The purpose of this work consists in a theoretical study of the functioning of the insurance market for property of legal entities, a study of the current state of the insurance market of the company "Insurance House All-Russian Insurance Company", problems and prospects for the development of insurance of property of legal entities in Russia.
The object of the study is economic relations that arise in the process of functioning of the property insurance market for legal entities.
To achieve this goal, the following tasks are defined: to analyze the state of the insurance market for property insurance of legal entities in the Russian Federation and on the example of the company "Insurance House All-Russian Insurance Company", to identify the features of the Russian market for insurance of property of legal entities, to identify the prospects for the development of this type of insurance.
At present, issues devoted to the study of problems and prospects for the development of property insurance of legal entities are becoming relevant.
In the process of work, an analysis was made of the insurance market for property insurance of legal entities in Russia, in the company "Insurance House All-Russian Insurance Company"
In the course of the analysis, relevant conclusions were made, an analysis of the insurance market was carried out.
Benefit The size of VSK's insurance reserves is about 11 billion rubles, the amount of own funds is 4.6 billion rubles. The complex of services of SOJSC "VSK" includes about 100 areas of insurance intended for both individuals and legal entities. VSK Insurance House has been carrying out insurance activities since February 11, 1992 and is now confidently among the leaders of the Russian insurance market.
The relevance of the topic of the work is due to the fact that insurance is one of the strategic sectors of the economy. Guaranteeing citizens and organizations the protection of their property interests, it ensures socio-economic stability in society. Insurance has a significant impact on strengthening the finances of the state, not only freeing the budget from expenses caused by the occurrence of emergency events of natural, man-made or social origin, but also being a stable internal source of investment in the economy of funds accumulated by insurance organizations. For modern Russia, with the current increased degree of vulnerability of the production and social sphere to the impact of various adverse factors that lead to harm to life and property, when the majority of the country's population experiences uncertainty about their future, the potential role of insurance as a mechanism for protecting the property interests of individuals and legal entities is especially great. .
In the context of the instability of the Russian economy, the negative consequences of the financial and economic crisis, insurance remains one of the few economic mechanisms that can have a significant impact on stabilizing the socio-economic situation, create prerequisites for economic recovery by attracting funds to the country's economy, and increase people's life confidence.
The dynamic development of insurance in modern Russia is associated, first of all, with overcoming the state monopoly on insurance in the early 1990s and the development of commercial insurance, and, above all, property insurance. So, along with the previously used types of property insurance, new types of insurance have arisen and are developing, such as business risk insurance, civil liability insurance.
The value of property insurance for the Russian Federation, which has taken the path of developing market relations in the economy, is difficult ...
In countries with developed market economies, insurance is one of the strategic sectors of the economy. Insurance ensures socio-economic stability in society, as it guarantees owners compensation for damage in case of loss or damage to property and loss of income. The role of insurance is manifested, first of all, at the microeconomic level, specific insurance contracts are concluded by legal entities and individuals in order to protect their property interests. In the event of major natural or man-made disasters covering vast territories, disrupting the activities of hundreds of enterprises that threaten the lives of thousands of residents, compensation for the corresponding damage through the insurance system has macroeconomic consequences. The macroeconomic proportions of the development of the world's leading states largely determine the huge investment resources of insurance companies.
A modern market society cannot be imagined without insurance as a special type of economic relations. There is a direct relationship between the level of welfare of society, the degree of development of market relations and the level of development of insurance. In countries that are world leaders in the field of social and market relations (USA, Japan, European countries and others), insurance is one of the most stable and dynamically developing sectors of the national economy.
Insurance is a necessary element of industrial relations. It is associated with compensation for material losses in the process of social production. The risky nature of social production gives rise to relations between people to prevent, overcome, localize and unconditionally compensate for the damage caused.
However, enterprises and organizations of various forms of ownership, acting as insurers, need not only compensation for damage, expressed in the loss or damage to fixed assets and working capital, but also compensation for lost profits or additional costs due to forced downtime (irregular supply of raw materials , insolvency of wholesale buyers).
That is why the state policy in the field of insurance should have a stimulating effect on this segment of the economy.
Centuries of experience and the history of insurance have convincingly proved that it is a powerful factor in the positive impact on the economy. However, there are various problems on the way to the development of insurance in Russia, which can be solved only if there are appropriate conditions.
To realize the potential of the insurance industry, active state support is needed, and the sooner the state realizes the role of insurance as a strategic sector of the economy, the sooner Russia will transition to a socially oriented market growth.
Property insurance of legal entities is currently a developing type of insurance. The founders of companies and enterprises began to realize the importance of this type of insurance and that property insurance is a guarantee of protecting their property from various risks (natural disasters, production downtime, adverse effects of third parties, and so on). Owners of companies and enterprises began to voluntarily insure their property, equipment, various transactions, and so on.
This type of insurance began to develop relatively recently and is gaining significant momentum in its development.
For insurance companies, the conclusion of an insurance contract with a legal entity is significantly beneficial. Since it brings a greater part of insurance premiums to the insurance company than insurance with an individual. An insurance contract with a legal entity is more expensive than an insurance contract with an individual. Therefore, insurance companies pay more attention to this type of insurance and try to conclude an agreement with as many legal entities as possible.
The purpose of this work is to determine:
- 1. The value of property insurance for society and for enterprises;
- 2. Rules for insurance of property of legal entities;
- 3. Analysis of the property insurance market in general and on the example of the company "VSK Insurance House";
- 4. Problems of development of insurance of property of legal entities;
- 5. Ways to solve the problems of property insurance of legal entities;
- 6. Prospects for the development of property insurance for legal entities.
Federal Agency for Education
State educational institution
higher professional education
Nizhny Novgorod State Linguistic University
them. N.A., Dobrolyubova
(GOU NGLU)
Department of Economics and Management
Course work
discipline State and municipal finance
on the topic: Financial bases of insurance activity
Performed:
student gr. 405 GMU FMOEU
Starkova O.A.
Scientific adviser:
Pryanichnikov S.B., Associate Professor, Ph.D. economy Sciences
Nizhny Novgorod
Introduction
Insurance as an element of social protection of the population has a high social significance and is an important source of domestic long-term investment in the country's economy. Positive trends in the development of the Russian insurance services market and the inevitable prospects for increasing competition with foreign insurance companies are forcing Russian insurers to pay more and more attention to understanding domestic and foreign experience in the functioning of insurance companies and the problems of scientific substantiation of rational strategies for their development.
The experience of developed countries, in which there has long been no discussion about what place insurance should take in the economy, clearly indicates the imperfections of the Russian insurance market and the need for a critical review of domestic approaches to this type of economic relations.
At the current stage of development, insurance companies have a real opportunity to determine the ratio of forthcoming payments under insurance policies in time with a sufficient degree of accuracy. This allows them to place the majority of their reserves in long-term, most profitable and reliable, as well as medium- and short-term assets.
Insurance companies operating in today's market are fully experiencing all the difficulties of survival and development in a competitive market environment. Under these conditions, the issues of competent financial planning of the activities of insurance organizations and the effective management of their financial resources are of particular importance.
The relevance of the chosen topic is determined not only by theoretical, but also by practical interest in studying the relevant range of issues, primarily devoted to the insufficient attention of insurers to the management of financial resources in terms of entrepreneurial risks, which naturally leads to negative consequences for the company itself and its clients.
The purpose of this course work is to study the process of formation and use of financial resources of insurance companies and develop recommendations for improving financial stability on the example of a particular insurance company (JSC "VSK Insurance House" (hereinafter "VSK")).
The set goal involves the solution of the following range of tasks:
· studying the organizational and legal foundations of insurance activities and substantiating the place of an insurance company in the system of economic relations;
· Consideration of the process of regulating the activities of insurance companies in Russia;
· study of the mechanism of formation and use of financial resources of insurance companies;
· analysis of the formation and use of financial resources "VSK";
development of proposals for improving the financial resource management system "VSK"
The subject of the study is economic relations regarding the formation and use of financial resources of insurance companies that arise between "VSK" and other subjects of insurance.
The object of the study is the activities of the VSK Insurance House, as well as certain aspects of the activities of the Russian insurance market as a whole.
Despite the theoretical and practical significance of the problem, the degree of research and development of issues related to the management of the financial potential of insurance companies in the domestic clearly does not correspond to its significance.
The existing methodological developments in this area mainly reflect the regulatory approach to insurance organizations by the state insurance supervision authorities. They do not focus on the need to assess the level of use of financial potential by insurance companies in order to ensure financial stability.
The information basis of the work is: the Civil and Tax Codes of the Russian Federation, the Law of the Russian Federation "On the organization of insurance business in the Russian Federation" dated 11/27/92. No. 4015-1, orders and instructions issued by bodies for the supervision of insurance activities.
The methodological basis of the work was the work of the authors Nikulina N.N., Grishchenko N.B., Shakhov V.R., Orlanyuk-Malitskaya L.A. and other sources.
The statistical base for writing the work is based on the forms of accounting and financial statements of insurance organizations submitted in the prescribed manner to the Federal Insurance Supervision Service.
The course work consists of three chapters. The first chapter deals with the theoretical foundations of the financial activities of insurance companies. In the second chapter, an analysis of the formation and use of financial resources of JSC "Insurance House VSK" is carried out. The third chapter is devoted to the prospects for improving the financial activities of VSK OJSC, taking into account its existing shortcomings.
Chapter 1. Theoretical foundations of the financial and economic activities of an insurance company
1.1 General characteristics of the finances of the insurance company
The economic essence of the finances of an insurance organization is primarily due to the main tasks of this type of organization, among which are:
Provision of insurance services to enterprises, institutions and the population on an individual and group basis;
Ensuring timely guaranteed payments of insurance compensation;
Implementation of insurance activities on the principles of financial stability and profitability of insurance operations.
All of the above tasks are, in turn, subject to the main goal of insurance as an economic category, which has its ultimate purpose of satisfying human needs through a system of insurance protection against accidental hazards.
To achieve this goal, the insurer forms and uses the funds of the insurance fund, which is the material embodiment of insurance protection. This is necessary to cover the loss resulting from the occurrence of an insured event, as well as to finance own costs associated with the costs of conducting cases and preventive measures.
So, the finances of insurance organizations are economic, monetary relations, regulated by the state, which develop regarding the formation, use of their own, attracted and borrowed resources, in order to realize the mission of the insurance organization and ensure an increase in its market value.
