109.5? (the most advantageous location; Fig. 2.2, a).
The spatial structure is depicted using stereochemical formulas. In these formulas, the sp 3 hybridized carbon atom and its two bonds are placed in the plane of the drawing and graphically denoted by a regular line. A bold line or a bold wedge denotes a connection that extends forward from the plane of the drawing and is directed towards the observer; a dotted line or a hatched wedge (..........) - a connection that goes away from the observer beyond the plane of the drawing

Rice. 2.2.Types of hybridization of the carbon atom. The dot in the center is the nucleus of the atom (small fractions of hybrid orbitals are omitted to simplify the figure; unhybridized p-AOs are shown in color)
zha (Fig. 2.3, a). The carbon atom is in the state sp 3-hybridization has a tetrahedral configuration.
sp 2-Hybridization.When mixing one 2s- and two 2p-AO of the excited carbon atom, three equivalent sp 2-hybrid orbitals and remains unhybridized 2p-AO. The carbon atom is in the state sp 2-hybridization has an electronic configuration 1s 2 2(sp 2) 3 2p 1 (see Fig. 2.1, d). This state of hybridization of the carbon atom is typical for unsaturated hydrocarbons (alkenes), as well as for some functional groups, such as carbonyl and carboxyl.
sp 2 - Hybrid orbitals are located in the same plane at an angle of 120?, and the non-hybridized AO is in a perpendicular plane (see Fig. 2.2, b). The carbon atom is in the state sp 2-hybridization has triangular configuration. The carbon atoms bound by a double bond are in the plane of the drawing, and their single bonds directed towards and away from the observer are designated as described above (see Fig. 2.3, b).
sp hybridization.When one 2s and one 2p orbitals of an excited carbon atom are mixed, two equivalent sp hybrid AOs are formed, while two p AOs remain unhybridized. The carbon atom in the sp hybridization state has the electronic configuration

Rice. 2.3.Stereochemical formulas of methane (a), ethane (b) and acetylene (c)
1s 2 2(sp 2) 2 2p 2 (see Fig. 2.1e). This state of hybridization of the carbon atom occurs in compounds having a triple bond, for example, in alkynes, nitriles.
sp-hybrid orbitals are located at an angle of 180?, and two unhybridized AOs are in mutually perpendicular planes (see Fig. 2.2, c). The carbon atom in the sp hybridization state has line configuration, for example, in an acetylene molecule, all four atoms are on the same straight line (see Fig. 2.3, v).
Atoms of other organogen elements can also be in a hybridized state.
2.2. Chemical bonds of carbon atom
Chemical bonds in organic compounds are mainly represented by covalent bonds.
A covalent bond is a chemical bond formed as a result of the socialization of the electrons of the bonded atoms.
These shared electrons occupy molecular orbitals (MOs). As a rule, MO is a multicenter orbital and the electrons filling it are delocalized (dispersed). Thus, MO, like AO, can be vacant, filled with one electron or two electrons with opposite spins*.
2.2.1. σ- andπ -Communications
There are two types of covalent bonds: σ (sigma)- and π (pi)-bonds.
A σ-bond is a covalent bond formed when an AO overlaps along a straight line (axis) connecting the nuclei of two bonded atoms with the overlap maximum on this straight line.
The σ-bond arises when any AO overlaps, including hybrid ones. Figure 2.4 shows the formation of a σ-bond between carbon atoms as a result of the axial overlap of their hybrid sp 3 -AO and C-H σ-bonds by overlapping the hybrid sp 3 -AO of carbon and the s-AO of hydrogen.
* For more details see: Popkov V.A., Puzakov S.A. General chemistry. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2007. - Chapter 1.

Rice. 2.4.Formation of σ-bonds in ethane by axial overlapping of AO (small fractions of hybrid orbitals are omitted, color shows sp 3 -AO carbon, black - s-AO hydrogen)
In addition to the axial overlap, another type of overlap is possible - the lateral overlap of the p-AO, leading to the formation of a π bond (Fig. 2.5).
p-atomic orbitals

Rice. 2.5.π-bond formation in ethylene by lateral overlap r-AO
A π-bond is a bond formed by lateral overlap of unhybridized p-AOs with a maximum of overlap on both sides of the straight line connecting the nuclei of atoms.
Multiple bonds found in organic compounds are a combination of σ- and π-bonds: double - one σ- and one π-, triple - one σ- and two π-bonds.
The properties of a covalent bond are expressed in terms of characteristics such as energy, length, polarity, and polarizability.
Bond energyis the energy released during the formation of a bond or required to separate two bonded atoms. It serves as a measure of bond strength: the greater the energy, the stronger the bond (Table 2.1).
Link lengthis the distance between the centers of bonded atoms. A double bond is shorter than a single bond, and a triple bond is shorter than a double bond (see Table 2.1). The bonds between carbon atoms in different states of hybridization have a common pattern -
Table 2.1.Main characteristics of covalent bonds

with an increase in the fraction of the s-orbital in the hybrid orbital, the bond length decreases. For example, in a series of compounds, propane CH 3 CH 2 CH 3, propene CH 3 CH=CH 2, propyne CH 3 C=CH CH 3 bond length -C, respectively, is equal to 0.154; 0.150 and 0.146 nm.
Communication polarity due to the uneven distribution (polarization) of the electron density. The polarity of a molecule is quantified by the value of its dipole moment. From the dipole moments of a molecule, the dipole moments of individual bonds can be calculated (see Table 2.1). The larger the dipole moment, the more polar the bond. The reason for the polarity of the bond is the difference in the electronegativity of the bonded atoms.
Electronegativity characterizes the ability of an atom in a molecule to hold valence electrons. With an increase in the electronegativity of an atom, the degree of displacement of the bond electrons in its direction increases.
Based on the values of the bond energy, the American chemist L. Pauling (1901-1994) proposed a quantitative characteristic of the relative electronegativity of atoms (Pauling's scale). In this scale (row), typical organogenic elements are arranged according to relative electronegativity (two metals are given for comparison) as follows:
Electronegativity is not an absolute constant of an element. It depends on the effective charge of the nucleus, the type of AO hybridization, and the effect of substituents. For example, the electronegativity of a carbon atom in the state of sp 2 - or sp-hybridization is higher than in the state of sp 3 -hybridization, which is associated with an increase in the proportion of the s-orbital in the hybrid orbital. During the transition of atoms from sp 3 - to sp 2 - and further to sp-hybridized state, the length of the hybrid orbital gradually decreases (especially in the direction that provides the greatest overlap during the formation of the σ-bond), which means that in the same sequence, the electron density maximum is located closer to the nucleus of the corresponding atom.
In the case of a non-polar or practically non-polar covalent bond, the difference in the electronegativity of the bonded atoms is zero or close to zero. As the difference in electronegativity increases, the polarity of the bond increases. With a difference of up to 0.4, they speak of a weakly polar, more than 0.5 - of a strongly polar covalent bond, and more than 2.0 - of an ionic bond. Polar covalent bonds are prone to heterolytic cleavage
(see 3.1.1).
Communication polarizability is expressed in the displacement of bond electrons under the influence of an external electric field, including another reacting particle. Polarizability is determined by the electron mobility. Electrons are more mobile the farther they are from the nuclei of atoms. In terms of polarizability, the π-bond significantly exceeds the σ-bond, since the maximum electron density of the π-bond is located farther from the bonded nuclei. Polarizability largely determines the reactivity of molecules with respect to polar reagents.
2.2.2. Donor-acceptor bonds
The overlap of two one-electron AOs is not the only way to form a covalent bond. A covalent bond can be formed by the interaction of a two-electron orbital of one atom (donor) with a vacant orbital of another atom (acceptor). Donors are compounds containing either orbitals with a lone pair of electrons or π-MO. Carriers of lone pairs of electrons (n-electrons, from the English. non-bonding) are nitrogen, oxygen, halogen atoms.
Lone pairs of electrons play an important role in the manifestation of the chemical properties of compounds. In particular, they are responsible for the ability of compounds to enter into a donor-acceptor interaction.
A covalent bond formed by a pair of electrons from one of the bond partners is called a donor-acceptor bond.

