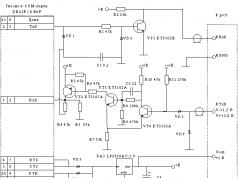
Charger for UC3842/UC3843 with voltage and current regulation
The charger described here is designed to charge lead-acid batteries. There are two adjustments: voltage and current. When one of these adjustments is triggered, the corresponding LED lights up, which is very convenient. The circuit and printed circuit board were taken from the radiocat forum:
The device is assembled on the common UC3842/UC3843 microcircuit. We have already described its use in power supplies. In this circuit, adjustment occurs at 1 pin. The power part is standard, the microcircuit is powered from a separate winding on the return stroke.

click to enlarge
Voltage and current adjustments were made according to a diagram from forum member FolksDoich. The TL431 contains a reference voltage source. Voltage and current adjustments are made on the halves of the LM358 op-amp. If you use LEDs as VD6 and VD7, they will indicate the current adjustment by their glow, which can be useful. For example, if the VD7 LED is lit, then current limitation occurs. The same with VD6, but in terms of voltage.
This circuit is designed to charge the battery with a current of up to 6 amperes, so it is proposed to parallel four electrolytic capacitors at the output, because one at high current will not work for long. Of course they all have to be LOW ESR.
How can this scheme be improved? If you use it to assemble not a charger, but a power supply, adjustable within certain limits, then you can make the usual improvements described in the previous article. In particular, you can power the UC3842/UC3843 microcircuit in direct mode, and use a separate transformer winding to power the op-amp and PC817. All this is justified only if it is necessary to expand the voltage regulation range.
In addition to LEDs, the circuit can be supplemented with an ammeter and voltmeter, both pointer and digital devices that show the value of voltage and current, and, possibly, also calculate the load power and control the cooling fan.
If you choose the right power field-effect transistor, its heating should be insignificant. It should be mentioned that in the diagram they forgot to draw a 2.2 nF capacitor between the hot and cold parts.

PCB: charger_12v_6a.lay6

There is another variation of this scheme in this form:

click to enlarge
Printed circuit boards from FolksDoich for devices of different power, the second board - up to 10 amperes. The UC384x chip is located on a separate small board, mounted vertically on the main one.

Every car enthusiast has for 12 V batteries. All these old chargers work and perform their functions with varying degrees of success, but they have a common drawback - they are too large in size and weight. This is not surprising, because a 200-watt power transformer alone can weigh up to 5 kg. That’s why I decided to assemble a pulse charger for a car battery. On the Internet, or rather on the Kazus forum, I found a diagram of this charger.
Schematic diagram of the charger - click to increase size
Assembled, works great! I charged a car battery, set the charger to 14.8 V and a current of about 6 A, there is no overcharging or undercharging, when the voltage at the battery terminals reaches 14.8 V, the charging current drops automatically. I also charged the gel lead battery from the PC's uninterruptible power supply - it was fine. This charger is not afraid of short circuits at the output. But you need to make protection against polarity reversal, I did it myself on the relay.

The printed circuit board, datasheets for some radio elements and other files can be found on the forum.

