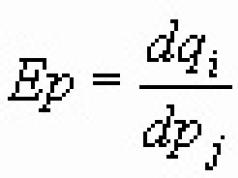Our state remains essentially social. Even in the current difficult financial conditions, he tries not to lower the bar of social obligations. It doesn't always work out. A single social tax serves as a certain support in the fulfillment of these tasks. About him now and will be discussed.
UST in 2020: why you need it
The abbreviation UST stands for Unified Social Tax. Before turning to the question of the size of the UST in 2020, let us briefly dwell on the nature of this tax, its tasks and objects of taxation.
To begin with, let us explain that legally this tax has not existed for several years, it was canceled 9 years ago. But out of habit, different contributions for this purpose are called a single social tax. In addition, there is a possibility that it will be returned.
It is calculated using both budgetary and extrabudgetary sources of funds. The purpose of the UST is to provide an opportunity for employees to receive a state pension and a number of social benefits in the future. From the same source, the necessary amounts are allocated for free assistance in medical organizations, the list of which is determined by law.
Who pays, what is the object of taxation
Everyone who officially works should deduct this type of tax. These are two large groups of taxpayers.
1. Individual entrepreneurs engaged in private practice.
2. Individuals who do not belong to the category of individual entrepreneurs; Individual entrepreneurs, enterprises and organizations, specific people that make payments to individuals.
These groups have slightly different objects of taxation under the unified social tax. The first group must make deductions from all types of income remaining after taking into account the expenses indicated by law. For those who fall into the second group, the entire volume of payments that were made to individuals under contracts of various types, both labor and the entire spectrum of civil law, becomes the object of taxation.
How is the UST rate calculated in 2020
For the main group of taxpayers, the UST rates in 2020 remained the same as before. What is it made up of? Of these three types of payments:
- mandatory pension insurance contributions, the rate of which is 22%;
- deductions for compulsory health insurance, their size is 5.1%;
- payments to the Insurance Fund, amounting to 2.9%.
- payments for accident insurance, the rate depends on the business risk group.
For the maximum amount of contributions to pension insurance in 2019, the amount of 234,832 rubles was accepted, in 2020 the bar for the maximum amount of pension contributions will increase to 259,584 rubles. As for the percentage of the rate, it varies somewhat depending on the amount of charges.
Upon reaching the limit set for a given year, it can be adjusted downward. In 2019, the above-mentioned rate of 2.9% for the Social Insurance Fund is applied for accruals for amounts less than 865,000 rubles. If the amounts are more than 865,000, then the rate on this fund will be zero. In 2020, contributions are paid to the FSS until the income of 912,000 rubles is received.
With regard to contributions to compulsory pension insurance, the rule is the same: if the accruals are less than 1,150,000 rubles, then the UST rate is set at 22%, and for payments in excess of 1,150,000 rubles, it is reduced to 10%. In 2020, with an income of 1,292,000, the rate is 22%, and above this amount, the rate is reduced to 10%. There are no maximum restrictions for compulsory health insurance; in 2019, 5.1% of the total amount of income is calculated.
Features of calculations for IP
How many percent of the UST in 2020 will have to be deducted by individual entrepreneurs? For IP, a slightly different system of calculations has been developed. First, they are not required to pay into insurance funds; they can only do so on a voluntary basis. Behind them are mandatory contributions to two funds: Pension and Medical Insurance. In 2017, both were calculated in proportion to the minimum wage.
The formula was this. We calculate contributions to the health insurance fund based on the rate of 5.1% of the minimum wage per year, that is, 12 * 5.1% * minimum wage. For the Pension Fund, the calculation is similar, only we apply the rate of 26%.
It must be borne in mind: if the income of an individual entrepreneur per year turns out to be more than three hundred thousand rubles, then one percent of the amount by which this limit is exceeded is added to all the above deductions.
Main changes in UST
Speaking about the table of UST rates in 2020, we must also remember a number of amendments related to the payment of UST, which were made this year in connection with the changes that affected the Tax Code of Russia.
1. Now it is impossible to round the amounts (in any direction) when deducting contributions for the UST.
2. The concept of the maximum indicator for calculating payments for pension insurance has appeared. It is fixed by law, and appropriate changes have been made to local regulations relating to taxation. But for compulsory medical insurance, such restrictions have not yet been provided.