The formed donor-acceptor bond differs only in the way of formation; its properties are the same as other covalent bonds. The donor atom acquires a positive charge.
Donor-acceptor bonds are characteristic of complex compounds.
2.2.3. Hydrogen bonds
A hydrogen atom bonded to a strongly electronegative element (nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, etc.) is able to interact with the lone pair of electrons of another sufficiently electronegative atom of the same or another molecule. As a result, a hydrogen bond arises, which is a kind of donor-
acceptor bond. Graphically, a hydrogen bond is usually represented by three dots.
The hydrogen bond energy is low (10-40 kJ/mol) and is mainly determined by the electrostatic interaction.
Intermolecular hydrogen bonds cause the association of organic compounds, such as alcohols.

Hydrogen bonds affect the physical (boiling and melting points, viscosity, spectral characteristics) and chemical (acid-base) properties of compounds. For example, the boiling point of ethanol C 2H5 OH (78.3 ? C) is significantly higher than that of dimethyl ether CH 3 OCH 3 (-24 ? C) of the same molecular weight, which is not associated due to hydrogen bonds.
Hydrogen bonds can also be intramolecular. Such a bond in the anion of salicylic acid leads to an increase in its acidity.
Hydrogen bonds play an important role in the formation of the spatial structure of macromolecular compounds - proteins, polysaccharides, nucleic acids.
2.3. Related systems
A covalent bond can be localized or delocalized. A bond is called localized, the electrons of which are actually divided between the two nuclei of the bonded atoms. If the bond electrons are shared by more than two nuclei, then one speaks of a delocalized bond.
A delocalized bond is a covalent bond whose molecular orbital spans more than two atoms.
Delocalized bonds in most cases are π-bonds. They are characteristic of coupled systems. In these systems, a special kind of mutual influence of atoms occurs - conjugation.
Conjugation (mesomeria, from the Greek. mesos- medium) is the alignment of bonds and charges in a real molecule (particle) in comparison with an ideal, but non-existent structure.
The delocalized p-orbitals participating in conjugation can belong either to two or more π-bonds, or to a π-bond and one atom with a p-orbital. In accordance with this, a distinction is made between π,π-conjugation and ρ,π-conjugation. The conjugation system can be open or closed and contain not only carbon atoms, but also heteroatoms.
2.3.1. Open circuit systems
π,π -Pairing. The simplest representative of π, π-conjugated systems with a carbon chain is butadiene-1,3 (Fig. 2.6, a). Carbon and hydrogen atoms and, consequently, all σ-bonds in its molecule lie in the same plane, forming a flat σ-skeleton. Carbon atoms are in a state of sp 2 hybridization. Unhybridized p-AOs of each carbon atom are located perpendicular to the plane of the σ-skeleton and parallel to each other, which is a necessary condition for their overlap. Overlapping occurs not only between the p-AO of the C-1 and C-2, C-3 and C-4 atoms, but also between the p-AO of the C-2 and C-3 atoms, resulting in the formation of a single π spanning four carbon atoms -system, i.e., a delocalized covalent bond arises (see Fig. 2.6, b).

Rice. 2.6.Atomic orbital model of the 1,3-butadiene molecule
This is reflected in the change in bond lengths in the molecule. The bond length C-1-C-2, as well as C-3-C-4 in butadiene-1,3 is somewhat increased, and the distance between C-2 and C-3 is shortened compared to conventional double and single bonds. In other words, the process of electron delocalization leads to the alignment of bond lengths.
Hydrocarbons with a large number of conjugated double bonds are common in the plant kingdom. These include, for example, carotenes, which determine the color of carrots, tomatoes, etc.
An open conjugation system can also include heteroatoms. An example of open π,π-conjugated systems with a heteroatom in the chainα,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds can serve. For example, the aldehyde group in acrolein CH 2 =CH-CH=O is a member of the chain of conjugation of three sp 2 -hybridized carbon atoms and an oxygen atom. Each of these atoms contributes one p-electron to the single π-system.
pn-pairing.This type of conjugation is most often manifested in compounds containing the structural fragment -CH=CH-X, where X is a heteroatom having an unshared pair of electrons (primarily O or N). These include, for example, vinyl ethers, in the molecules of which the double bond is conjugated with R the orbital of an oxygen atom. A delocalized three-center bond is formed by overlapping two p-AO sp 2 -hybridized carbon atoms and one R-AO of a heteroatom with a pair of n-electrons.

The formation of a similar delocalized three-center bond exists in the carboxyl group. Here, the π-electrons of the C=O bond and the n-electrons of the oxygen atom of the OH group participate in conjugation. Conjugated systems with fully aligned bonds and charges include negatively charged particles, such as the acetate ion.

The direction of electron density shift is indicated by a curved arrow.
There are other graphical ways to display pairing results. Thus, the structure of the acetate ion (I) assumes that the charge is evenly distributed over both oxygen atoms (as shown in Fig. 2.7, which is true).
Structures (II) and (III) are used in resonance theory. According to this theory, a real molecule or particle is described by a set of certain so-called resonance structures, which differ from each other only in the distribution of electrons. In conjugated systems, the main contribution to the resonant hybrid is made by structures with different π-electron density distributions (the two-sided arrow connecting these structures is a special symbol of resonance theory).
Limit (boundary) structures do not really exist. However, they "contribute" to some extent to the real distribution of electron density in a molecule (particle), which is represented as a resonant hybrid obtained by superimposition (superposition) of limiting structures.
In ρ,π-conjugated systems with a carbon chain, conjugation can occur if there is a carbon atom with an unhybridized p-orbital next to the π-bond. Such systems can be intermediate particles - carbanions, carbocations, free radicals, for example, allyl structures. Free radical allyl fragments play an important role in the processes of lipid peroxidation.
In the allyl anion CH 2 \u003d CH-CH 2 sp 2 -hybridized carbon atom C-3 delivers to the common conjugated

Rice. 2.7.Electron density map of the COONa group in penicillin
two electron system, in the allyl radical CH 2=CH-CH 2+ - one, and in the allyl carbocation CH 2=CH-CH 2+ does not supply any. As a result, when the p-AO overlaps three sp 2 -hybridized carbon atoms, a delocalized three-center bond is formed, containing four (in the carbanion), three (in the free radical), and two (in the carbocation) electrons, respectively.