External manifestations of the essence of the finances of insurance organizations are their following functions:
Mobilization: finds its expression through the accumulation of financial resources through monetary contributions to compensate for possible damage to business entities or losses of individuals due to the consequences of insured events;
Distributive: implies the presence of redistributive relations associated, on the one hand, with the formation of an insurance fund with the help of pre-fixed insurance payments, on the other hand, with compensation for damage from this fund to insurance participants;
Control: implies the obligatory control over the formation and use of funds of funds both from external authorized structures in relation to the insurance company, and from the organization itself through the internal controlling system.
In the process of carrying out its financial and economic activities, the insurance organization enters into various kinds of financial relations, among which the following groups can be distinguished:
1) external financial relations, implying relations with budgets of all levels and extra-budgetary funds, with direct participants in the financial market infrastructure, with partners in operating activities and other economic entities;
2) internal financial relations, i.e. relations between parent and subsidiary insurance organizations, between their various structural divisions (“responsibility centers”), relations with the owners of the insurance organization, with its founders and staff.
Important aspects of insurance activities are: 1) the probabilistic nature of the occurrence of an insured event and payments on it; 2) a closed solidary distribution of damage among the insurers; 3) commercial calculation as the basis for organizing the finances of the insurer. All this directly affects the structure of tariff rates, reflecting the price of insurance risk and other expenses of the insurer under the concluded insurance contract. The tariff rate at which the insurance contract is concluded consists of two parts: the net rate and the burden, which includes, in addition to the costs of organizing and conducting the insurance business, elements of the insurer's profit.
Financial resources that are in economic circulation and used for insurance operations and investment activities are called the financial potential of the insurance organization. The financial potential consists of own, attracted and borrowed capital, the ratio of proportions of which depends on the financial capabilities and needs of a particular organization.
The equity capital of an organization is formed primarily from the authorized capital formed from the contributions of its founding members, additional capital, reserve capital, which is formed from profits and the emergence of which does not entail any associated financial obligations and has the sole purpose of supplementing the authorized capital in case of need to compensate for unplanned losses and damages in the absence of other means, as well as retained earnings of the organization. According to the conditions for ensuring financial stability, set out in Article 25 of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On the Organization of Insurance Business in the Russian Federation” (hereinafter referred to as the Law), insurers must have a fully paid authorized capital, the amount of which must not be lower than the minimum amount of authorized capital established by the Law.
The attracted capital of an insurance company is represented by insurance reserves, the source of which is the aggregate net rate of insurance premiums (contributions) received by the insurance company and reflecting the amount of the insurer's unfulfilled obligations under the contracts concluded with the insured at the moment. It is important to note that these funds are at the disposal of the insurance organization temporarily, for the period of the insurance contract, after which they are used to pay the sum insured, or are converted into a revenue base when the contract breaks even.
The composition of the borrowed capital of the insurer includes accounts payable, bank loans and borrowings.
The initial source of cash flow to the insurance company is the insurance premium (contribution) of the insured. As the insurance contract temporarily passes and in the absence of insurance payments, one part of insurance premiums, which is called earned, is attributed to income from insurance activities, the other - unearned - represents deferred expenses. Schematically, the time process of distribution of insurance premiums can be depicted as follows:
It can be seen from this diagram that one of the features of the organization of finance in insurance is that the insurance funds and insurance reserves of the insurer have different economic content and, therefore, are reflected in different sections of the balance sheet of the insurance organization.
1.2 Insurance reserves: essence, classification, calculation methods and placement rules
“In order to ensure the fulfillment of obligations under insurance, reinsurance, insurers, in the manner established by the regulatory legal act of the insurance supervisory authority, form insurance reserves”, which are used exclusively for making insurance payments (from Article 26 of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On the organization of insurance business in the Russian Federation”) .
Insurance reserves are a set of special purpose funds of funds that provide a joint distribution of losses among insurance participants and are intended for making insurance payments, as well as used as temporarily free funds as a source of investment activity.
The presence of insurance reserves is the basis of the solvency of the insurance company. The concept of "the amount of insurance reserves" is extremely arbitrary, since the amount of liability of the insurer under insurance contracts due to the continuity of insurance operations and periodic changes in the number of policyholders is in constant dynamics. The composition and volume of insurance reserves depend on the degree of influence of various factors, such as:
the specifics of the insurance activity of a particular organization;
· the structure of the insurance portfolio;
· development of reinsurance;
· the level and rate of inflation, reflecting the relationship between the decrease in the purchasing power of reserves and the depreciation of liabilities.
By transferring part of the risks to reinsurance, the insurer relieves itself of the obligation to form the corresponding special reserves.
In accordance with the requirements of the insurance legislation of the Russian Federation, the reserves of insurance companies are divided into reserves for life insurance and reserves for types of insurance other than life insurance (ie risk types).
Such a division is associated with different content of insurance coverage, the nature of the risk, function, tasks and, as a result, the methodology for calculating tariffs. There is also a further, more in-depth classification of insurance reserves by their types. To better visualize it, let's turn to the following figure:
· established in agreement with the Federal Service for Insurance Supervision. (FSSN).
Life insurance reserves are intended for settlements with the insured after the expiration of the contract.
At present, there are no general mandatory rules for the formation of insurance reserves in the life insurance practice, which allows insurance companies to independently develop documents that determine the procedure for the formation of the relevant reserves, subject to further approval by the insurance supervisory authorities.
The basis for calculating the amount of this reserve is the net insurance premium received as a result of the conclusion of life insurance contracts in the reporting period.
If the insurance organization does not have its own regulation on the formation of an insurance reserve for life insurance, approved by the relevant authorized body, the amount of reserves is calculated in accordance with the recommendations of Rosstrakhnadzor dated December 27, 1997 No. 09 / 2-16r / 02.
The unearned premium reserve (URP) represents the underlying insurance premium received under insurance contracts in force in the reporting period and related to the period of validity of the insurance contract that goes beyond the reporting period.
Regular reporting involves determining the scope of the insurer's liability for a specific reporting date. The liability of the insurer under insurance contracts concluded from the reporting date and effective after it, in the relevant part, is transferred to the future period.
The premium corresponding to the amount of liability carried over to the next period is referred to as unearned premium. Part of the liability attributable to the reporting period is recognized as conditionally fulfilled, and the share of the premium corresponding to this part is considered earned. The unearned portion of the insurance premium is subject to reservation.
The reserve of unearned risk premium (net premium) is usually called the reserve for unfinished liability, or, in short, the premium reserve.
The procedure for calculating the reserve for losses for insured events is of great importance in the practice of insurance. Insurance practice shows that for most types of insurance (especially such complex ones as insurance of ships, construction and installation risks, liability insurance, etc.), it takes a long time to finalize and pay for the loss. Considered, but not yet fully paid, the loss is called an unfinished loss. For the amount of considered but not settled losses, the insurer creates a reserve for reported but not settled losses (RZU). The RZU value is determined for each unsettled claim. If the loss is declared, but the amount of damage is not established, then the maximum possible amount of loss, not exceeding the sum insured, is taken into account for calculation. RZU is created to ensure the fulfillment of obligations, including expenses for the settlement of losses under insurance contracts that have not been performed or not fully performed as of the reporting date.
The reserve for incurred but not reported losses (RPR) is intended for the insurer to fulfill its obligations, including the costs of settling losses under insurance contracts that arose in connection with insured events that occurred during the reporting period, the occurrence of which was not declared to the insurer in the prescribed manner on reporting date.
As a general rule, the amount of the reserve is calculated in the amount of:
10% of the amount of the basic insurance premium received in the reporting period, if the reporting period is a year;
10% of the amount of the basic insurance premium received in the reporting period, and for the three periods preceding the reporting period, if the reporting period is a quarter.
According to paragraph 6 of Article 26 of the Law, "an insurance company has the right to form a fund of preventive measures in order to finance measures to prevent the occurrence of an insured event." Rationing of the reserve of preventive measures (RPM) is carried out by insurers independently. The reserve is formed by deductions from the gross insurance premium received under insurance contracts in the reporting period. The value of RPM corresponds to the amount of deductions to this reserve in the reporting period, increased by the amount of the reserve at the beginning of the reporting period and reduced by the amount of funds spent on preventive measures in the reporting period.
These funds can be used to finance:
Construction and reconstruction of fire stations, testing laboratories and ranges, diagnostic stations of the State traffic inspectorate to check the technical condition of vehicles;
Purchase of equipment for the prevention of road accidents;
Carrying out preventive and sanitary-hygienic measures to protect public health and reduce injuries (professional examination, vaccinations, vaccinations) and many other types of preventive measures aimed at reducing the risk of losses and reducing their possible scale.
Control over the spending of RPM funds is carried out by supervisory authorities in the manner prescribed by applicable law.
Formation of a group of additional insurance reserves is carried out in agreement with the Federal Insurance Supervision Service.
The stabilization reserve is an assessment of the insurer's obligations related to the implementation of future insurance payments in the event of a negative financial result from insurance operations due to the action of factors beyond the control of the insurer, or in the event that the incurred loss ratio exceeds its average calculated value.
Due to the fact that insurance reserves belong to the category of borrowed funds of an insurance company, they must be used strictly for their intended purpose in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation. For these purposes, the federal executive body for the supervision of insurance activities adopted a document - the Rules for the placement of insurance reserves by insurers - defining the requirements for the composition and structure of assets accepted to cover (secure) insurance reserves, control over compliance with which is carried out by the Federal Insurance Supervision Service.
Assets accepted to cover insurance reserves must meet the conditions of diversification, repayment, profitability and liquidity.
Compliance of the insurer's activities in the placement of insurance reserves with the principles of diversification, repayment, profitability and liquidity is determined by the fulfillment of the structural ratios specified in the Appendix to the Rules for the placement of insurance reserves by insurers. When calculating these structural ratios, the book value of the assets is used. The total value of assets accepted to cover insurance reserves must not be less than the total amount of insurance reserves.
1.3 Investment activity of an insurance company: conditions, regulation, evaluation indicators
According to the insurance legislation of the Russian Federation, "insurers have the right to invest and otherwise place the funds of insurance reserves in the manner prescribed by the regulatory legal acts of the insurance supervisory authority",
The insurance business has a number of specific features that leave a deep imprint on the nature of the investment activity of insurers. First of all, the federal legislation on insurance presents a list of mandatory conditions for the implementation of investment activities, such as:
The condition of return (reliability), which aims to ensure maximum security of investments;
Profitability condition, indicating the possibility of obtaining income from investment activities;
A liquidity condition that provides for the quick and harmless conversion of assets into cash.