3. Insurance premiums will not be recovered from the amount of compensation payments that is less than three average monthly earnings if the employee leaves. This innovation also concerns the payment of travel expenses. And insurance interest will not be accrued on them, but only if these expenses are documented.
4. From now on, employers will also be required to pay the necessary amounts for the purposes of pension insurance for foreign citizens hired. Exceptions are provided only for high-class foreign specialists.
5. The number of businesses eligible for electronic reporting has increased.
6. Fixed IP contributions will not be calculated based on the minimum wage.
Changes related to deferrals and control checks
Supervisory enterprises can now, if there are serious reasons, increase the duration of inspections from the previous four months to six. These grounds are:
- serious violations that require urgent verification and immediate action; they must be recorded and documented;
- violations in branches located in different constituent entities of the Russian Federation requiring verification;
- inaccuracy in documents or lack of requested data;
- untimely insurance deductions, including due to force majeure circumstances.
The employer (IE) has the right and even must, in the event of such emergency circumstances, ask for a deferral or installment plan for payments on the unified social tax. These may be such reasons as unreasonable delay in financing, and for enterprises conducting seasonal work, also force majeure: man-made and natural disasters, military operations, etc.
The subject of taxation will need to submit an application of the established form to the appropriate organization. Based on that, a decision will be made.
UST rate tables in 2020
Insurance premium rates in 2020
Reduced insurance premium rates in 2020
|
OKVED codes for activities* |
Fee for calculating contributions |
|||
|
in the FIU |
in the FSS at VNiM |
in FFOMS |
||
|
Organizations and individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system that conduct a privileged type of activity, the income from which is at least 70% of the total income of the simplifier. Wherein the annual income of a simplifier should not exceed 79 million rubles. If this limit is exceeded, the contributor loses the right to reduced tariffs from the beginning of the billing period |
13, 14, 15, 16, etc. |
|||
|
Pharmacy organizations, as well as individual entrepreneurs licensed to conduct pharmaceutical activities, for UTII. Reduced contribution rates apply only to employees engaged in pharmaceutical activities (clause 6 clause 1, clause 3 clause 2 article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended, effective from 01/01/2017) |
46.18.1, 46.46.1, 47.73 |
|||
|
Individual entrepreneurs applying the patent system of taxation - in relation to payments and remuneration of employees who are engaged in a patent type of activity. For some types of activities, this “benefit” does not apply (clause 9 clause 1, clause 3 clause 2 article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended, effective from 01/01/2017) |
||||
|
Non-profit organizations on the simplified tax system, except for state and municipal institutions, operating in the field of social services for citizens, research and development, education, healthcare, culture, art and mass sports (clause 7, clause 1, clause 3, clause 2, clause 7 article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended, effective from 01.01.2017) |
37, 86, 87, 88, 93, etc. |
|||
|
Charitable organizations on the simplified tax system (clause 8 clause 1, clause 3 clause 2, clause 8 article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended, effective from 01/01/2017) |
||||
|
Organizations operating in the field of information technology (clause 3, clause 1, clause 1, clause 2, clause 5, article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended, effective from 01/01/2017). |
||||
|
Business companies and partnerships on USN, who are engaged in the implementation of the results of intellectual activity (inventions, utility models, etc.), the rights to which belong to budgetary and autonomous (including scientific) institutions (clause 1, clause 1, clause 1, clause 2, clause 4 article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended, effective from 01.01.2017). |
||||
|
Organizations and individual entrepreneurs that have concluded agreements with the governing bodies of special economic zones on the implementation of technical and innovative activities, as well as tourist and recreational activities (clause 2, clause 1, clause 1, clause 2, article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as amended, valid from 01.01.2017). |
65.20, 79.1, 94.99, 62.0, 63.1, 63.11.1, etc. |
|||
|
Payers of contributions making payments and remuneration to crew members of ships registered in the Russian International Register of Ships (with some exceptions) in respect of these payments (clause 4, clause 1, clause 2, clause 2, article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as amended, valid from 01.01.2017) |
||||
|
Organizations that have received the status of a participant in the project for the implementation of research, development and commercialization of their results "Skolkovo" |
72.1 (Part 8, Article 10 of the Law of September 28, 2010 No. 244-FZ) |