Formally, the C-3 atom in the allyl cation carries a positive charge, in the allyl radical it has an unpaired electron, and in the allyl anion it has a negative charge. In fact, in such conjugated systems, there is a delocalization (dispersal) of the electron density, which leads to the alignment of bonds and charges. The C-1 and C-3 atoms are equivalent in these systems. For example, in an allyl cation, each of them carries a positive charge+1/2 and is connected by a "one and a half" bond with the C-2 atom.
Thus, conjugation leads to a significant difference in the electron density distribution in real structures compared to structures represented by conventional structure formulas.
2.3.2. Closed loop systems
Cyclic conjugated systems are of great interest as a group of compounds with increased thermodynamic stability compared to conjugated open systems. These compounds also have other special properties, the totality of which is united by the general concept aromaticity. These include the ability of such formally unsaturated compounds
enter into substitution reactions, not addition, resistance to oxidizing agents and temperature.
Typical representatives of aromatic systems are arenes and their derivatives. Features of the electronic structure of aromatic hydrocarbons are clearly manifested in the atomic orbital model of the benzene molecule. The benzene framework is formed by six sp 2 hybridized carbon atoms. All σ-bonds (C-C and C-H) lie in the same plane. Six unhybridized p-AOs are located perpendicular to the plane of the molecule and parallel to each other (Fig. 2.8, a). Each R-AO can equally overlap with two neighboring R-AO. As a result of this overlap, a single delocalized π-system arises, in which the highest electron density is located above and below the σ-skeleton plane and covers all carbon atoms of the cycle (see Fig. 2.8, b). The π-electron density is evenly distributed throughout the cyclic system, which is indicated by a circle or a dotted line inside the cycle (see Fig. 2.8, c). All bonds between carbon atoms in the benzene ring have the same length (0.139 nm), intermediate between the lengths of single and double bonds.
Based on quantum mechanical calculations, it was established that for the formation of such stable molecules, a planar cyclic system must contain (4n + 2) π-electrons, where n= 1, 2, 3, etc. (Hückel's rule, 1931). Taking into account these data, it is possible to concretize the concept of "aromaticity".
A compound is aromatic if it has a planar ring and a conjugatedπ -electronic system covering all atoms of the cycle and containing(4n+ 2) π-electrons.
Hückel's rule applies to any planar condensed systems in which there are no atoms that are common to more than

Rice. 2.8.Atomic orbital model of the benzene molecule (hydrogen atoms omitted; see text for explanation)
two cycles. Compounds with condensed benzene rings, such as naphthalene and others, meet the criteria for aromaticity.

Stability of coupled systems. The formation of a conjugated and especially aromatic system is an energetically favorable process, since the degree of overlapping of the orbitals increases and delocalization (dispersal) occurs. R-electrons. In this regard, conjugated and aromatic systems have increased thermodynamic stability. They contain a smaller amount of internal energy and in the ground state occupy a lower energy level compared to non-conjugated systems. The difference between these levels can be used to quantify the thermodynamic stability of the conjugated compound, i.e., its conjugation energy(delocalization energy). For butadiene-1,3, it is small and amounts to about 15 kJ/mol. With an increase in the length of the conjugated chain, the conjugation energy and, accordingly, the thermodynamic stability of the compounds increase. The conjugation energy for benzene is much higher and amounts to 150 kJ/mol.
2.4. Electronic effects of substituents 2.4.1. Inductive effect
A polar σ-bond in a molecule causes polarization of the nearest σ-bonds and leads to the appearance of partial charges on neighboring atoms*.
Substituents cause polarization not only of their own, but also of neighboring σ-bonds. This type of transmission of the influence of atoms is called the inductive effect (/-effect).
Inductive effect - the transfer of the electronic influence of substituents as a result of the displacement of electrons of σ-bonds.
Due to the weak polarizability of the σ-bond, the inductive effect is attenuated after three or four bonds in the circuit. Its action is most pronounced in relation to the carbon atom adjacent to the one that has a substituent. The direction of the inductive effect of the substituent is qualitatively estimated by comparing it with the hydrogen atom, the inductive effect of which is taken as zero. Graphically, the result of the /-effect is depicted by an arrow coinciding with the position of the valence line and pointing towards the more electronegative atom.
/v\stronger than a hydrogen atom, exhibitsnegativeinductive effect (-/-effect).
Such substituents generally lower the electron density of the system, they are called electron-withdrawing. These include most of the functional groups: OH, NH 2, COOH, NO2 and cationic groups, such as -NH 3+.
A substituent that shifts the electron density compared to the hydrogen atomσ -bonds towards the carbon atom of the chain, exhibitspositiveinductive effect (+/- effect).
Such substituents increase the electron density in the chain (or ring) and are called electron donor. These include alkyl groups located at the sp 2 -hybridized carbon atom, and anionic centers in charged particles, for example -O - .
2.4.2. mesomeric effect
In conjugated systems, the main role in the transfer of electronic influence is played by π-electrons of delocalized covalent bonds. The effect that manifests itself in a shift in the electron density of a delocalized (conjugated) π-system is called the mesomeric (M-effect), or conjugation effect.
Mesomeric effect - the transfer of the electronic influence of substituents along the conjugated system.
In this case, the substitute is itself a member of the conjugated system. It can introduce into the conjugation system either a π-bond (carbonyl, carboxyl groups, etc.), or an unshared pair of electrons of a heteroatom (amino and hydroxy groups), or a vacant or one-electron-filled p-AO.
A substituent that increases the electron density in a conjugated system exhibitspositivemesomeric effect (+M- effect).
Substituents that include atoms with a lone pair of electrons (for example, an amino group in an aniline molecule) or a whole negative charge have an M-Effect. These substitutes are capable
to the transfer of a pair of electrons to a common conjugated system, that is, they are electron donor.
A substituent that lowers the electron density in a conjugated system exhibitsnegativemesomeric effect (-M- effect).
The M-effect in the conjugated system is possessed by oxygen or nitrogen atoms bound by a double bond to a carbon atom, as shown in the example of acrylic acid and benzaldehyde. Such groupings are electron-withdrawing.