In the general case, the conditions of reliability, profitability and liquidity contradict each other, since reliable investments are initially less profitable and liquid, and vice versa. However, this contradiction is overcome when the diversification condition is met.
Diversification condition - implies the distribution of capital between various investment objects in order to reduce the risk of possible losses of the capital itself and income from it;
An investment portfolio that meets all of the above requirements is called a balanced investment portfolio.
Due to the obligation to comply with these requirements and the constant impact of various types of investment risks, the behavior of insurers as investors is characterized by conservatism and caution. Investment risks introduce uncertainties into the possibility of earning income and cause the likelihood of loss of assets or shortfall in income on them, which can lead to a violation of the financial stability of the insurance company and, as a result, to the failure of the insurer to fulfill its obligations for insurance payments. There are many different types of investment risks, such as, for example: the risk of inadequate valuation of assets, the risk of depreciation of assets, the risk of non-compliance of assets with assumed obligations, the risk of illiquid assets, the risk of rate of return, the risk of participation, the risk of legislative changes, etc. - each of which should be taken into account when planning and implementing investment activities.
The investment activity of insurance organizations regulates investments both at the macro level and at the micro level. The purpose of macroeconomic regulation of investment activity is to ensure compliance with the requirements arising from the role of insurance as an institution of financial protection. As a reliable generator of financial capital, insurance organizations have a significant impact on the investment market. An objective prerequisite for this is the fact that the receipt of insurance premiums precedes the provision of insurance services. The resulting time lag allows insurance organizations to accumulate significant amounts of money and place them in various financial instruments and non-financial investment assets for a given period. The provision of insurance services, during which significant insurance funds are formed at the expense of funds received from policyholders, stimulates the circulation of funds in the capital market and contributes to the transformation of household savings into investment resources.
The fundamental goal of microeconomic regulation is to achieve a situation in which the placement of assets of insurance organizations in terms of investment volumes and income received from them, in place and time, corresponded to the volume and quality characteristics of the obligations assumed.
Considering that most of the insurance contracts other than life insurance are concluded for a period not exceeding one year, while some, not known in advance, part of the accumulated resources may be required at any time to pay insurance claims, the funds received by insurers at the expense of insurance premiums should be invested primarily in highly liquid, medium and short-term assets. The same applies to part of the unearned premium reserves.
The situation is different with insurance premiums received under life insurance contracts. Firstly, insurers can invest a significant part of life insurance reserves in relatively long-term investment projects, and secondly, in this case, it seems possible to reduce the liquidity requirements for such investments. However, at this stage in the development of the Russian insurance market, long-term investment (cumulative) life insurance is still in its infancy, while in other countries it is this sector that provides the vast majority of insurers' investments.
In addition to borrowed funds, at the expense of which insurance reserves are formed, insurers have their own funds in the form of authorized, reserve, additional capital, as well as retained earnings, which can also be used in investment activities. As a guarantee of the stability of the insurance organization and its ability to fulfill its obligations and develop, these resources are usually free from specific obligations, which allows the insurer to invest part of them in long-term, low-liquid types of investments,
Among other sources of the insurer's funds that serve as an investment object, reserves of preventive measures can be distinguished. Despite the fact that the formation of this type of reserves is voluntary, the “investment in security” implemented at their expense must also comply with the principles of return and payback.
The following sequence of stages of building an investment portfolio is distinguished:
1) setting a goal and choosing an investment strategy, which involves, first of all, identifying investment potential in accordance with the possibilities of temporarily free financial resources, as well as finding the optimal time interval, taking into account the structure of the insurance portfolio;
2) collection of information on financial instruments, the use of which satisfies the parameters and proportions specified by the regulatory framework;
3) identification of the main and secondary factors affecting the change in the structure of the investment portfolio; creation of a database for monitoring the assessment of the quality of investments;
4) determination of the effectiveness of various options for the formation of an investment portfolio; substantiation of the optimal portfolio option in accordance with the chosen strategy with the optimal ratio of risk and profitability
5) drawing up, based on the analysis of the information received, an optimal investment portfolio that can provide reliable and profitable placement of temporarily free funds.
According to analysts' forecasts, due to the steady growth of the domestic insurance market as an industry that is extremely important for the economic and social prosperity of the country, the trend towards increasing the investment opportunities of insurers, taking into account the balance of interests of all participants in insurance activities, will become inevitable in the coming years.
1.4 Analysis of the activities of the insurance company. Financial stability: concept, factors, legal regulation
In connection with the increase in the turnover of funds circulating in the segment of the insurance business and the expansion of the range of insurance services, there is an objective need for a methodology for effective control over the performance of insurance organizations both by the state and other interested parties.
A decisive role in the information support of insurance activities is played by financial statements, which, regardless of the organizational and legal form of the insurance organization, are subject to publication in the media.
The necessary conditions for the publication of the financial statements of an insurance company are, firstly, its verification and confirmation by an independent audit firm and, secondly, its approval by the general meeting of shareholders.
Publication is mandatory for the Balance Sheet (form No. 1 - insurer) and the Statement of Financial Results (form No. 2 - insurer).
Moreover, the list of forms of financial statements sent to the Federal Service for Social Insurance and its territorial bodies in the order of supervision ¨ is defined by law.
Improving the quality of information generated in accounting in order to adequately disclose the financial position and financial results of the insurer is one of the most important tasks of the financial services of insurance organizations. A special role in this in recent years has been played by the reform of the Russian accounting system in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), which makes it possible to ensure the comparability of financial indicators of companies on a global scale and increase the availability of reporting information for external users.
Financial statements prepared in accordance with IFRS differ significantly from those prepared in accordance with Russian Accounting Standards. However, in whatever format the financial statements of the insurance company are presented, its task is to assess the financial position and financial performance of the insurance company.
The financial position of the insurer is disclosed by interpreting the indicators of assets, liabilities and equity (primarily on the basis of balance sheet data), and financial results - by interpreting the indicators of income, expenses and profits reflected in the income statement.
To analyze various aspects of the insurance company's activities, absolute cost estimates are used that characterize the volume of activities, as well as relative indicators (coefficients) that reflect the quality of the insurance business.
When assessing the financial condition of the insurer, approximately the following set of indicators is used:
Dynamics and structure of assets and liabilities of the balance sheet;
Business activity and profitability;
Estimation of insurance liabilities;
Liquidity and solvency;
Security with own working capital, etc.
The concept of financial stability of insurance organizations implies their ability to fulfill their obligations under the existing conditions, as well as in the event of probable adverse changes in the external and internal environment.
Considering that finance as an economic category has the property of quantitatively displaying the production process through financial resources, financial stability has an objective basis for quantitative expression, on the basis of which financial stability can also be considered as the ability of a market entity to maintain the quantity and quality of its financial resources when the environment changes. In this case, the quality of financial resources is understood as the degree of their compliance with the main goal of the subject - survival and development in a market environment.
The state of stability (instability) of an insurance company is formed under the influence of factors of different nature. Some of these factors are manageable to some extent, and some are not. On this basis, they can be grouped as follows:
The insurance company, in comparison with many other business entities, has significant features in the sources of formation of financial resources, their structure and movement, which is due to the place of the insurance industry in the economy.
The insurance risk underlying insurance operations objectively causes an increase in the requirements for the quality of the financial resources of an insurance company. These requirements make it possible to single out a specific sign of financial stability, inherent only to an insurance company: the correspondence of the quantity and quality of resources to the magnitude and structure of the accepted insurance risk, which primarily means the possibility of fulfilling the obligations of the insurer to policyholders.
In order to strengthen the positions of insurers as market entities and to assess their financial stability in the course of supervision of insurance activities by the state, there are certain standards, the observance of which is mandatory. The procedure for calculating and evaluating such standards is regulated by a number of documents, primarily by the Law “On the Organization of Insurance Business in the Russian Federation”. In particular, it states that economically justified insurance rates are guarantees for ensuring the financial stability of the insurer; reinsurance; own funds; insurance reserves sufficient to fulfill obligations under contracts of insurance, co-insurance, reinsurance, mutual insurance. Insurers are obliged to comply with the established financial stability requirements in terms of the formation of insurance reserves, the composition and structure of assets accepted to cover insurance reserves, reinsurance quotas, the standard ratio of the insurer's own funds and assumed liabilities, the composition and structure of assets accepted to cover the insurer's own funds, and as well as the issuance of bank guarantees.
Another document defining financial standards for insurance organizations is the “Regulation on the procedure for calculating by insurers the normative ratio of assets and insurance liabilities assumed by them”, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance dated 02.11.2001 No. 90-n. This Regulation establishes the methodology for quarterly calculation of the solvency margin, which is understood as the amount within which the insurer, based on the specifics of the contracts concluded and the volume of insurance obligations assumed, must have or has own capital, free from any future obligations, except for the rights of claim of the founders, reduced on the amount of intangible assets and overdue receivables. At the same time, the actual size of the solvency margin of the insurer should not be less than the standard size of the solvency margin of the insurer.
If at the end of the reporting year the actual size of the solvency margin of the insurer exceeds the standard size of the solvency margin by less than 30%, the insurer submits for approval to the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation as part of the annual financial statements a plan to improve the financial situation.
The plan indicates specific measures that contribute to the stabilization of the financial situation, indicating the duration of the event and the amount of income (savings) planned to be received from this event.
When drawing up a plan, priority should be given to measures that lead to the improvement of the financial situation of the insurer in the shortest possible time.
As financial recovery measures, the following may be envisaged: changing the size of the authorized capital, expanding reinsurance operations, changing the tariff policy, reducing accounts receivable and payable, changing the structure of assets, as well as using other methods of maintaining solvency that do not contradict the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Another important document aimed at stabilizing the financial position of insurance organizations and the insurance market as a whole is the order of the Ministry of Finance dated December 16, 2005 No. 149-n, containing “Requirements for the composition and structure of assets accepted to cover the own funds of insurers” .
To a large extent, the financial stability of an insurance organization is ensured by maintaining the authorized capital at the proper level and providing it with net assets, i.e. own highly liquid funds. In accordance with paragraph 3 of article 25 of the Law, the minimum amount of the authorized capital is determined on the basis of the base amount equal to 30 million rubles, and the corresponding coefficients (from 1 to 4), established depending on the nature of the activity carried out.