|||
|
Contribution payers who have received the status of a participant in a free economic zone on the territory of the Republic of Crimea and the federal city of Sevastopol (clause 11, clause 1, clause 5, clause 2, clause 10, article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended, effective from 01.01. 2017) |
Any OKVED codes, except for 05, 06, 07, 08, 09.1, 71.12.3 (part 2 of article 12 of the Law of November 29, 2014 No. 377-FZ) |
|||
|
Payers of contributions who have received the status of a resident of the territory of rapid socio-economic development (clause 12 clause 1, clause 5 clause 2, clause 10 article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended, effective from 01/01/2017) |
The types of activities are established separately for each territory (clause 1, part 2, article 3 of the Law of December 29, 2014 No. 473-FZ). |
|||
|
Contribution payers who have received the status of a resident of the free port "Vladivostok" |
Any types of activity, except for those prohibited by the decision of the Supervisory Board of the Free Port of Vladivostok (parts 1.2 of Article 6 of the Law of July 13, 2015 No. 212-FZ). For example, activities for the extraction of oil and natural gas are prohibited, OKVED code 06.1 |
|||
Categories of individual entrepreneurs for which the preferential tariff was canceled in 2020
|
Organizations and individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system conducting a privileged type of activity, the income from which amounted to at least 70% of the total income of the simplified person. At the same time, the annual income of the simplistic did not exceed 79 million rubles. |
13, 14, 15, 16, etc. |
|||
|
Pharmacy organizations, as well as individual entrepreneurs licensed to conduct pharmaceutical activities, for UTII. |
46.18.1, 46.46.1, 47.73 |
|||
|
Individual entrepreneurs applying the patent system of taxation - in relation to payments and remuneration of employees who are engaged in a patent type of activity. For some types of activities, this “benefit” was not applied (clause 9, clause 1, clause 3, clause 2, article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended, effective from 01/01/2017) |
31.0, 74.20, 75.0, 96.01, 96.02, etc. |
Individual entrepreneur insurance premiums "for oneself" in 2019
Individual entrepreneur insurance premiums "for oneself" in 2020
It may also be useful:
Is the information useful? Tell friends and colleagues
Dear readers! The materials of the site site are devoted to typical ways of solving tax and legal issues, but each case is unique.
If you want to know how to solve your particular issue, please contact the online consultant form. It's fast and free! You can also consult by phone: MSK +7 499 938 52 26. SBP +7 812 425 66 30, ext. 257. Regions - 8 800 350 84 13 ext. 257
A year has passed since control over the payment of insurance premiums was again transferred to the Federal Tax Service. According to officials, the administration of contributions by tax inspectorates has a much better effect on their collection. The Social Insurance Fund was left only to collect contributions in case of injuries and occupational diseases of workers. How to calculate and pay insurance premiums in 2018 - we will tell you all the changes and the latest news on this topic.
How much should IP pay for themselves
First, about the amount of contributions that each entrepreneur must make for himself in 2018, even if he does not conduct real activities or has no business income. The formula for calculating these amounts has changed compared to previous years. Now contributions are no longer tied to the minimum wage, which shows a rapid and significant increase - from 7,500 rubles at the beginning of 2017 to 9,485 rubles at the beginning of 2018.
It is expected that the minimum wage will be equated to the minimum subsistence level already to. If we take into account that this amount is 11,163 rubles, then the previous linkage of the amount of insurance premiums to the minimum wage would have caused a sharp increase in IP payments for itself. To prevent this, the Government decided to set a fixed amount of insurance premiums for 2018.
Law No. 335-FZ dated November 27, 2017 changed the norms of Article 430 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, establishing individual entrepreneurs' insurance premiums for 2018 in a fixed amount:
- for mandatory pension insurance 26 545 rubles;
- for compulsory health insurance 5 840 rubles.
Thus, each entrepreneur will have to pay for himself in 2018 at least 32 385 rubles, which, compared with the previous year, means an increase of 4395 rubles. If the entrepreneur was not registered in this capacity for the whole year, then the annual amount is recalculated accordingly.
The rule for calculating the additional contribution for incomes over 300,000 rubles per year has not changed: 1% of the amount in excess of the limit is still charged for pension insurance. There is also a limit on the amount of contributions made by an entrepreneur for his or her pension insurance. The maximum contributions to the PFR in 2018 for an individual entrepreneur are 212,360 rubles: at the rate of 8 * 26,545 * 12 months * 26%. Individual entrepreneurs pay contributions to their social insurance voluntarily for themselves.