The displacement of the electron density is indicated by a curved arrow, the beginning of which shows which p- or π-electrons are being displaced, and the end is the bond or atom to which they are displaced. The mesomeric effect, in contrast to the inductive effect, is transmitted over a system of conjugated bonds over a much greater distance.
When evaluating the influence of substituents on the distribution of electron density in a molecule, it is necessary to take into account the resulting action of the inductive and mesomeric effects (Table 2.2).
Table 2.2.Electronic effects of some substituents

The electronic effects of substituents make it possible to give a qualitative estimate of the electron density distribution in a nonreacting molecule and to predict its properties.
In the ground state, the carbon atom C (1s 2 2s 2 2p 2) has two unpaired electrons, due to which only two common electron pairs can be formed. However, in most of its compounds, carbon is tetravalent. This is due to the fact that the carbon atom, absorbing a small amount of energy, goes into an excited state in which it has 4 unpaired electrons, i.e. able to form four covalent bonds and take part in the formation of four common electron pairs:
6 C 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 6 C * 1s 2 2s 1 2p 3 .
| ↓ | ||||||||||||
| 1 | ↓ | p | ↓ | p | ||||||||
| s | s | |||||||||||
The excitation energy is compensated by the formation of chemical bonds, which occurs with the release of energy.
Carbon atoms have the ability to form three types of hybridization of electron orbitals ( sp 3, sp 2, sp) and the formation of multiple (double and triple) bonds between themselves (Table 2.2).
Table 2.2
Types of hybridization and geometry of molecules
A simple (single) s-bond occurs when sp 3-hybridization, in which all four hybrid orbitals are equivalent and have a spatial orientation at an angle of 109 ° 29 ’ to each other and are oriented towards the vertices of a regular tetrahedron (Fig. 2.8).

Rice. 2.8. The formation of a methane CH 4 molecule
If hybrid orbitals of carbon overlap with spherical s-orbitals of the hydrogen atom, then the simplest organic compound methane CH 4 is formed - a saturated hydrocarbon.
Of great interest is the study of the bonds of carbon atoms with each other and with atoms of other elements. Consider the structure of the molecules of ethane, ethylene and acetylene.
The angles between all bonds in the ethane molecule are almost exactly equal to each other (Fig. 2.9) and do not differ from the C - H angles in the methane molecule.
Therefore, the carbon atoms are in the state sp 3-hybridization.

Rice. 2.9. Ethane molecule C 2 H 6
Hybridization of electron orbitals of carbon atoms can be incomplete, i.e. it can involve two sp 2-hybridization) or one ( sp-hybridization) of three R-orbitals. In this case, between the carbon atoms are formed multiple bonds (double or triple). Hydrocarbons with multiple bonds are called unsaturated or unsaturated. A double bond (C=C) is formed when sp 2-hybridization.
In this case, each of the carbon atoms has one of three R-orbitals are not involved in hybridization, resulting in the formation of three sp 2- hybrid orbitals located in the same plane at an angle of 120 ° to each other, and non-hybrid 2 R-orbital is perpendicular to this plane. Two carbon atoms are connected to each other, forming one s-bond due to the overlap of hybrid orbitals and one p-bond due to overlap R-orbitals.
Interaction of free hybrid orbitals of carbon with 1 s-orbitals of hydrogen atoms leads to the formation of an ethylene molecule C 2 H 4 (Fig. 2.10) - the simplest representative of unsaturated hydrocarbons.

Rice. 2.10. The formation of an ethylene molecule C 2 H 4
The overlap of electron orbitals in the case of a p-bond is less and the zones with increased electron density lie farther from the nuclei of atoms, so this bond is less strong than the s-bond.
A triple bond is formed by one s-bond and two p-bonds. In this case, the electron orbitals are in a state of sp-hybridization, the formation of which occurs due to one s- and one R-orbitals (Fig. 2.11).
The two hybrid orbitals are located at an angle of 180° relative to each other, and the remaining two non-hybrid R-orbitals are located in two mutually perpendicular planes. The formation of a triple bond takes place in the C 2 H 2 acetylene molecule (see Fig. 2.11).

Rice. 2.11. The formation of an acetylene molecule C 2 H 2
A special type of bond arises during the formation of a benzene molecule (C 6 H 6) - the simplest representative of aromatic hydrocarbons.
Benzene contains six carbon atoms linked together in a cycle (benzene ring), while each carbon atom is in a state of sp 2 hybridization (Fig. 2.12).

Rice. 2.12. sp 2 - orbitals of the benzene molecule C 6 H 6
All carbon atoms included in the benzene molecule are located in the same plane. Each carbon atom in the sp 2 hybridization state has another non-hybrid p-orbital with an unpaired electron, which forms a p-bond (Fig. 2.13).
Axis like this R-orbital is located perpendicular to the plane of the benzene molecule.
All six non-hybrid R-orbitals form a common bonding molecular p-orbital, and all six electrons are combined into a p-electron sextet.
The boundary surface of such an orbital is located above and below the carbon s-skeleton plane. As a result of circular overlap, a single delocalized p-system arises, covering all carbon atoms of the cycle (Fig. 2.13).
Benzene is schematically depicted as a hexagon with a ring inside, which indicates that there is a delocalization of electrons and the corresponding bonds.

Rice. 2.13. -bonds in the benzene molecule C 6 H 6
Ionic chemical bond
Ionic bond- a chemical bond formed as a result of mutual electrostatic attraction of oppositely charged ions, in which a stable state is achieved by a complete transition of the total electron density to an atom of a more electronegative element.
A purely ionic bond is the limiting case of a covalent bond.
In practice, a complete transition of electrons from one atom to another atom through a bond is not realized, since each element has a greater or lesser (but not zero) EO, and any chemical bond will be covalent to some extent.
Such a bond arises in the case of a large difference in the ER of atoms, for example, between cations s-metals of the first and second groups of the periodic system and anions of non-metals of groups VIA and VIIA (LiF, NaCl, CsF, etc.).
Unlike a covalent bond, ionic bond has no direction . This is explained by the fact that the electric field of the ion has spherical symmetry, i.e. decreases with distance according to the same law in any direction. Therefore, the interaction between ions is independent of direction.
The interaction of two ions of opposite sign cannot lead to complete mutual compensation of their force fields. Because of this, they retain the ability to attract ions of the opposite sign in other directions. Therefore, unlike a covalent bond, ionic bond is also characterized by unsaturability .
The lack of orientation and saturation of the ionic bond causes the tendency of ionic molecules to associate. All ionic compounds in the solid state have an ionic crystal lattice in which each ion is surrounded by several ions of the opposite sign. In this case, all bonds of a given ion with neighboring ions are equivalent.
metal connection
Metals are characterized by a number of special properties: electrical and thermal conductivity, characteristic metallic luster, malleability, high ductility, and high strength. These specific properties of metals can be explained by a special type of chemical bond called metallic .
A metallic bond is the result of overlapping delocalized orbitals of atoms approaching each other in the crystal lattice of a metal.
Most metals have a significant number of vacant orbitals and a small number of electrons at the outer electronic level.
Therefore, it is energetically more favorable that the electrons are not localized, but belong to the entire metal atom. At the lattice sites of a metal, there are positively charged ions that are immersed in an electron "gas" distributed throughout the metal:
Me ↔ Me n + + n .
Between positively charged metal ions (Me n +) and non-localized electrons (n) there is an electrostatic interaction that ensures the stability of the substance. The energy of this interaction is intermediate between the energies of covalent and molecular crystals. Therefore, elements with a purely metallic bond ( s-, and p-elements) are characterized by relatively high melting points and hardness.
The presence of electrons, which can freely move around the volume of the crystal, and provide specific properties of the metal
hydrogen bond
hydrogen bond – a special type of intermolecular interaction. Hydrogen atoms that are covalently bonded to an atom of an element that has a high electronegativity value (most commonly F, O, N, but also Cl, S, and C) carry a relatively high effective charge. As a result, such hydrogen atoms can electrostatically interact with the atoms of these elements.
So, the H d + atom of one water molecule is oriented and accordingly interacts (as shown by three points) with the O d atom - another water molecule:

The bonds formed by an H atom located between two atoms of electronegative elements are called hydrogen bonds:
d- d+ d-
A − H × × × B
The energy of a hydrogen bond is much less than the energy of an ordinary covalent bond (150–400 kJ / mol), but this energy is sufficient to cause the aggregation of molecules of the corresponding compounds in a liquid state, for example, in liquid hydrogen fluoride HF (Fig. 2.14). For fluorine compounds, it reaches about 40 kJ/mol.