The value of net assets and its positive dynamics are one of the indicators of the financial well-being of any company, so insurance organizations should regularly monitor the value of net assets. Since 2007, it has been determined in accordance with the joint order dated February 1, 2007 of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 7-n and the Federal Service for Financial Markets dated No. joint-stock companies". According to this document, the value of net assets is determined according to the balance sheet of the insurance company by reducing the amount of assets by the amount of liabilities (ie, the volume of liabilities) accepted for calculation. Estimation of the value of net assets must be made by the company quarterly and at the end of the year on the relevant reporting dates and disclosed in the interim and annual financial statements.
A detailed assessment of the insurer's activities using various financial indicators allows interested parties to obtain comprehensive information about its financial position and financial results of its activities.
Chapter 2
2.1 Economic characteristics of OJSC Insurance House VSK
The analysis of the dynamics of the financial performance of VSK reflects a qualitative progressive movement towards increasing the profitability of its insurance operations, as evidenced by the value of the Company's net profit, which steadily demonstrates a confident upward trend (see Table No. 5).
Table number 5. Key financial indicators of VSK Insurance House
Unfortunately, at the time of writing this term paper, VSK has not yet published official financial statements for 2007, therefore, there are no reliable data on the amount of profit received for the previous reporting period, as well as information on other financial indicators of the Company for 2007. Naturally, this does not allow to fully compare the current financial position of VSK with the previously achieved results, however, based on the positive dynamics of past years, it is possible to predict with a high degree of confidence that the emerging favorable trend towards improving the financial stability and solvency of the Company will continue. This contributes, first of all, to the efficient and rational use of the financial resources of the company in order to most fully realize the interests of insurers.
2.2 Dynamics of financial performance indicators of SD VSK
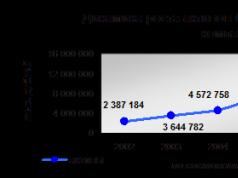
In 2007, the growth of the main financial indicators of VSK Insurance House continued, as well as the strengthening of its financial position. Net profit increased by 250%, from 493 million rubles to 1234.8 million rubles. Profitability (the ratio of annual profit to the Company's premium) increased from 5.35% in 2006 to 9.85% in 2007.
The main factors of such growth were: the dynamic development of voluntary types of insurance, the tariff policy of the Company adequate to the market situation, the strict control of the VSK Board over the structure of the insurance portfolio and the costs of doing business.
As we can see from this diagram, the level of insurance indemnity payments, which shows what percentage of payments are in the total amount of collected insurance premiums, is significantly lower than the level of premiums (total contributions of policyholders).
During the reporting period, the Company's assets increased by 138% and exceeded 13,509 million rubles. The volume of receivables from insurance operations also increased. This circumstance affected the indicators presented in VSK's balance sheet. Nevertheless, a comparison of dimensional indicators, reduced by the amount of receivables from insurance operations, allows us to trace the continuation of the trend of the Company's uniform development.
The steady growth in the value of assets allows us to make a well-founded conclusion about the steadily increasing volume of work and literacy of the insurance activities carried out by the company.

As of January 1, 2007, the Company's fixed assets amounted to 935.7 million rubles, which is almost 41 million rubles more than in 2006. This steady upward trend is fully in line with the growth rates of previous years. The structure of fixed assets in the dynamics of the last two years is as follows:
Dynamics of the structure of fixed assets of JSC "VSK" (thousand rubles)
| Name of indicator | Availability as of 01/01/2006 | Received | dropped out | Availability as of 1/01/2007 | |
| 1. | Building | 608 654 | 58 329 | (79 406) | 587 377 |
| 2. | Structures and transmission devices | 3 090 | 75 | - | 3 615 |
| 3. | cars and equipment | 167 306 | 34 489 | (3 325) | 198 470 |
| 4. | Vehicles | 77 188 | 31 522 | (7 379) | 101 331 |
| 5. | Household inventory | 36 391 | 7 032 | (1 146) | 42 277 |
| 6. | Other types of fixed assets | 1 302 | 636 | (24) | 1 914 |
| 7. | Land plots and nature management objects | - | 930 | - | 930 |
| Total: | 893 931 | 133 013 | (91280) | 935 664 | |
Maintaining high solvency and readiness of the Company to promptly fulfill obligations arising in the course of insurance activities is one of the most important areas of work of the VSK Board. To this end, a high level of current liquidity of assets was ensured.

The share of absolutely liquid assets - cash in 2007 exceeded the average market level and amounted to 22.4% of the balance sheet. Despite the fact that during the year this indicator fluctuated, it should be noted that the Company maintains instant liquidity at a sufficient level. Thus, over the past two years, the amount of funds on the Company's settlement and foreign currency accounts has constantly exceeded 370 million rubles. In addition, liquidity is supported by other banking instruments - deposits and bills. As a result, the Company's real working assets belonging to the first liquidity group significantly exceed its liabilities.
It should be noted the positive impact on the level of the Company's solvency of a balanced placement of assets accepted to cover insurance reserves.
Independent experts of the rating agency "Expert RA" estimate the adequacy ratio of VSK's own funds (the ratio of own funds to net contributions for voluntary types of insurance) as superior to the average market level.
The main financial resource for expanding the activities of VSK is its own funds, a sufficient amount of which makes it possible to create new insurance services, improve service, and develop a branch and agent network.
In 2006, the Company's own funds increased by 1.4 times and amounted to 3,483,632,000 rubles. The stable growth of own funds is a direct evidence that the company is developing, that it is able to take on more obligations, because. has sufficient financial resources to service a larger number of insurance contracts.
At the end of the reporting period, the own funds of Insurance House VSK JSC consisted of 49% of the authorized capital, 47% of retained earnings of the reporting year and previous years, 0.36% of additional capital and 2.95% of reserve funds formed in accordance with the law.

As a positive fact based on the results of 2007, it is necessary to note the increased efficiency of the use of equity capital (the ratio of the Company's profit to equity). During the year, this figure increased from 19% to 35%.
As of the beginning of 2007, the Company's paid-in authorized capital amounted to 1,700 million rubles, which exceeds the authorized capital of 2004 by 1 billion rubles. A regular increase in the authorized capital indicates an increase in the stability and responsibility of the insurer, its readiness to assume obligations to a growing number of customers.
This indicator corresponds to the volume and nature of VSK's activities, the status of a federal company, and significantly exceeds the requirements of the insurance supervisory authorities. In terms of its authorized capital, VSK is one of the ten largest insurance companies in Russia.
In the short term, VSK plans to significantly increase the volume of insurance operations, primarily in the insurance market for individuals. In this regard, an increase in the authorized capital is a guarantee of the successful implementation of the company's plans and a guarantee of VSK's responsibility to each client.
Insurance reserves increased by 1.37 times compared to 2006 and as of 01.01.2007 amounted to 8,854 million rubles. Due to the specifics of the insurance business as such, this indicator is of particular importance for clients of insurance companies. The amount of insurance reserves shows whether the insurance company will be able to fulfill its obligations to customers under any conditions and in any situation.

Let's analyze the financial condition of VSK Insurance House JSC as of 01/01/2007 based on the balance sheet data:
1. Current liquidity ratio (gives an overall assessment of the liquidity of assets):
The value of current current assets / the value of short-term liabilities = ((220) + (250) + (270)) / (690) = (799,071 + 60,735 + 3,027,111) / 1,171,696 = 3.317.
This result indicates that for 1 ruble of current liabilities JSC VSK has 3.317 rubles of liquid assets, which is quite in line with the norm, because the basis for recognizing the balance sheet structure as unsatisfactory, and the enterprise insolvent is the value< 2.
2. Ratio of own working capital:
Sources of own funds / value of non-current assets = (total of section II of the balance sheet, (490)) / ((110) + (122) + (230) + (240)) = 3,483,632 / (24 + 12,535 + 935,664 + 162 240) = 3.137
The actual indicator of the provision with own working resources many times exceeds the minimum standard indicator (0.1), which again allows us to conclude that the structure of the balance sheet is satisfactory.
3. Absolute liquidity ratio (solvency) - the most stringent indicator for determining the liquidity of an enterprise (shows what part of short-term borrowed funds can be repaid immediately if necessary):
Cash / current liabilities = (270) / (690) = 3,027,111 / 11,171,696 = 2.58
Given that the lower limit of this indicator is set at 0.2, i.e. a solvent organization must be able to immediately pay off at least 20% of its short-term liabilities, VSK in this sense is an absolutely liquid insurance company.
4. Financial risk ratio - the ratio of equity to borrowed funds, showing how much borrowed funds the company has attracted for 1 ruble of its own funds:
Borrowed funds / own funds = (690) / (490) = 1,171,696 / 3,483,632 = 0.33.
It is believed that if the value of this indicator exceeds one, then the financial autonomy and stability of the assessed organization reach a critical point. The recommended value is no more than 0.7. The indicator of JSC "VSK" satisfies the recommended value, which positively characterizes the financial stability of the company.
5. Debt ratio calculated as the ratio of borrowed funds to the balance sheet currency:
= (690) / (300) = 1 171 696 / 13 509 646 = 0, 0867
The normative value of the ratio of attracted capital should be less than or equal to 0.4, which is quite consistent with the result of JSC "VSK". Given that the share of borrowed funds in VSK's balance sheet currency has remained at a consistently low level over the past years, we can conclude that the company's financial stability is strengthening, which makes it more attractive to business partners.
6. Coefficient of maneuverability of own sources:
Own working capital / sum of sources of own funds = ((250) + (270)) / (490) = 3,087,846 / 3,483,632 = 0.88
This indicator reflects the degree of mobility (flexibility) in the use of own funds, i.e. shows what part of VSK's equity capital is not fixed in non-current values and gives the Company's management the opportunity to maneuver with these funds. The calculated indicator of VSK slightly exceeds the normative one, set at the level of 0.2-0.5. This is due to the high share of cash in the total assets of VSK. The resulting value indicates that the insurer has extremely wide opportunities for financial maneuvers.
7. Return on equity ratio:
Profit of the reporting year / equity = 1,234,318 / 3,483,632 = 0.35
A high profitability ratio (35 kopecks of profit per 1 ruble of own funds) is an indisputable proof of the financial stability and profitability of the insurer's activities.