The table shows the mandatory payments of the entrepreneur in 2018, calculated according to the new law
The terms for payment of IP payments have partially changed: a fixed amount of 32,385 rubles must be paid no later than December 31, 2018, and an additional 1% contribution can now be paid later - until July 1, 2019, and not until April 1, as it was before.
IP Sergienko A.M. received in 2018 an income of 1.3 million rubles.The additional contribution for pension insurance will be ((1,300,000 - 300,000) * 1%) = 10,000 rubles. That is, the total IP Sergienko A.M. must pay for himself with such an income 42,385 rubles. At the same time, a fixed amount of 32,385 rubles must be transferred no later than 12/31/18, and 10,000 rubles can be paid both in 2018 and before 07/01/19.
For the convenience of paying taxes and insurance premiums, we recommend opening a current account. Especially now, many banks offer favorable conditions for opening and maintaining a current account.
How much do payers of employee contributions have to pay?
According to the new chapter 34 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, payers of insurance premiums (except for individual entrepreneurs without employees, notaries, lawyers engaged in private practice) are also persons making payments and other remuneration to individuals. This category includes:
- employers under employment contracts;
- customers under civil law contracts;
- ordinary individuals who are not registered as individual entrepreneurs.
Payers pay contributions at their own expense, and do not withhold them from payments to an individual. In 2018, insurance premium rates remained at the same level and generally amount to 30% of payments to employees. In addition, there are some categories of payers for whom the rate of insurance premiums in 2018 has been significantly reduced. In order to be able to make deductions at these reduced rates, the payer must comply with the mandatory conditions of Article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 15, 2017 No. 1378 established the maximum base for calculating insurance premiums in 2018:
- for pension insurance - 1,021,000 rubles;
- for compulsory social insurance - 815,000 rubles.
Upon reaching these payments (separately for each employee), the payer pays contributions. If the payer is included in the preferential category, then after reaching the marginal base, contributions for pension and social insurance of the employee are not paid. As for payments for health insurance, their tariff does not change when the marginal base is reached.
Insurance premiums in 2018 rates established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation(table of general and reduced tariffs)
Pension insurance | Social insurance | Health insurance |
|
|---|---|---|---|
Policyholders not eligible for benefits before the contribution base limit is reached | 2,9% | 5,1% |
|
Non-eligible policyholders after reaching the contribution base ceiling | 5,1% |
||
1. Organizations and individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system, for certain types of activities (Article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) 2. Pharmacies operating on UTII 3. IP on PSN, except for those engaged in trade, catering, rent 4. Non-profit and charitable organizations on the simplified tax system | |||
1. Economic companies and partnerships on the simplified tax system that implement inventions, patents, designs. 2. Or-ga-ni-za-tion and individual entrepreneurs who have entered into agreements with special economic zones for tech-no-to-implemented-ren-che-sky and tourist-sko-re-kre-a-tsi-on -nuyu de-I-tel-no-st | 13% | 2,9% | 5,1% |
| Accredited IT organizations | 8% | 2% | 4% |
Insurers in respect of crew members of vessels registered in the Russian International Register of Ships | |||
Participants of the Skol-ko-vo project in Russia | |||
1. Participants of the free economic zone on the territory of the Republic of Crimea and Sevastopol 2. Residents of the territory of rapid socio-economic development 3. Residents of the free port "Vladivostok" | 1,5% | 0,1% |
Additionally, a contribution is paid to the FSS for compulsory insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases (from 0.2% to 8.5%). The terms for transferring contributions for employees have not changed: no later than the 15th day of the month following the reporting one (clause 3 of article 431 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
New contribution reporting
Although since 2017 all functions for monitoring the payment of contributions (except for contributions for injuries) have been transferred to the Federal Tax Service, there remains reporting that must be submitted to the funds.
IN Pension Fund:
- monthly - no later than the 15th day of the month following the reporting one (previously it was before the 10th day);
- once a year personalized accounting information (SZV-Experience) - no later than March 1, 2019 for 2018.
IN Social Insurance Fund:
- updated form, the deadlines are the same - no later than the 20th day of the month following the reporting quarter (on paper) and no later than the 25th day for electronic reporting (with more than 25 employees).