Rice. 2.14. Aggregation of HF molecules due to hydrogen bonds
The length of the hydrogen bond is also less than the length of the covalent bond. So, in the polymer (HF) n, the F−H bond length is 0.092 nm, and the F∙∙∙H bond is 0.14 nm. For water, the O−H bond length is 0.096 nm, and the O∙∙∙H bond length is 0.177 nm.
The formation of intermolecular hydrogen bonds leads to a significant change in the properties of substances: an increase in viscosity, dielectric constant, boiling and melting points.
Similar information.
Most organic compounds have a molecular structure. Atoms in substances with a molecular type of structure always form only covalent bonds with each other, which is also observed in the case of organic compounds. Recall that a covalent bond is such a type of bond between atoms, which is realized due to the fact that atoms socialize part of their outer electrons in order to acquire the electronic configuration of a noble gas.
According to the number of socialized electron pairs, covalent bonds in organic substances can be divided into single, double and triple. These types of connections are indicated in the graphic formula, respectively, by one, two or three lines:
The multiplicity of the bond leads to a decrease in its length, so a single C-C bond has a length of 0.154 nm, a double C=C bond - 0.134 nm, a triple C≡C bond - 0.120 nm.
Types of bonds according to the way the orbitals overlap
As is known, orbitals can have different shapes, for example, s-orbitals are spherical, and p-dumbbell-shaped. For this reason, bonds can also differ in the way electron orbitals overlap:
ϭ-bonds - are formed when the orbitals overlap in such a way that the region of their overlap is intersected by a line connecting the nuclei. Examples of ϭ-bonds:
π-bonds - are formed when the orbitals overlap, in two areas - above and below the line connecting the nuclei of atoms. Examples of π bonds:
How to know when there are π- and ϭ-bonds in a molecule?
With a covalent type of bond, there is always a ϭ-bond between any two atoms, and it has a π-bond only in the case of multiple (double, triple) bonds. Wherein:
- Single bond - always a ϭ-bond
- A double bond always consists of one ϭ- and one π-bond
- A triple bond is always formed by one ϭ and two π bonds.
Let us indicate these types of bonds in the propinoic acid molecule:
Hybridization of carbon atom orbitals
Orbital hybridization is a process in which orbitals that originally have different shapes and energies are mixed, forming in return the same number of hybrid orbitals, equal in shape and energy.
For example, when mixing one s- and three p- four orbitals are formed sp 3-hybrid orbitals:

In the case of carbon atoms, hybridization always takes part s- orbital, and the number p-orbitals that can take part in hybridization varies from one to three p- orbitals.
How to determine the type of hybridization of a carbon atom in an organic molecule?
Depending on how many other atoms a carbon atom is bonded to, it is either in the state sp 3, or in the state sp 2, or in the state sp- hybridization:
Let's practice determining the type of hybridization of carbon atoms using the example of the following organic molecule:
The first carbon atom is bonded to two other atoms (1H and 1C), so it is in the state sp-hybridization.
- The second carbon atom is bonded to two atoms - sp-hybridization
- The third carbon atom is bonded to four other atoms (two C and two H) - sp 3-hybridization
- The fourth carbon atom is bonded to three other atoms (2O and 1C) - sp 2-hybridization.
Radical. Functional group
The term "radical" most often means a hydrocarbon radical, which is the remainder of a molecule of any hydrocarbon without one hydrogen atom.
The name of the hydrocarbon radical is formed based on the name of the corresponding hydrocarbon by replacing the suffix –en to suffix –silt .
Functional group - a structural fragment of an organic molecule (a certain group of atoms), which is responsible for its specific chemical properties.
Depending on which of the functional groups in the molecule of the substance is the eldest, the compound is assigned to one or another class.

R is the designation of a hydrocarbon substituent (radical).
Radicals can contain multiple bonds, which can also be considered as functional groups, since multiple bonds contribute to the chemical properties of the substance.
If an organic molecule contains two or more functional groups, such compounds are called polyfunctional.
Variety of inorganic and organic substances
Organic chemistry is chemistry carbon compounds. Inorganic carbon compounds include: carbon oxides, carbonic acid, carbonates and bicarbonates, carbides. Organic matter other than carbon contain hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur and other elements. Carbon atoms can form long unbranched and branched chains, rings, attach other elements, so the number of organic compounds has approached 20 million, while there are a little more than 100 thousand inorganic substances.
The basis for the development of organic chemistry is the theory of the structure of organic compounds by A. M. Butlerov. An important role in describing the structure of organic compounds belongs to the concept of valency, which characterizes the ability of atoms to form chemical bonds and determines their number. Carbon in organic compounds always tetravalent. The main postulate of the theory of A. M. Butlerov is the position on the chemical structure of matter, that is, the chemical bond. This order is displayed using structural formulas. Butlerov's theory states the idea that every substance has certain chemical structure and the properties of substances depend on the structure.

Theory of the chemical structure of organic compounds A. M. Butlerova
Just as for inorganic chemistry the basis of development is the Periodic law and the Periodic system of chemical elements of D. I. Mendeleev, for organic chemistry it has become fundamental.
 Theory of the chemical structure of organic compounds A. M. Butlerova
Theory of the chemical structure of organic compounds A. M. Butlerova The main postulate of Butlerov's theory is the position on the chemical structure of a substance, which is understood as the order, the sequence of the mutual combination of atoms into molecules, i.e. chemical bond.
Chemical structure- the order of connection of atoms of chemical elements in a molecule according to their valency.
This order can be displayed using structural formulas, in which the valences of atoms are indicated by dashes: one dash corresponds to the unit of valence of an atom of a chemical element. For example, for the organic substance methane, which has the molecular formula CH 4, the structural formula looks like this:

The main provisions of the theory of A. M. Butlerov:
The atoms in the molecules of organic substances are connected to each other according to their valency. Carbon in organic compounds is always tetravalent, and its atoms are able to combine with each other, forming various chains.
The properties of substances are determined not only by their qualitative and quantitative composition, but also by the order of connection of atoms in a molecule, i.e. the chemical structure of matter.
The properties of organic compounds depend not only on the composition of the substance and the order of connection of atoms in its molecule, but also on mutual influence of atoms and groups of atoms to each other.
The theory of the structure of organic compounds is a dynamic and developing doctrine. With the development of knowledge about the nature of the chemical bond, about the influence of the electronic structure of the molecules of organic substances, they began to use, in addition to empirical and structural, electronic formulas. These formulas show the direction shifts of electron pairs in a molecule.
Quantum chemistry and chemistry of the structure of organic compounds confirmed the theory of the spatial direction of chemical bonds (cis- and trans isomerism), studied the energy characteristics of mutual transitions in isomers, made it possible to judge the mutual influence of atoms in the molecules of various substances, created the prerequisites for predicting the types of isomerism and directions and mechanisms of chemical reactions.
Organic substances have a number of features.
The composition of all organic substances includes carbon and hydrogen, therefore, when burned, they form carbon dioxide and water.
・Organic matter built complex and can have a huge molecular weight (proteins, fats, carbohydrates).
Organic substances can be arranged in rows similar in composition, structure and properties homologues.
For organic substances, it is characteristic isomerism.
Isomerism and homology of organic substances
The properties of organic substances depend not only on their composition, but also on order of connection of atoms in a molecule.

isomerism- this is the phenomenon of the existence of different substances - isomers with the same qualitative and quantitative composition, i.e. with the same molecular formula.
There are two types of isomerism: structural and spatial(stereoisomerism). Structural isomers differ from each other in the order of bonding of atoms in a molecule; stereoisomers - the arrangement of atoms in space with the same order of bonds between them.
The main types of isomerism:
Structural isomerism - substances differ in the order of bonding of atoms in molecules:
1) isomerism of the carbon skeleton;
2) position isomerism:
- multiple bonds;
- deputies;
- functional groups;
3) isomerism of homological series (interclass).
· Spatial isomerism - molecules of substances differ not in the order of connection of atoms, but in their position in space: cis-, trans-isomerism (geometric).


Classification of organic substances
It is known that the properties of organic substances are determined by their composition and chemical structure. Therefore, it is not surprising that the classification of organic compounds is based on the theory of structure - the theory of A. M. Butlerov. Classify organic substances by the presence and order of connection of atoms in their molecules. The most durable and least changeable part of an organic substance molecule is its skeleton - a chain of carbon atoms. Depending on the order of connection of carbon atoms in this chain, substances are divided into acyclic, not containing closed chains of carbon atoms in molecules, and carbocyclic containing such chains (cycles) in molecules.
In addition to carbon and hydrogen atoms, molecules of organic substances may contain atoms of other chemical elements. Substances in the molecules of which these so-called heteroatoms are included in a closed chain are classified as heterocyclic compounds.
heteroatoms(oxygen, nitrogen, etc.) can be part of molecules and acyclic compounds, forming functional groups in them, for example,
hydroxyl
carbonyl
 ,
,
carboxyl
 ,
,
amino group
 .
.
Functional group- a group of atoms that determines the most characteristic chemical properties of a substance and its belonging to a certain class of compounds.
Nomenclature of organic compounds
At the beginning of the development of organic chemistry, discovered compounds were assigned trivial names, often associated with the history of their production: acetic acid (which is the basis of wine vinegar), butyric acid (formed in butter), glycol (i.e. "sweet"), etc. As the number of new discovered substances increased, the need arose associate names with their structure. This is how rational names appeared: methylamine, diethylamine, ethyl alcohol, methyl ethyl ketone, which are based on the name of the simplest compound. For more complex compounds, rational nomenclature is unsuitable.

The theory of structure of A. M. Butlerov provided the basis for the classification and nomenclature of organic compounds according to structural elements and the arrangement of carbon atoms in a molecule. Currently, the most used is the nomenclature developed by International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), which is called the nomenclature IUPAC. IUPAC rules recommend several principles for the formation of names, one of them is the principle of substitution. Based on this, a replacement nomenclature has been developed, which is the most universal. Here are a few basic rules of substitution nomenclature and consider their application using the example of a heterofunctional compound containing two functional groups - the amino acid leucine:

1. The name of the compounds is based on the parent structure (the main chain of an acyclic molecule, a carbocyclic or heterocyclic system). The name of the ancestral structure is the basis of the name, the root of the word.
In this case, the parent structure is a chain of five carbon atoms linked by single bonds. Thus, the root part of the name is pentane.
2. Characteristic groups and substituents (structural elements) are denoted by prefixes and suffixes. Characteristic groups are subdivided according to seniority. The order of precedence of the main groups:
The senior characteristic group is identified, which is designated in the suffix. All other substituents are named in the prefix in alphabetical order.
In this case, the senior characteristic group is carboxyl, i.e. this compound belongs to the class of carboxylic acids, so we add -oic acid to the root part of the name. The second most senior group is the amino group, which is denoted by the prefix amino-. In addition, the molecule contains a hydrocarbon substituent methyl-. Thus, the basis of the name is aminomethylpentanoic acid.
3. The name includes the designation of a double and triple bond, which comes immediately after the root.
The compound under consideration does not contain multiple bonds.
4. The atoms of the parent structure are numbered. Numbering starts from the end of the carbon chain, which is closer to the highest characteristic group:

The chain numbering starts from the carbon atom that is part of the carboxyl group, it is assigned the number 1. In this case, the amino group will be at carbon 2, and methyl at carbon 4.
Thus, the natural amino acid leucine, according to the IUPAC nomenclature rules, is called 2-amino-4-methylpentanoic acid.
Hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbon classification
hydrocarbons are compounds that consist only of hydrogen and carbon atoms.




Depending on the structure of the carbon chain, organic compounds are divided into compounds with an open chain - acyclic(aliphatic) and cyclic- with a closed chain of atoms.
Cycles are divided into two groups: carbocyclic compounds(cycles are formed only by carbon atoms) and heterocyclic(the cycles also include other atoms, such as oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur).
Carbocyclic compounds, in turn, include two series of compounds: alicyclic and aromatic.
Aromatic compounds in the basis of the structure of molecules have planar carbon-containing cycles with a special closed system of p-electrons, forming a common π-system (a single π-electron cloud). Aromaticity is also characteristic of many heterocyclic compounds.
All other carbocyclic compounds belong to the alicyclic series.
Both acyclic (aliphatic) and cyclic hydrocarbons can contain multiple (double or triple) bonds. These hydrocarbons are called unlimited(unsaturated), in contrast to the limiting (saturated), containing only single bonds.
Limit aliphatic hydrocarbons are called alkanes, they have the general formula C n H 2n+2, where n is the number of carbon atoms. Their old name is often used today - paraffins:
Unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons containing one double bond are called alkenes. They have the general formula C n H 2n:

Unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons with two double bonds are called alkadienes. Their general formula is C n H 2n-2:
Unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons with one triple bond are called alkynes. Their general formula is C n H 2n - 2:

Limit alicyclic hydrocarbons - cycloalkanes, their general formula C n H 2n:

A special group of hydrocarbons, aromatic, or arenes(with a closed common n-electron system), known from the example of hydrocarbons with the general formula C n H 2n - 6:

Thus, if in their molecules one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by other atoms or groups of atoms (halogens, hydroxyl groups, amino groups, etc.), hydrocarbon derivatives are formed: halogen derivatives, oxygen-containing, nitrogen-containing and other organic compounds.
Homologous series of hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons and their derivatives with the same functional group form homologous series.
Homologous series a number of compounds belonging to the same class (homologues) are called, arranged in ascending order of their relative molecular weights, similar in structure and chemical properties, where each member differs from the previous one by the homological difference CH 2 . For example: CH 4 - methane, C 2 H 6 - ethane, C 3 H 8 - propane, C 4 H 10 - butane, etc. The similarity of the chemical properties of homologues greatly simplifies the study of organic compounds.
Isomers of hydrocarbons
Those atoms or groups of atoms that determine the most characteristic properties of a given class of substances are called functional groups.