8. Profitability of certain types of insurance:
Life insurance profitability = profit from life insurance operations / amount of insurance premiums * 100% = 24,488 /102,370 * 100% = 23.9% (in 2006, the same indicator was 4.6%)
Profitability of insurance other than life insurance = 2,388,501 / 12,013,555 * 100% = 19.88% (2006: 16.88%)
So, let's summarize the analysis of the financial condition of VSK Insurance House OJSC: this organization uses all sources of financial resources, fully covers reserves and costs, has excellent indicators of financial stability and solvency. Its activities are generally successful and comply with the requirements of the current legislation, which indicates its competitiveness and attractiveness for potential insurers. Such a high rating has been repeatedly confirmed by the highest reliability rating assigned to the Company annually - “Class A ++”
The main condition for achieving such a level of success and efficiency of the insurance business, which we observed on the example of VSK Insurance House OJSC, is complete transparency of financial and insurance operations, stable mutually beneficial partnerships with customers, and high professionalism of employees.
2.3 Structure and efficiency of investment activities of VSK OJSC
When analyzing the investment activities of OJSC "Military Insurance Company", the consolidated financial statements of this insurance organization as of January 1, 2007, as well as a part of the annual report devoted to the financial performance of VSK for 2005, were used.
Investment activity is important for the functioning of insurance organizations in general, therefore, the resources used for these purposes make up a fairly significant part of their financial flow. In particular, in 2005 and 2006 the Military Insurance Company invested almost half of its total assets in various financial instruments: 49 and 43.8 percent, respectively.

However, despite the fact that the achieved indicator generally corresponds to the market average, it must be admitted that it is still significantly lower than the similar average indicator recorded by the largest insurance companies in Moscow at the level of 75-80%. The main reason for this is a consistently large share of cash in the assets of VSK: according to the financial statements as of 01/01/2007 - 22.4%.
As mentioned in the previous chapter, the largest source of resources that form the investment potential, in addition to the insurer's own funds, are the funds of insurance reserves. In the insurance company in question, they are represented by:
life insurance reserves
Loss reserves
Unearned premium reserve
Reserves for future expenses
Reserves for doubtful debts
Allowance for depreciation of securities
As well as reserves of preventive measures.
The share of equity in the structure of investment sources of VSK, according to data published on the official website of VSK on the Internet (www.vsk.ru), is approximately 30% of the funds accumulated by the Company for investment purposes.
As of January 1, 2007, the insurance reserves of OJSC Military Insurance Company amounted to 8,854,318 thousand rubles. Thus, VSK's insurance reserves accounted for more than half of the organization's sources of funds, to be more precise: more than 65% of its total assets (13,509,646 thousand rubles). However, life insurance reserves, which are the most reliable source of "long" money for investment purposes, accounted for an extremely small share in the total mass: only 2.5%.
Due to the fact that the main part of insurance reserves falls on types of insurance other than life insurance (contracts under which, as a rule, are concluded for a period of not more than one year), the funds received by the Company under these contracts are invested mainly in highly liquid, medium and short-term assets in case of an urgent and sudden need of the Company for cash to make insurance payments.
The structure of investments of the analyzed insurance organization is presented in the table below.
Structure of investments of JSC "Military Insurance Company"
| Investments | Short term | Long term | ||
| 2006 | 2007 | 2006 | 2007 | |
| Land | - | - | - | - |
| Building | - | - | - | - |
| Financial investments in subsidiaries, affiliates and other organizations | 35 210 | 15 000 | 60 566 | 25 795 |
including: Shares of subsidiaries and affiliates |
- | - | 64 | 851 |
| - debt securities (bonds) ~ | - | -- | - | - |
| - bills ~ | 35 210 | 15 000 | - | - |
| - granted loans | - | - | - | - |
| - contributions to authorized (share) capital ~ | - | - | 60 502 | 24 944 |
| Financial investments in other organizations | 2 652 481 | 3 073 781 | 76 100 | 76 920 |
including: Shares of other organizations |
472 192 | 956 281 | 20 | 840 |
| - bonds | 241 816 | 276 228 | - | - |
| - bills | 1 938 471 | 1 838 272 | - | - |
| - contributions to authorized (share) capitals | - | - | 76 080 | 76 080 |
| State and municipal securities | 95 714 | 58 753 | - | - |
| Deposits | 1 524 612 | 2 016 595 | - | - |
| Investment shares | 308 562 | 649 273 | - | - |
| Other investments | - | - | - | - |
| TOTAL: | 4 616 579 | 5 813 402 | 136 666 | 102 715 |
*data from the Appendix to the balance sheet (form No. 5)
As we can see, short-term investments vastly outnumber long-term investments, the share of which in the total volume of investments in 2005 barely reached 2.9%, and by the beginning of the next reporting period it had dropped to 1.7%.
According to the data given in the table, promissory notes of third-party organizations, as well as deposits, which account for more than a third of investments in both reporting periods, have the largest share.
On a much smaller scale, the Company allocates funds to assets associated with obtaining ownership shares in other organizations, preferring to such investments options for placing temporarily free funds: contributions to the authorized (reserve) capital of other organizations account for more than 55% of the value of long-term investments, however, in general In the volume of financial investments, contributions to the authorized capitals of other organizations are stable at only 1.6%.
To deepen the analysis of the investment policy pursued by VSK, let us consider the structure of investments of insurance reserves. In some respects, it differs significantly from the investment of all assets, including VSK's own funds. This is primarily due to the fact that the requirements for the structure of mobilized insurance reserves, which are investment objects, have recently been quite strictly regulated by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation,
The largest share is held by funds placed on the current accounts of banks. VSK accounts for more than 43% of total financial investments in this type of placement.
As you can see, VSK places more than one third of its insurance reserves in banks. Since most of the deposits are opened in such large commercial banks as Sberbank of Russia, VTB, Zenit Bank, AlfaBank and a number of other financial institutions with a reliability rating of BB- and Ba3 and higher from international rating agencies, the requirement of the supervisory authority not to exceed the value of bank deposits The 40% level of the total amount of insurance reserves is strictly observed.
As for investments in debt securities, in accordance with the new Rules, according to which investments in promissory notes of any organizations should not exceed 10% of insurance reserves. Based on this requirement, investments of VSK funds in bank bills, according to indicators at the beginning of 2006 and 2007, exceed the legally permissible rate by 32% and 21.6%, respectively.
On this basis, in the near future, VSK will be forced to reduce such investments, bringing them in line with federal rules.
Investments of insurance reserves in shares are significantly inferior to investments in various banking assets. In general, the share of investments of VSK reserves in shares for a period of not more than 1 year, according to the indicators as of 01/01/2006, was less than 11%. However, it should be noted that a year later this type of investment reached the level of 16.45%, while the total volume of short-term investments increased by 26%.
Investments in bonds in 2006 accounted for slightly more than 5% (5.2%) of VSK insurance reserves and slightly less than 5% (4.75%) - in 2007.
It is impossible not to pay attention to the fact that VSK places a much smaller share of insurance reserves in bonds than it is allowed by the relevant federal Rules, which establish a level of 20% of the total amount of insurance reserves as the upper limit.
According to the information published in the annual reports of VSK, after 2002, contributions to the authorized capital of limited liability companies and share capital of limited partnerships were excluded from the structure of its investment portfolio, since the new Rules for the placement of insurance reserves do not provide for this type of investment at the expense of insurance reserves.
Investments in mutual funds are a relatively new investment object, but despite this, this source of investment income is already characterized by a steady trend towards increasing its share in the total financial investments of the insurer. If at the beginning of 2006, the share of investment units in the structure of VSK's short-term investments was 6.7%, then at the same date in 2007 in absolute terms it more than doubled (from 308,562 thousand rubles to 649,273 thousand rubles ), and in relative terms by 1.6 times and amounted to 11.2%.
Investments in general bank management funds, housing certificates, and gold and silver bullion are not popular among Russian insurers in general. As of the beginning of 2006 and 2007, they were completely absent in the investment portfolio of VSK.
VSK's investments in state and municipal securities in 2005 amounted to 2%, and in 2006 their volume decreased quite sharply and barely reached 1% of the total size of VSK's financial investments.
As the calculation of the profitability of investment activities in 2006 shows, the profit of VSK from investment investments reached 735,053 thousand rubles, or 12.3% of the annual size of its investments, which in absolute terms exceeds the same indicator of 2005 by 2.6 times.
Chapter 3
3.1 The need to strengthen the financial foundations of the insurance business
Due to the high social importance of insurance as an institution of insurance protection, as well as the obvious trend towards raising the standards of insurance activities, it is extremely important for insurers to take measures to strengthen the financial foundations of their activities, increase guarantees, resulting in increased confidence on the part of potential customers and active attraction of business partners.
The state, for its part, is obliged to provide market participants with an adequate, actually functioning legislative and regulatory framework that meets all objective requirements and in no way hinders the development of insurance as an industry and its individual elements.
An objective need to strengthen the financial foundations of activity exists for all insurance organizations, regardless of the size of their authorized capital, the size of insurance reserves, the volume of the insurance portfolio and the set of specialized types of insurance. In particular, the need to strengthen the financial foundations and improve the quality of assets of VSK Insurance House OJSC is revealed in a detailed study of the financial results and relative indicators of its current, financial and investment activities. As our analysis showed, despite the fact that the financial position of VSK is generally very good and there are no grounds for suspicion of the insolvency of the insurer, there are still some slight deviations of the actual indicators from the recommended standards, some of which indicate an excessive conservativeness of the financial policy insurer. In this regard, no matter how good and optimistic the financial results of an insurance organization are, there is always the possibility (and with it the need) for their further improvement.
All aspects of activity related to financial management of insurance companies, incl. analysis and monitoring of the financial condition, forecasting of financial activity, study of factors of the external and internal financial environment and financial market conditions, formation of target indicators, development of financial policy, etc., are the object of financial planning.
To achieve the most positive results of the main activity, it is necessary that the preparation of financial plans is carried out at 3 time levels: the development of financial strategies, current plans and operational financial plans. It is important that the individual financial strategy of each insurance organization, based on increasing their market value and increasing competitiveness, would allow developing and substantiating a general strategy for creating an effective national insurance system.