IN tax office surrenders, which combines information that was previously included in the RSV and 4-FSS forms. A single calculation of contributions must be submitted no later than the 30th day following the reporting period (clause 7, article 431 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
A rollback to those laws that were once abandoned has become a regularity in our time. This category can also include the restoration of "in rights" canceled in 2010, Article 24 of the tax legislation, which tells about the unified social tax. In general, the state plans not only to restore previously forgotten taxes, but also to increase them. This is evidenced by UST rates in 2017, table which have been published relatively recently.
UST and ESSC - two names of one fee
The innovation was not perceived very positively by the townsfolk, but among entrepreneurs it caused bewilderment and many questions. The reason for this was the two names of the same collection, which caused confusion in the minds of people. So, in the beginning of the year, a decision was made to combine all insurance premiums into a single fee, and the authority to consolidate payments was transferred to the tax authorities. In order to avoid a situation where citizens have to pay for the same thing twice, it was decided to rename the UST to ESS.
As for the issues of calculation, tax bases, benefits and reporting, in these issues the introduced unified social tax from 2017 will not differ.
Debriefing in detail: rates, benefits, accruals, reporting
The categories of payers of this fee or tax have not yet been fully decided on this moment, they will remain the same. They will be individuals, entrepreneurs and organizations that make payments to citizens. Also, the obligation to pay the fee will be with legal professionals engaged in private practice, as well as notaries.
It is noteworthy that if the payer belongs to several categories at the same time, then the charge will have to be paid for each.
The tax base of the UST from 2017 will be the total amount of income and profits, after deducting from them all the costs and expenses associated with their extraction. As for the calculations, the tax percentage will be calculated from the profit for a specific tax period.
Another "trouble" for organizations was the need to calculate tax bases separately for each hired and full-time employee. In addition, when calculating, it is necessary to take into account both financial income, or monetary, and natural - physical, for example, the harvest obtained for agricultural enterprises. 
As for interest rates, they increase with the increase in the profitability of the enterprise. In this way, unified social tax UST from 2017 will be established for all kinds and types of enterprises and will affect all working citizens.
Certain exemptions will also be included in the calculation. They will affect the disabled, whose annual income is not higher than 100 thousand rubles. For them, the tax is not relevant. The same principle is provided for organizations that have hired disabled people, and the total payments to them during the year will not exceed the specified threshold. Those working under the simplified tax calculation and payment system may also not pay ESN. Tax payers on imputed incomes are also exempted from the social tax.
In addition, UST is not charged:

If UST is not paid
The consequences of non-payment of the unified social tax or fee will be fully felt by the employees of the “unscrupulous” enterprise or entrepreneur. Thus, they run the risk of losing “years” of work experience, receiving underestimated amounts of pension components (accumulative, insurance part), and losing the opportunity to receive investment income from pension savings. It is noteworthy that against the backdrop of non-payment of contributions, the country has already developed a practice of lawsuits, the essence of the requirements, within which it meant the payment of underpaid insurance premiums.
Our state is trying to protect the rights of the working population by introducing various contributions for employers. If an organization has employees, it means that it is obliged to be fully responsible for them, to pay mandatory contributions to various funds.
One of these taxes is the unified social tax - UST. Let's figure out what this tax means for company employees, for employers and what is its rate.
All the working population of the country, commercial and budgetary organizations are familiar with this tax. By establishing such a contribution, the state realized the right of the working population of the country to free medical care in state medical institutions, provided the working population with a pension and provides social benefits. Payments for this tax amounted to 26-30 percent of wages. But the Government of Russia in 2010 abolished this tax.
Instead, three different insurance taxes began to operate - Pension, honey. fear and social fear.
The government plans to return the single social tax. If this contribution is returned, this will simplify the rules for its payment. It will also reduce the number of checks. With the help of the introduced tax, the authorities hope to increase revenues to the treasury from those citizens of the country who, in one way or another, tried to evade paying taxes.
Who are the UST taxpayers
The payers of this tax will remain those market participants who paid contributions to the PFS, honey. fear, FSS:
- Jur. persons who make payments to individuals.
- Entrepreneurs who have employees.
- Notaries and lawyers in private practice.
Thus, all commercial and state organizations are taxpayers. If this is an individual entrepreneur without employees, then he pays a contribution for himself.
What is the object of taxation
In order to pay this tax to the state, it is necessary on the basis of Art. 235 of the Tax Code to make payments or other remuneration to individuals, which are carried out on the basis of employment contracts or civil law.
If a person has performed any work or service on the basis of an agreement, an author's agreement and received remuneration or wages for his work, the employer transfers social tax for him.