In general, I advise everyone to do it, since this charger has many advantages: small size, the base of radio elements is not in short supply, you can buy a lot of things, including a ready-made pulse transformer. I bought it myself in an online store - they sent it quickly and cheaply. I’ll make a reservation right away, instead of a VD6 Schottky diode (thermal stabilization), I just put a 100 Ohm resistance, a charger, and it works great with it! I assembled and tested the circuit:Demo.
Any developer may be faced with the problem of creating a simple and reliable power source for the device he is designing. Currently, there are quite simple circuit solutions and the corresponding element base that make it possible to create switching power supplies using a minimum number of elements. We present to your attention a description of one of the options for a simple network switching power supply. The power supply is based on the UC3842 chip. This microcircuit has become widespread since the second half of the 90s. It implements many different power supplies for TVs, faxes, VCRs and other equipment. The UC3842 gained such popularity due to its low cost, high reliability, simplicity of circuit design and minimal required wiring.
At the input of the power supply (Fig. 5.34), there is a mains voltage rectifier, including a 5 A fuse FU1, a 275 V varistor P1 to protect the power supply from excess voltage in the network, a capacitor C1, a 4.7 Ohm thermistor R1, diode bridge VD1...VD4 on FR157 diodes (2 A, 600 V) and filter capacitor C2 (220 µF at 400 V). Thermistor R1 in a cold state has a resistance of 4.7 Ohms, and when the power is turned on, the charge current of capacitor C2 is limited by this resistance. Next, the resistor heats up due to the current passing through it, and its resistance drops to tenths of an ohm. However, it has virtually no effect on the further operation of the circuit.
Resistor R7 provides power to the IC during the startup period of the power supply. Winding II of transformer T1, diode VD6, capacitor C8, resistor R6 and diode VD5 form the so-called feedback loop (Loop Feedback), which provides power to the IC in operating mode, and due to which the output voltages are stabilized. Capacitor C7 is a power filter for the IC. Elements R4, C5 make up the timing chain for the internal pulse generator of the IC.
The converter transformer is wound on a ferrite core with an ETD39 frame from Siemens+Matsushita. This set features a round center ferrite core and plenty of space for thick wires. The plastic frame has leads for eight windings.

The transformer is assembled using special mounting springs. Particular attention should be paid to the thorough insulation of each layer of windings using varnished cloth, and several layers of varnished cloth should be laid between windings I, II and the remaining windings, ensuring reliable insulation of the output part of the circuit from the network. The windings should be wound in a “turn to turn” manner, without twisting the wires. Naturally, the wires of adjacent turns and loops should not be allowed to overlap. The winding data of the transformer are given in table. 5.5.
The output part of the power supply is shown in Fig. 1. It is galvanically isolated from the input part and includes three functionally identical blocks, consisting of a rectifier, an LC filter and a linear stabilizer. The first block - a 5 V (5 A) stabilizer - is made on the A2 SD1083/84 (DV, LT) linear stabilizer IC. This chip has a switching circuit, housing and parameters similar to the KPI42EH12 MS, however, the operating current is 7.5 A for SD1083 and 5 A for SD1084.
The second block - stabilizer +12/15 V (1 A) - is made on the IC linear stabilizer A3 7812 (12 V) or 7815 (15 V). Domestic analogues of these ICs are KR142EN8 with the corresponding letters (B, V), as well as Kl 157EH12/15. The third block - stabilizer -12/15 V (1 A) - is made on the IC linear stabilizer A4 7912 (12 V) or 7915 (15 V). Domestic analogues of these ICs are K1162EH12J5.
Resistors R14, R17, R18 are necessary to dampen excess voltage at idle. Capacitors C12, C20, C25 were selected with a voltage reserve due to a possible increase in voltage at idle. It is recommended to use capacitors C17, C18, C23, C28 type K53-1A or K53-4A. All ICs are installed on individual plate radiators with an area of at least 5 cm2.
Table 5.5
Contacts | Purpose | Limit current, A | Open circuit voltage, V |
||
Primary | 4ХПЭВ-2, 0.15 | ||||
Feedback | ZxPEV-2, 0.15 | ||||
+5 V output | 4ХПЭВ-2, 0.35 | ||||
Output +15/12 V | 2ХПЭВ-2, 0.35 | ||||
Output - 15/12 V | 2ХПЭВ-2, 0.35 |
Structurally, the power supply is made in the form of one single-sided printed circuit board installed in the case from the power supply of a personal computer. The fan and network input connectors are used for their intended purpose. The fan is connected to a +12/15V stabilizer, although it is possible to make an additional +12V rectifier or stabilizer without much filtering.
All radiators are installed vertically, perpendicular to the air flow exiting through the fan. Four wires 30...45 mm long are connected to the outputs of the stabilizers; each set of output wires is crimped with special plastic clamps-straps into a separate bundle and is equipped with a connector of the same type that is used in a personal computer to connect various peripheral devices.
Stabilization parameters are determined by the parameters of the stabilizer ICs. Ripple voltages are determined by the parameters of the converter itself and are approximately 0.05% for each stabilizer.
Sometimes the battery in a car discharges very quickly. As a result, you have to use various devices in order to start the car. Today, pulse chargers are very popular. Their main manufacturers are considered to be Sonar and Bosch.
However, some people cannot afford to buy these devices because they are expensive. In such a situation, you can try to assemble the model yourself. In order to understand pulse charging, you need to look at the standard circuit diagram of the device.
Diagram of a conventional charging model
They include a transformer with a magnetic core, as well as transistors. To adjust the voltage, regulators are used that are connected to the modulators. Also, the pulse charger circuit includes special triggers. Their main task is to increase voltage stability. There are clamps for connecting the device to the charger. Electricity itself is supplied directly through the cable.
6 V device: diagram and instructions
Making a 6 V pulse is quite simple. For this purpose, a small platform is built for the transformer. It is also necessary to prepare insulators in advance. The transformer itself is often used as a power type. Its current conductivity is on average 6 microns. It is also important to note that the system is able to cope with increased negative resistance. Oscillators are used of the pulse type.
For normal operation of the device you will also need a linear tetrode. It should be selected with a lining. Some experts strongly advise using filters. In this way, it is possible to stabilize the voltage when network overloads exceed 20 V. The operating instructions for the pulse charger are very simple. To connect the device you will need clamps. In this case, the plug should be plugged into the socket.
How to make a 10V charger?
Pulse charger circuits for car batteries include: You should start assembling the model by finding a high-quality transformer. In this case, a powerful magnetic circuit will be required. Pulse circuits also include insulators. Many experts install regulators with modulators. Thus, the input voltage can be decreased or increased. In this case, much depends on the power of the car battery.
Tetrodes themselves are used only with plates. Resistors are used as expansion type. Some modifications have triggers. These elements make it possible to cope with short-wave interference that occurs in an AC network when the clock frequency level rises sharply.