As part of strategic financial planning in an organization, the following types of plans can be drawn up:
Plan for the receipt of insurance premiums (contributions);
reinsurance plan;
Plan for placement of insurance reserves;
Consolidated balance sheet of income and expenses, including:
Cash flow plan;
profit plan;
Forecast of the state of assets and liabilities;
Solvency forecast.
According to the current legislation, only the balance sheet (form No. 1) and income statement (form No. 2) are subject to mandatory official publication, respectively, insurance companies are not required to publish other financial statements. Moreover, this information in relation to each specific organization is a trade secret. Therefore, when speaking about recommendations for strengthening the sustainability and improving the quality of financial and investment activities, one can only be based on generalized data and offer not specific practical measures actually planned by a particular company, but again generalized measures that can strengthen the financial foundations of insurers, provided appropriate approach to them.
The list of key measures that can hypothetically lead to strengthening the financial positions of insurers include:
a) on the part of the state: improving the methodological approach to legal support in the development of legislative, regulatory and forecast documents that determine the key areas of the financial management system of the insurance system, as well as the introduction of uniform standards for supervision of the financial activities of organizations;
b) on the part of insurance organizations:
constant monitoring of the financial condition of the organization, development and timely refinement of indicators of the financial strategy; development of information technologies in the field of financial planning; conducting market research, studying its capacity and real needs; optimization of the sales system for specific insurance products; access to regional insurance markets, as well as markets of neighboring countries for a constructive exchange of experience with foreign colleagues.
3.2 Ways to improve the quality of assets and capital of an insurance company
financial reserve insurance
The quality of the assets and capital of an insurance organization directly indicates the financial condition of the organization. In relation to JSC "VSK Insurance House", based on the information obtained during the analysis of its financial position, in order to improve its financial condition, it is proposed to develop and implement a set of measures aimed at improving certain financial indicators of its activities. In particular:
1) optimize the ratio of equity and debt capital. VSK's balance sheet is dominated by its own funds, which, although it indicates a high degree of its financial stability, indirectly limits the pace of strategic development and the possibility of increasing financial profitability. In this regard, it is necessary to expand the financial potential by increasing the volume of debt financing. This measure, however, will be accompanied by an increase in financial risks, which will require a more thorough financial analysis.
Also, taking into account the size of individual reserve funds, it is proposed to direct part of the profit after taxation, in addition to repaying losses, to increase the reserve capital and to increase the accumulation fund;
2) in relation to investment activities: it is necessary, taking into account the requirements of the law, to reduce investments in government securities and shares and transfer them into deposits characterized by a higher return with an acceptable level of risk. In order to improve the financial performance of VSK's investment activities, it would also be advisable to expand the list of objects for investing temporarily free funds (which VSK does not lack at all), paying special attention to such promising financial market instruments as mutual funds and OFBU.
3) in relation to the costs of doing business: the data of the VSK balance sheet indicate the possibility of maximizing profits by reducing the costs of doing business by reducing management, administrative and other expenses;
4) in relation to debts: a favorable impact on the financial condition of VSK can have a reduction in accounts receivable, the total amount of which in the asset balance is quite a significant amount. As mentioned earlier, accounts payable are extremely insignificant and even have some "reserve" for its increase in order to further develop the company.
5) in relation to the tariff policy of the insurance organization: it is important to review and change the structure of the insurance portfolio, taking into account the possibility of termination (suspension) of activities by types of insurance that adversely affect the financial position of VSK.
On the whole, VSK's insurance portfolio is balanced: the unprofitability of some types of insurance is compensated by the high potential profitability of others. In particular, an analysis of the dynamics of receipt of premiums and payment of compensations showed that the mandatory state insurance of employees of the Tax Service of the Russian Federation is consistently unprofitable, and the type of insurance close to unprofitable is state insurance of military personnel and persons equated to them in state insurance. In this regard, in order to improve the financial performance of VSK, it is recommended to expand the scale of voluntary liability insurance and compulsory personal insurance of passengers and at the same time gradually reduce the number of contracts for unprofitable types of insurance.
Also, in order to prevent the acceptance of excessive risks for insurance, overloading the insurance portfolio, it is necessary to introduce limits on the maximum insurance amount for individual contracts. Moreover, synthesizing the experience of past years, VSK should eliminate the risks that affected the loss ratio of insurance operations.
To do this, it is advisable to increase the share of reinsurers in bearing risks for the most unprofitable types of insurance by concluding facultative and obligatory reinsurance contracts.
An important tool for the implementation of the financial strategy that can improve the efficiency of VSK performance should be the use of a balanced scorecard by management, which allows the systematic implementation of its strategic projects, translating them [indicators] into the language of operational management and monitoring the implementation of the financial strategy based on them. Those. we are talking about the need to introduce a system of individually justified standards that improve the comparability of the intended and actual results for their timely adjustment in case of deviation from the planned norm.
Summing up, let's summarize the content of this paragraph with what has already been said earlier.
1) The basis of the financial stability of any insurance organization is its real authorized capital, not inflated at the expense of those funds that cannot be used for compensation in full. It is important to ensure that the ratio of the obligations assumed by the insurance company to the level of resource provision does not exceed 1.
2) The surest way to improve the quality of assets is to place them in highly reliable instruments that meet the balance of risk and return.
3) The institution of reinsurance becomes an indispensable "assistant" in releasing the assets and capital of the insurer from excessive risks.
4) And, finally, another phenomenon that has, as a probable consequence, an improvement in assets and capital, which was not mentioned earlier, is the consolidation of an insurance company through merger or merger with another insurance company (including an organization with foreign capital ), which naturally rids the market of organizations with little capital and weak positions.
3.3 New sources and opportunities for the investment activity of an insurance organization
An important feature of insurance activity is that, with its proper planning, the organization has the ability to accumulate a huge amount of temporarily free funds and, subject to a number of requirements, place them for one or another period, depending on the number of upcoming payments and their urgency. Therefore, an insurer who wants to receive income from investments along with current operating and financial activities, one way or another, has to become an investor and resolve issues related to quality: reliability and profitability of investments made. It is important not to forget that at the same time as acquiring an additional source of income, the organization exposes itself to additional risks that inevitably involve investment activities.
As foreign experience shows, insurance as an institution has a huge potential of opportunities (including financial ones), so providing insurance organizations with a powerful stable inflow of “long” money into the economy would be a significant contribution of the insurance business to the sustainable economic development of the country.
At the present stage of development of insurance activity in Russia, the share of investments in the assets of insurers in comparison with large foreign companies is very small. To overcome this gap, Russian insurers will need to significantly increase the volume of investment. However, the instruments of investment activity currently available to domestic insurance companies do not fully meet the main requirement for the placement of insurance funds. It consists in achieving a sufficient level of profitability with a justified level of risk. This implies an objective market need for the development and implementation of new (or "updating" existing) investment instruments that meet the specified requirement and allow sufficient diversification of investments, and at the same time, the risks of insurers. In this sense, the following can be distinguished as possible investment objects:
Investments in government securities;
Investments in real estate;
Contributions to authorized (share) capitals of leasing companies;
Investment life insurance;
Investments in mutual funds and equity participation certificates in general funds of banking management.
Now I would like to talk in more detail in order about each of the listed instruments of investment activity.
Government securities, as one of the types of investments, are characterized, as a rule, by a guaranteed, however, extremely low yield, which in most cases lags far behind the average market rate and often does not even cover the current inflation rate. This is the main reason for the unpopularity of this type of investment among both commercial and insurance organizations, despite the fact that the latter impose special requirements on the reliability of investments.
Given that at the moment the state does not have a great need for borrowing from the population and organizations, it is impossible to predict with certainty that, even in the long term, the placement of funds in government savings bonds with coupon income will lead to the development of real savings insurance. However, this does not exclude the possibility of insurers using government securities to diversify their investments and, as a result, increase their reliability.
Interest from various categories of investors in investing in real estate is supported primarily due to their relatively stable high returns. Moreover, what is especially important for insurance companies: over the past 10-15 years, the mortgage market has been rapidly growing and developing in Russia, which opens up considerable additional opportunities for insurers. Insurers, in turn, are actively using the opportunities provided, as evidenced by a noticeable increase in the volume of mortgage risk insurance operations, the object of which may be the property that serves as the subject of mortgage, the health and working capacity of the mortgage borrower, as well as his liability for failure to fulfill his obligations. Thus, by investing the money of insurance reserves in the authorized capital of mortgage banks, insurance organizations can count not only on profits from mortgage operations, but on a significant expansion of their client base.
Another promising area of investment activities of insurance organizations is the insurance of leasing operations, which are essentially investment. In this case, we are talking about concluding long-term contracts with the lessee, which can provide the insurer with a long-term source of business. The lessee, in turn, thanks to insurance protection, gets the opportunity to purchase modern equipment and modernize technological processes without resorting to critical burdens on their budget.
Similarly to the previous example, insurance companies can become co-founders and participants in leasing companies and as such receive their share of the income from leasing payments. However, it is important to note here that when planning investment activities, the insurer in such cases must conduct a thorough assessment of the solvency of customers offering their investment instruments in exchange for concluding insurance contracts.
As noted earlier, one of the most powerful channels for raising funds for a long period is the monetary resources of the population, which are mostly passive and are often kept at home in cash. Abroad, temporarily free funds of the population form the basis of long-term accumulative life insurance, which, due to its specificity, is increasingly called investment. The accumulative nature of this type of insurance is ensured by a long period of attracting funds from insurers, during which the fluctuations in the value of securities that underlie the risk in short-term investment are leveled out, and an upward trend is more clearly manifested. However, in order for investment life insurance to become a significant source of long-term money in our country, large-scale work must be done to popularize life insurance as such.
And, finally, the last tool that can open up new opportunities for the investment activities of insurers and increase its efficiency, which I would also like to mention, is investments in shares of mutual funds (mutual funds) and in certificates of equity participation in general funds of banking management (OFBU). Due to the strict regulation of the requirements for the structure and quality of insurance reserves, the freedom of action of professional management companies and mutual funds that redistribute the insurer's financial resources received for management is largely limited. If the main goal of such legislative regulation is to increase the level of reliability of assets taken to cover reserves, then it is not logical that the maximum allowable amount of investments in shares, obviously more risky investment instruments, is 6 (!) times higher than the maximum value specified by the regulatory framework investments in mutual funds and OFBU, which, according to the requirements of the FSIS, should not exceed 5%. And this is despite the fact that the latter reduce the risk of possible losses due to diversification.