This tax is imposed on the activities of entrepreneurs, farms, which, taking into account the taxation regime, calculate the tax.
The following payments are not subject to social taxes:
- Which were made within the framework of legal contracts during the transfer of property rights.
- Accrued in favor of foreign citizens or LBG, concluded with a separate division of the Russian organization under employment contracts.
Jur. persons and merchants make payments for hired employees, the object of taxation of which is wages or other remuneration.
Lawyers and notaries, heads of farms pay this tax when calculating income minus expenses.
Depending on the tax regime, different calculations can be made. For example, a single tax under OSNO is calculated according to the general rules for this system.
How the tax base is determined
In order to determine the tax base, it is necessary to take into account any payments and remuneration that were made to employees. This is how the tax base is formed.
Employers pay this tax based on payments based on employment and legal contracts. The tax rate is set on the basis of Art. 241 Tax Code - the maximum was 26% with a tax base of less than 300 thousand rubles. If the income is higher, then you need to beat another percentage. This rate was distributed as follows:
- 20% went to the federal budget.
- Social fear took 2.9%.
- Federal Medical Fund. fear - 1.1%.
- Regional honey. fear - 2%.
Bases and rates are subject to change. Currently, the total UST tax is 30%, but for some taxpayers a reduced rate of 26% is set.
To make a calculation, you need to know the tax base, whether the payer has a reduced rate or pays on a general basis. For example, a single tax under the simplified tax system can be considered at reduced rates in percent.
Depending on which mode the company uses, the calculation is made. If this is a simplistic person with income, then the calculation is taken from his main profit. If the simplified tax regime is income minus expenses, then the calculation is taken from the difference.
Also, the calculation of the tax may vary, it depends on the annual income of the merchant and tax deductions that have a certain margin.
The rate of social tax varies from the amount of accrual, that is, it decreases when a certain limit is reached. The rate and limit change every year. Therefore, it is necessary to make a calculation based on the amount received by the entrepreneur. The organization needs to look at how many charges have been made and whether the amount paid has reached a certain limit.
Control over the payment of insurance premiums passed to the tax service, with the exception of premiums for injuries. In the article we will tell you: what is the UST rate applied in 2020.
Calculate the contribution rate in the BukhSoft program.
Calculate online
What is the rate of the unified social tax (UST) on insurance premiums
The insurance contribution rates remained unchanged compared to 2018, while the marginal insurance base increased.
UST rate and marginal insurance base in 2020.
At present, the general UST rate is 30%. The table shows the amount of social taxes in 2020 by fund.
|
Fund |
The maximum size of the base for calculating insurance premiums |
Bid |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
up to 1,150,000 (inclusive) |
||||
|
over 1 150 000 |
||||
|
up to 865,000 (inclusive) |
||||
|
over 865 000 |
||||
Who is eligible to apply the reduced UST rate
Payers on the simplified taxation system have the right to apply "preferential" insurance rates. This category includes:
- representatives of small and medium-sized businesses operating in the social and industrial sectors
- payers carrying out technical and innovative activities in the special economic zone
- payers carrying out tourist and recreational activities in the special economic zone
- pharmacies
- charity organisations
- socially oriented non-profit companies
- organizations operating in the field of information technology
- economic companies and partnerships whose activities consist in the practical application of the results of intellectual activity
- payers making payments and other remuneration to crew members of ships registered in the Russian International Register of Ships, which apply a 0% tariff until 2028
- participants of the Skolkovo project
- payers who have received the status of a participant in the free economic zone in the territories of the Republic of Crimea and Sevastopol, the status of a resident of the territory of advanced socio-economic development, the status of a resident of the port of Vladivostok
What is the rate at the reduced UST tariff
Reduced tariff rates have also not changed. Most of the simplified people have already switched to the general tariff of 30 percent, as the grace transition period will end. A reduced rate of 20 percent will be left to non-profit and charitable organizations on the simplified tax system. The benefit can be used for six years - until 2024. There will be no planned increase in contributions for simplified users who applied the general tariff.
It was previously planned that from 2021 the overall tariff would increase from 30 to 34 percent. Now the code has left the tariff of 30 percent. The company's pension contributions will, as now, be calculated at the rate of 22 percent from payments within the limit and 10 percent from excess amounts. How will it affect work? The burden of contributions will increase one and a half times for those simplified workers who previously used a preferential tariff. But there are ways to save on fees.