Halogen derivatives of hydrocarbons can be considered as products of substitution in hydrocarbons of one or more hydrogen atoms by halogen atoms. In accordance with this, there can be limiting and unlimiting mono-, di-, tri- (in the general case, poly-) halogen derivatives.
The general formula of monohalogen derivatives of saturated hydrocarbons:

and the composition is expressed by the formula

where R is the remainder of the saturated hydrocarbon (alkane), hydrocarbon radical (this designation is used further when considering other classes of organic substances), Г is a halogen atom (F, Cl, Br, I).
For instance:

Here is one example of a dihalogen derivative:

TO oxygenated organic matter include alcohols, phenols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, ethers and esters. Alcohols are derivatives of hydrocarbons in which one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by hydroxyl groups.
Alcohols are called monohydric if they have one hydroxyl group, and limiting if they are derivatives of alkanes.
General formula for limit monohydric alcohols:

and their composition is expressed by the general formula:
For instance:

Known examples polyhydric alcohols, i.e. having several hydroxyl groups:

Phenols- derivatives of aromatic hydrocarbons (benzene series), in which one or more hydrogen atoms in the benzene ring are replaced by hydroxyl groups.
The simplest representative with the formula C 6 H 5 OH or

called phenol.
Aldehydes and ketones- derivatives of hydrocarbons containing a carbonyl group of atoms

(carbonyl).
in molecules aldehydes one bond of the carbonyl goes to the connection with the hydrogen atom, the other - with the hydrocarbon radical. General formula of aldehydes:

For instance:

When ketones the carbonyl group is bonded to two (generally different) radicals, the general formula of ketones is:

For instance:

The composition of limiting aldehydes and ketones is expressed by the formula C 2n H 2n O.
carboxylic acids- derivatives of hydrocarbons containing carboxyl groups

(or -COOH).
If there is one carboxyl group in the acid molecule, then the carboxylic acid is monobasic. The general formula of saturated monobasic acids:

Their composition is expressed by the formula C n H 2n O 2 .
For instance:

Ethers are organic substances containing two hydrocarbon radicals connected by an oxygen atom: R-O-R or R 1 -O-R 2 .
The radicals may be the same or different. The composition of ethers is expressed by the formula C n H 2n+2 O.
For instance:
Esters- compounds formed by replacing the hydrogen atom of the carboxyl group in carboxylic acids with a hydrocarbon radical.
General formula of esters:

For instance:

Nitro compounds- derivatives of hydrocarbons in which one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by a nitro group -NO 2 .
General formula of limiting mononitro compounds:

and the composition is expressed by the general formula C n H 2n+1 NO 2 .
For instance:

Arene nitro derivatives:

Amines- compounds that are considered as derivatives of ammonia (NH 3), in which hydrogen atoms are replaced by hydrocarbon radicals. Depending on the nature of the radical, amines can be aliphatic, for example:

and aromatic, for example:

Depending on the number of hydrogen atoms replaced by radicals, there are:
primary amines with the general formula:

secondary- with the general formula:

tertiary- with the general formula:

In a particular case, secondary as well as tertiary amines may have the same radicals.
Primary amines can also be considered as derivatives of hydrocarbons (alkanes), in which one hydrogen atom is replaced by an amino group -NH 2 . The composition of limiting primary amines is expressed by the formula C n H 2n + 3 N.
For instance:

Amino acids contain two functional groups connected to a hydrocarbon radical: the amino group -NH 2 and carboxyl -COOH.
The general formula of α-amino acids (they are most important for building the proteins that make up living organisms):

The composition of limiting amino acids containing one amino group and one carboxyl is expressed by the formula C n H 2n+1 NO 2.
For instance:

Other important organic compounds are known that have several different or identical functional groups, long linear chains associated with benzene rings. In such cases, a strict definition of whether a substance belongs to a particular class is impossible. These compounds are often isolated into specific groups of substances: carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, antibiotics, alkaloids, etc.
Currently, there are also many compounds that can be classified as both organic and inorganic. x are called organoelement compounds. Some of them can be considered as derivatives of hydrocarbons.
For instance:

There are compounds that have the same molecular formula expressing the composition of substances.
The phenomenon of isomerism consists in the fact that there can be several substances with different properties that have the same composition of molecules, but different structures. These substances are called isomers.
In our case, these are interclass isomers: cycloalkanes and alkanes, alkadienes and alkynes, saturated monohydric alcohols and ethers, aldehydes and ketones, saturated monobasic carboxylic acids and esters.


Structural isomerism
There are the following varieties structural isomerism: carbon skeleton isomerism, position isomerism, isomerism of various classes of organic compounds (interclass isomerism).
The isomerism of the carbon skeleton is due to different bond order between carbon atoms that form the skeleton of the molecule. As already shown, the molecular formula C 4 H 10 corresponds to two hydrocarbons: n-butane and isobutane. For the hydrocarbon C 5 H 12, three isomers are possible: pentane, isopentane and neopentane.

With an increase in the number of carbon atoms in a molecule, the number of isomers increases rapidly. For the hydrocarbon C 10 H 22 there are already 75 of them, and for the hydrocarbon C 20 H 44 - 366 319.
Position isomerism is due to the different position of the multiple bond, substituent, functional group with the same carbon skeleton of the molecule:

The isomerism of various classes of organic compounds (interclass isomerism) is due to the different position and combination of atoms in the molecules of substances that have the same molecular formula, but belong to different classes. So, the molecular formula C 6 H 12 corresponds to the unsaturated hydrocarbon hexene-1 and the cyclic hydrocarbon cyclohexane.

The isomers are a hydrocarbon related to alkynes - butyne-1 and a hydrocarbon with two double bonds in the butadiene-1,3 chain:
Diethyl ether and butyl alcohol have the same molecular formula C 4 H 10 O:
Structural isomers are aminoacetic acid and nitroethane, corresponding to the molecular formula C 2 H 5 NO 2:

Isomers of this type contain different functional groups and belong to different classes of substances. Therefore, they differ in physical and chemical properties much more than carbon skeleton isomers or position isomers.
Spatial isomerism
Spatial isomerism divided into two types: geometric and optical.
Geometric isomerism is characteristic of compounds, containing double bonds, and cyclic compounds. Since the free rotation of atoms around a double bond or in a cycle is impossible, substituents can be located either on one side of the plane of the double bond or cycle (cis position), or on opposite sides (transposition). The designations cis- and trans- usually refer to a pair of identical substituents.