Summing up, let us list again the main points, the consideration of which will probably allow insurance companies to expand the possibilities of investment activities and improve its performance indicators.
First, it is necessary to expand the range of investment instruments used in a timely manner. Secondly, analytical work, which involves an assessment of the stock market situation and the search for suitable investment objects, should be carried out regularly. Thirdly, special attention should be paid to improving the culture and a kind of "literacy", awareness of consumers of insurance services, which is necessary for the formation of potential effective demand.
Conclusion
Currently, the Russian insurance market is regulated by legislation in the field of administrative, financial, civil law, the structure of which today objectively requires a number of improvements, without which the qualitative and, to some extent, quantitative development of the domestic insurance business seems hardly possible.
An extremely important event in the Russian insurance market was the reform of the financial performance standards of Russian insurance companies, which provides for a change in the rules for placing insurance reserves, as well as requirements for the composition and structure of assets accepted to cover insurers' own funds. However, it is likely that over time these rules will undergo certain changes.
An analysis of the current state and major trends in the development of the national insurance system indicates not only an increase in the level of state regulation of the market, but also the possibility of a qualitative increase in the role of insurance in the socio-economic system of the state.
The main point of the effective activity of insurance companies is the rational use of financial resources, which is achieved primarily through the formation of their sufficient volume and further competent use in the context of the main activities of the insurance company.
Based on the analysis of the financial statements of VSK Insurance House, the results of which, with a certain degree of error, reflect the general average market trends and can be projected onto other market participants, it can be concluded that the balance sheet is growing, while deposits in banks and cash funds, however, financial and investment investments in market instruments of other organizations are being reduced. At the same time, systematic work is being carried out to reduce accounts receivable from insurance and reinsurance operations.
In the future, for the effective development of financial activities, insurance companies should focus on solving such key tasks as:
Proper organization of marketing, building a sales system and infrastructure;
· development of skills and development of asset management technologies for insurance companies;
Improving the quality of customer service.
The most important directions for the development of "Insurance House" VSK "for the coming years are:
increase in the capitalization of the company;
· Expansion of investment activity with a reasonable correlation of liquid assets and liabilities according to the degree of urgency;
· activation of regional policy (increase in the share of regional fees);
· entering the markets of neighboring countries in order to assimilate the successful long-term experience of foreign insurance companies and expand the client base.
List of used literature
1. Laws and regulations
1.1. Civil Code of the Russian Federation (part two)
1.2. Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two)
1.3. Law of the Russian Federation "On the organization of insurance business in the Russian Federation" dated November 27, 1992 No. 4015-1
1.4. Regulations on the procedure for calculating by insurers the normative ratio of assets and insurance liabilities assumed by them, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 2, 2001 No. 90-n
1.5. Rules for the placement of insurance reserves by insurers, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of February 22, 1999 No. 16-n (with subsequent amendments and additions of August 8, 2005 No. 100-n)
1.6. Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation "Requirements for the composition and structure of assets accepted to cover the insurer's own funds" dated December 16, 2005 No. 149-n
1.7. Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation "On the Forms of Accounting Statements of Insurance Organizations and Reporting Submitted in the Order of Supervision" dated December 8, 2003 No. 113-n
2. Educational and special literature
2.1. Grishchenko N.B. Fundamentals of insurance activity: Proc. allowance. - M.: Finance and statistics, 2006. - 352 p.: ill.
2.2. Milyakov N.V. Finance: Textbook. - 2nd ed. - M .: INFRA_M, 2004. - 543 p., (Higher education)
2.3. Nikulina N.N., Berezina S.V. Insurance. Theory and practice: textbook. allowance (for university students). - 2nd ed., revised. and additional – M.: UNITI-DANA, 2007. – 511 p.
2.4. Orlanyuk-Malitskaya L.A. On the concepts and factors of financial stability. - M., 1996
2.5. Insurance: Textbook / under. ed. T.A. Fedorova, - 2nd ed., revised. and additional - M.: Economist, 2005. - 875 p.
2.6. Shakhov V.V. Insurance: Textbook for universities. - M.: UNITI, 2000. - 311 p.
3. Periodicals
3.1. Grebenshchikov E.S. The investment component of the insurance business: new sources and opportunities, Finance magazine No. 3 (2005), pp. 30-34
3.2. Kormanovskaya M.Yu. The evolution of state regulation of the solvency of insurers, magazine "Finance" No. 2 (2008), pp. 62-64
3.3. Merenkov, A.V. Implementation of the Balanced Scorecard / A.V. Merenkov // Management in an insurance company. - 2007. - No. 1. – P.18-19
3.4. Nikulina, N. N. A new paradigm of cash flows as an object of managing the financial resources of an insurer / N.N. Nikulina //. - 2007.- N 2. - S. 7-13
3.5. Plaskova N.S. Analysis of the activities of an insurance organization, magazine "Finance" No. 12, 2007, pp. 41-45
3.6. Samiev P.A. Structure and efficiency of investments of Russian insurers, magazine "Finance" No. 3 (2006), pp. 45-49
3.7. Spletukhov Yu.A. Analysis of the investment activity of insurers, magazine "Finance" No. 1 (2006), pp. 43-47
4. Electronic sources:
4.1. www.vsk.ru/ (official website of OJSC VSK Insurance House)
4.2. www.insur-info.ru/statistics (Website "Insurance today", section 'Insurers' -> 'Market dynamics')
4.3. www.raexpert.ru/database/companies/strahovoi_dom_vsk/ (website of the Expert RA rating agency)
In addition to mutual insurance companies that insure exclusively their members (clause 2 of article 25 of the Law of the Russian Federation "On the organization of insurance business in the Russian Federation" as amended on June 21, 2004)
Formulas for calculating insurance reserves are given in Appendix No. 2
An exhaustive list of assets accepted in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Finance dated August 8, 2005 No. 100-n to cover insurance reserves is set out in Appendix No. 1 (paragraph 6)
See Appendix No. 1a.
The volume of the investment life insurance market (LIS), for example, in Poland in 2003 amounted to 859 million dollars; in France, the size of this segment in monetary terms exceeded 14.2 billion euros. The volume of ILI contributions in Russia, according to 2005 data, was estimated at only 150-180 million dollars, and only by the end of 2008, according to the optimistic forecasts of the Expert RA rating agency, should it reach 700 million dollars. .
See Appendix #3
IFRS are rules that establish the requirements for the recognition, measurement and disclosure of financial and economic transactions for the preparation of financial statements of companies around the world.
This Regulation does not apply to insurance medical organizations in terms of operations on compulsory medical insurance.
See Appendix No. 4
Calculations are made on the basis of the data of the Profit and Loss Statement for 2006 (see Appendix No. 5)
Class A++ means that in the short term the Company is highly likely to ensure the timely fulfillment of all financial obligations, both current and arising in the course of insurance activities. In the medium term, there is a high probability of performance of obligations under insurance contracts even in the face of significant adverse changes in macroeconomic and market (insurance market) indicators.
Cash means funds in bank accounts and cash
Insurance Joint Stock Company "VSK" has been operating since 1992. The property insurance programs offered by the company allow you to reliably protect real estate and receive compensation in case of fire, explosion, flooding, theft and other unforeseen incidents.
Advantages of property insurance in VSK
At the end of 2015, the company ranked 4th among Russian insurance organizations in the property insurance segment, having collected 2,533,471 thousand rubles. premiums and paid 385,780 thousand rubles. for insured events.
The authorized capital of CJSC "VSK" is 3.65 billion rubles, and the reliability rating of the company is estimated by the "Expert RA" agency as exceptionally high "A ++" with a stable outlook. The company's insurance obligations in terms of making payments are guaranteed by the largest reinsurers, including Swiss Re, Hannover Re, Gen Re, Munich Re, SCOR. More than 14 million individuals and 200 thousand legal entities use the services of the VSK insurance company.
Types of property insurance programs
SO "VSK" offers a wide range of real estate insurance programs that differ in terms of insurance and the amount of insurance coverage.
"Classic building insurance"
The basic insurance program for suburban real estate, which guarantees compensation for losses associated with the occurrence of the following insured events:
- fire, explosion;
- flooding;
- accidents in heating systems, water supply, etc.;
- natural disasters;
- glass breakage;
- collision with vehicles;
- the fall of aircraft and their fragments;
- soil subsidence;
- defrosting engineering systems;
- causing harm to life, health or property of third parties.
The following items are covered under this program:
- House;
- internal and external finishing;
- engineering equipment;
- household property;
- Civil responsibility.
The client individually forms an insurance program for himself, choosing the necessary insurance objects, the list of insured risks and the amount of insurance compensation.
"Successful"
This insurance package is designed to insure suburban real estate worth up to 1 million rubles. All insurance conditions are listed in the classic program.
"Lucky Plus"
An insurance product designed to insure suburban real estate worth up to 3 million rubles. The insurance conditions are identical to those of the classic program.
"Maximum Protection"
A comprehensive apartment insurance program that guarantees coverage of costs associated with such insurance risks as:
- fire, explosion;
- exposure to water;
- accidents of engineering systems;
- natural disasters;
- illegal actions of third parties;
- short circuit of the wiring;
- collision with vehicles;
- terrorism.
The following objects can be insured under this program:
- internal and external finishing;
- engineering equipment;
- household property;
- civil liability.
"Full construction"
This program is intended for quick insurance of an apartment under a standard package. Insurance conditions completely duplicate the conditions of the previous program, except that the list of insured objects does not include the structural elements of the apartment.
"For rest time"
Short-term holiday apartment insurance program (from 1 to 9 months). The program provides insurance for the following objects:
- interior and exterior decoration of the apartment;
- engineering equipment;
- household property;
- civil liability.
The insured risks of the program include:
- fire, explosion;
- exposure to water;
- accidents of engineering systems;
- natural disasters;
- falling foreign objects;
- illegal actions of third parties (including terrorism);
- collision with vehicles;
- civil liability to neighbors.
"I rent"
This program is designed to insure rental apartments and guarantees compensation for losses associated with such insurance risks as:
- fire, explosion;
- natural disasters;
- flooding;
- accidents of engineering systems;
- falling foreign objects;
- collision with vehicles;
- illegal actions of third parties;
- causing damage to the property of third parties.
In accordance with the terms of the program, the following objects are subject to insurance:
- interior and exterior decoration of the apartment;
- engineering equipment;
- household property;
- Civil responsibility.
"Removing"
The program is designed to insure household property and liability to neighbors in case of living in a rented apartment. The insured risks include the risks listed in the "I rent" program.
"Investment apartment"
This program is designed for clients who expect a rise in prices on the real estate market in order to sell an apartment at a higher price. The set of covered insurance risks corresponds to the list of risks of the "Maximum Protection" program. The following objects are subject to insurance under the program:
- structural elements of the apartment;
- Civil responsibility.
The cost of property insurance programs
The table shows indicative data on the cost of property insurance in VSK IJSC as of the beginning of 2017.
| The name of the program |
Objects of insurance |
Sum insured, rub. |
Cost of insurance, rub./year |
| "Classic building insurance" |
|
No restrictions |
Calculated individually |
| "Maximum Protection" |
|
3 100 000
|
14 670
|
| "Full construction" |
|
700 000
|
3 330
|
| "I rent" |
400 000
|
2 160
|
|
| "Removing" |
|
400 000
|
2 133
|
| "Investment apartment" |
|
1 200 000
|
1 350
|
Page 2
The military insurance company is included in the list of insurers recommended for work with enterprises servicing government contracts. Moreover, VSK Insurance House is a repeated winner of the competition of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation for the right to insure its property interests.
After receiving a new version of the license, which combined all licensed types of insurance, VSK Insurance House offers its customers 103 insurance products.
Returning to the structure of the insurance portfolio, I would like to note that, excluding contracts for compulsory medical insurance, according to the results of the first half of 2007, the share of compulsory insurance is 38.74%; the share of voluntary insurance reaches almost 60%, and the share of incoming reinsurance (that is, contracts accepted from reinsurers for cession) barely exceeds 1.7%. The gap between VSK Insurance House and the undisputed leader - the Rosgosstrakh group of companies - in terms of the total contributions of policyholders (and reinsurers) is 268% (that is, the premiums received by Rosgosstrakh exceed the corresponding indicator of VSK by 2.68 times), however this does not prevent VSK for many years from taking a strong position in the first lines of the rating of the largest insurance companies in Russia (see Table No. 1).
According to Table No. 2, in the structure of voluntary insurance, almost 2/3 of the concluded contracts fall on property insurance. It is closely followed by personal insurance other than life insurance (19.4%). VSK's life insurance is only 0.46%, which is one of the lowest figures in this table. The remaining approximately 6% is accounted for by liability insurance.
An analysis of the dynamics of the structure of the insurance portfolio in terms of the loss ratio of each type of insurance separately allows us to draw conclusions about how competently the company's insurance portfolio is balanced, and about which types of insurance bring loss and which potential profit. The results obtained during the analysis are summarized in the table below:
Table number 3. Receipts and payments of VSK for 2005, 2006, 2007.
|
INDICATOR | |||
|
VOLUNTARY INSURANCE, thousand rubles |
|||
|
LIFE INSURANCE: Total insurance premiums (contributions) Insurance payments Loss ratio | |||
|
PERSONAL INSURANCE (except life insurance) Income Payouts Loss ratio | |||
|
PROPERTY INSURANCE Income Payouts Loss ratio | |||
|
LIABILITY INSURANCE Income Payouts Loss ratio | |||
|
MANDATORY INSURANCE, thousand rubles |
|||
|
PERSONAL INSURANCE OF PASSENGERS (TOURISTS, TOUR GUIDES) Income Payouts Loss ratio | |||
|
GOS. PERSONAL INSURANCE FOR STATE EMPLOYEES TAX. RF SERVICES Income Payouts Loss ratio | |||
|
GOS. INSURANCE OF MILITARY SERVICE SERVANTS AND EQUATED TO THEM IN MANDATORY. GOS. INSURANCE OF PERSONS Income Payouts Loss ratio | |||
|
CIVIL LIABILITY INSURANCE FOR VEHICLE OWNERS Income Payouts Loss ratio | |||
|
MANDATORY HEALTH INSURANCE | |||
|
Income Payouts Loss ratio | |||
Analysis of the financial activity of an insurance organization (on the example of JSC VSK Insurance House)
Economic characteristics of OJSC Insurance House VSK
JSC Insurance House VSK Since November 2001, the Military Insurance Company has been offering its services under a new trade name - Insurance House VSK (author's note) has been operating in the Russian insurance market since 1992 and is a universal insurer on a federal scale, providing insurance services to both legal entities and individuals. The main activities of the company are represented by compulsory state insurance of military personnel (in this type the company occupies a leading position), property insurance, OSAGO, personal insurance and life insurance.
The main shareholders of the Company include: LLC VSK-Liniya Zhizni, LLC Waid-Company, CJSC Base Holding, LLC Credo-TM, LLC Vek-B.
June 26, 2007 Rating agency "Expert RA" conducted an annual procedure for updating the reliability rating of VSK Insurance House. Based on the results of the study of the solvency and financial stability of the insurer, it was decided to maintain the highest reliability rating of the company at the level of A ++ "High level of reliability with positive prospects", assigned to the company five years ago by the Expert RA rating agency.
The main factors that allowed such a high assessment of the reliability of the insurer were: a high level of insurance portfolio balance, a large customer base, high liquidity of assets and profitability of the company, high quality of reinsurance protection and investment portfolio.
The company offers its clients more than 100 modern insurance products that are in steady demand from both individuals and legal entities, as well as from state authorities and local governments throughout the Russian Federation. More than 300 branches and departments of VSK Insurance House in all constituent entities of the Russian Federation allow the Company to promptly and efficiently support insurance contracts and settle losses throughout Russia, regardless of the place where the insurance contract was concluded. Among the company's clients are 14 federal ministries and departments, 70 thousand enterprises and organizations of all forms of ownership, more than 10 million Russians. The authorized capital of VSK Insurance House is 1.7 billion rubles.
VSK Insurance House has been among the leaders of the Russian insurance market for many years. According to the results of 2006, the company took the 6th place in terms of premiums (excluding obligatory medical insurance) among all Russian insurance companies.
Table number 1. Place "Insurance House VSK" in the list of the largest companies
|
Place in the list of the largest insurance companies |
||
The military insurance company is included in the list of insurers recommended for work with enterprises servicing government contracts. Moreover, VSK Insurance House is a repeated winner of the competition of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation for the right to insure its property interests.
After obtaining a new version of the license, license FSSN C No. 0621 77 dated 06/20/2006, which combined all licensed types of insurance, VSK Insurance House offers its customers 103 insurance products.
Returning to the structure of the insurance portfolio, I would like to note that, excluding contracts for compulsory medical insurance, according to the results of the first half of 2007, the share of compulsory insurance is 38.74%; the share of voluntary insurance reaches almost 60%, and the share of incoming reinsurance (that is, contracts accepted from reinsurers for cession) barely exceeds 1.7%. The gap between VSK Insurance House and the undisputed leader - the Rosgosstrakh group of companies - in terms of the total contributions of policyholders (and reinsurers) is 268% (that is, the premiums received by Rosgosstrakh exceed the corresponding indicator of VSK by 2.68 times), however this does not prevent VSK for many years from taking a strong position in the first lines of the rating of the largest insurance companies in Russia (see Table No. 1).
According to the data in Table No. 2, see Appendix No. 6, in the structure of voluntary insurance, almost 2/3 of the concluded contracts fall on property insurance. It is closely followed by personal insurance other than life insurance (19.4%). VSK's life insurance is only 0.46%, which is one of the lowest figures in this table. The remaining approximately 6% is accounted for by liability insurance.
Analysis of the dynamics of the structure of the insurance portfolio in terms of the loss ratio The loss ratio is found as the ratio of the amount of insurance compensation to the amount of insurance premium. The more this coefficient tends to zero, the higher the profitability of the corresponding type of insurance. Each type of insurance separately allows you to draw conclusions about how competently the company's insurance portfolio is balanced, and about which types of insurance bring loss and which potential profit. The results obtained during the analysis are summarized in the table below:
Table number 3. Receipts and payments of VSK for 2005, 2006, 2007.
|
INDICATOR |
|||
|
VOLUNTARY INSURANCE, thousand rubles |
|||
|
LIFE INSURANCE: Total insurance premiums (contributions) Insurance payments Loss ratio |
|||
|
PERSONAL INSURANCE (except life insurance) Income Payouts Loss ratio |
|||
|
PROPERTY INSURANCE Income Payouts Loss ratio |
|||
|
LIABILITY INSURANCE Income Payouts Loss ratio |
|||
|
MANDATORY INSURANCE, thousand rubles |
|||
|
PERSONAL INSURANCE OF PASSENGERS (TOURISTS, TOUR GUIDES) Income Payouts Loss ratio |
|||
|
GOS. PERSONAL INSURANCE FOR STATE EMPLOYEES TAX. RF SERVICES Income Payouts Loss ratio |
|||
|
GOS. INSURANCE OF MILITARY SERVICE SERVANTS AND EQUATED TO THEM IN MANDATORY. GOS. INSURANCE OF PERSONS Income Payouts Loss ratio |
|||
|
CIVIL LIABILITY INSURANCE FOR VEHICLE OWNERS Income Payouts Loss ratio |
|||
|
MANDATORY HEALTH INSURANCE |
|||
|
Income Payouts Loss ratio |
In terms of total assets, VSK Insurance House ranks 7th, behind such well-known insurance companies as: Rosgosstrakh, Ingosstrakh, SOGAZ, Kapital, RESO-Garantia and ROSNO, see Appendix No. 6, table No. 4.
The analysis of the dynamics of the financial performance of VSK reflects a qualitative progressive movement towards increasing the profitability of its insurance operations, as evidenced by the value of the Company's net profit, which steadily demonstrates a confident upward trend (see Table No. 5).
5. Key financial indicators of VSK Insurance House
Unfortunately, at the time of writing this term paper, VSK has not yet published official financial statements for 2007, therefore, there are no reliable data on the amount of profit received for the previous reporting period, as well as information on other financial indicators of the Company for 2007. Naturally, this does not allow to fully compare the current financial position of VSK with the previously achieved results, however, based on the positive dynamics of past years, it is possible to predict with a high degree of confidence that the emerging favorable trend towards improving the financial stability and solvency of the Company will continue. This contributes, first of all, to the efficient and rational use of the financial resources of the company in order to most fully realize the interests of insurers.