Geometric isomers differ in physical and chemical properties.
Optical isomerism occurs if the molecule is incompatible with its image in the mirror. This is possible when the carbon atom in the molecule has four different substituents. This atom is called asymmetric. An example of such a molecule is the α-aminopropionic acid (α-alanine) CH 3 CH(NH 2)OH molecule.
The α-alanine molecule cannot coincide with its mirror image under any movement. Such spatial isomers are called mirror, optical antipodes, or enantiomers. All physical and almost all chemical properties of such isomers are identical.
The study of optical isomerism is necessary when considering many reactions occurring in the body. Most of these reactions are under the action of enzymes - biological catalysts. The molecules of these substances must approach the molecules of the compounds on which they act like a key to a lock, therefore, the spatial structure, the relative position of the molecular regions and other spatial factors are of great importance for the course of these reactions. Such reactions are called stereoselective.
Most natural compounds are individual enantiomers, and their biological action (from taste and smell to medicinal action) differs sharply from the properties of their optical antipodes obtained in the laboratory. Such a difference in biological activity is of great importance, since it underlies the most important property of all living organisms - metabolism.

 isomerism
isomerism The electronic structure of the carbon atom
Carbon, which is part of organic compounds, exhibits a constant valence. The last energy level of the carbon atom contains 4 electrons, two of which occupy the 2s orbital, which has a spherical shape, and two electrons occupy the 2p orbitals, which have a dumbbell shape. When excited, one electron from the 2s orbital can go to one of the vacant 2p orbitals. This transition requires some energy costs (403 kJ/mol). As a result, the excited carbon atom has 4 unpaired electrons and its electronic configuration is expressed by the formula 2s 1 2p 3 .. Thus, in the case of the methane hydrocarbon (CH 4), the carbon atom forms 4 bonds with the s-electrons of hydrogen atoms. In this case, 1 bond of the s-s type (between the s-electron of the carbon atom and the s-electron of the hydrogen atom) and 3 p-s bonds (between 3 p-electrons of the carbon atom and 3 s-electrons of 3 hydrogen atoms) should have been formed. This leads to the conclusion that the four covalent bonds formed by the carbon atom are not equivalent. However, the practical experience of chemistry indicates that all 4 bonds in the methane molecule are absolutely equivalent, and the methane molecule has a tetrahedral structure with valence angles of 109.5 0, which could not be the case if the bonds were not equivalent. After all, only the orbitals of p-electrons are oriented in space along mutually perpendicular axes x, y, z, and the orbital of an s-electron has a spherical shape, so the direction of formation of a bond with this electron would be arbitrary. The theory of hybridization was able to explain this contradiction. L. Polling suggested that in any molecules there are no bonds isolated from each other. When bonds are formed, the orbitals of all valence electrons overlap. Several types are known hybridization of electron orbitals. It is assumed that in the molecule of methane and other alkanes 4 electrons enter into hybridization.
Hybridization of carbon atom orbitals
Hybridization of orbitals- this is a change in the shape and energy of some electrons during the formation of a covalent bond, leading to a more efficient overlap of orbitals and an increase in the strength of bonds. Orbital hybridization always occurs when electrons belonging to different types of orbitals participate in the formation of bonds.


1. sp 3 -hybridization(the first valence state of carbon). With sp 3 hybridization, 3 p-orbitals and one s-orbital of an excited carbon atom interact in such a way that orbitals are obtained that are absolutely identical in energy and symmetrically located in space. This transformation can be written like this:

During hybridization, the total number of orbitals does not change, but only their energy and shape change. It is shown that the sp 3 hybridization of the orbitals resembles a three-dimensional figure-eight, one of the blades of which is much larger than the other. Four hybrid orbitals are extended from the center to the vertices of a regular tetrahedron at angles of 109.5 0 . The bonds formed by hybrid electrons (for example, the s-sp 3 bond) are stronger than the bonds made by unhybridized p-electrons (for example, the s-p bond). Because the hybrid sp 3 orbital provides a larger area of electron orbital overlap than the unhybridized p orbital. Molecules in which sp 3 hybridization is carried out have a tetrahedral structure. In addition to methane, these include methane homologues, inorganic molecules such as ammonia. The figures show a hybridized orbital and a tetrahedral methane molecule.


Chemical bonds that arise in methane between carbon and hydrogen atoms are of the type of σ-bonds (sp 3 -s-bond). Generally speaking, any sigma bond is characterized by the fact that the electron density of two interconnected atoms overlaps along the line connecting the centers (nuclei) of atoms. σ-Bonds correspond to the maximum possible degree of overlap of atomic orbitals, so they are strong enough.
2. sp 2 -hybridization(the second valence state of carbon). Occurs as a result of the overlap of one 2s and two 2p orbitals. The resulting sp 2 hybrid orbitals are located in the same plane at an angle of 120 0 to each other, and the unhybridized p orbital is perpendicular to it. The total number of orbitals does not change - there are four of them.
The sp 2 hybridization state occurs in alkene molecules, in carbonyl and carboxyl groups, i.e. in compounds containing a double bond. So, in the ethylene molecule, the hybridized electrons of the carbon atom form 3 σ-bonds (two sp 2 -s type bonds between the carbon atom and hydrogen atoms and one sp 2 -sp 2 type bond between carbon atoms). The remaining unhybridized p-electron of one carbon atom forms a π-bond with the unhybridized p-electron of the second carbon atom. A characteristic feature of the π bond is that the overlap of electron orbitals goes beyond the line connecting the two atoms. Orbital overlap goes above and below the σ-bond connecting both carbon atoms. Thus, a double bond is a combination of σ- and π-bonds. The first two figures show that in the ethylene molecule the bond angles between the atoms that form the ethylene molecule are 120 0 (corresponding to the orientation of three sp 2 hybrid orbitals in space). The figures show the formation of a π bond.


Since the area of overlap of unhybridized p-orbitals in π-bonds is less than the area of overlapping of orbitals in σ-bonds, the π-bond is less strong than the σ-bond and is more easily broken in chemical reactions.
3. sp hybridization(the third valence state of carbon). In the state of sp-hybridization, the carbon atom has two sp-hybrid orbitals located linearly at an angle of 180 0 to each other and two unhybridized p-orbitals located in two mutually perpendicular planes. sp hybridization is characteristic of alkynes and nitriles; for compounds containing a triple bond.
So, in an acetylene molecule, the bond angles between atoms are 180 o. The hybridized electrons of a carbon atom form 2 σ-bonds (one sp-s bond between a carbon atom and a hydrogen atom and another sp-sp type bond between carbon atoms. Two unhybridized p-electrons of one carbon atom form two π-bonds with unhybridized p electrons of the second The overlap of p-electron orbitals goes not only above and below the σ-bond, but also in front and behind, and the total p-electron cloud has a cylindrical shape.Thus, a triple bond is a combination of one σ-bond and two π-bonds. The presence of less strong two π-bonds in the acetylene molecule ensures the ability of this substance to enter into addition reactions with the breaking of the triple bond.


Reference material for passing the test:
Mendeleev table
Solubility table