Reviews of 12 V models
Pulse chargers for 12 V batteries are in great demand these days. If you believe the reviews of experts, step-down transformers are used to assemble the model. In this case, an oscillator will be required with high current conductivity. It is also important to note that only trimmer triggers are suitable for the models.
Tetrodes, in turn, are used of the linear type. The permissible overload parameter in devices does not exceed 15 W. The rated current is on average 4 A. The magnetic cores of the models are installed behind the transformers. It is necessary to select high-quality insulators especially for them. To connect the charger you will need clamps. If you believe the experts, you should take into account that making them yourself will be quite difficult.

Single-phase modifications
You can make a single-phase pulse charger with your own hands using a step-down transformer. Regulators are also used to assemble them. Modulators in this case are suitable only for the switched type. The triggers themselves are installed with insulators. Some experts also recommend using rubber pads.
Tetrodes are selected with high throughput. The regulators are installed above the modulator. In this case, three resistors are required. they must withstand 10 V. To connect the prior, you will need metal clamps.
Two-phase devices
The two-phase automatic pulse charger is assembled quite simply. However, in this situation you cannot do without Also, only expansion resistors are used for assembly. The input voltage in the network, as a rule, does not exceed 12 V. Thyristors for models are used with insulators. The modulator is directly installed on the lining. In this case, the regulator is of the rotary type. To overcome interference, magnetic circuits are used. Devices of this type are connected via a wire. They can also work from a 220 V network. Clamps are required to connect to batteries.
Reviews of three-phase modification
The three-phase pulse charger has good reviews from experts. The advantage of the models is that they are able to withstand more overload. In this case, the magnetic cores are installed with a conductivity of 6 microns. Linear resistors are used to stabilize the output voltage. In some cases, code analogues are also installed. However, their service life is not long.
It is also important to note that the maximum voltage in devices should be adjusted using modulators. They are installed immediately behind the transformers. To overcome magnetic interference, tuning triggers are used. Many experts recommend installing filters for assembling chargers. These elements will help to significantly reduce the negative resistance parameter in the circuit.

Application of pulse transformer PP20
Car chargers (pulse) with these transformers are common. First of all, it should be noted that their rated voltage does not exceed 10 V. The operating current parameter is on average 3 A. Oscillators for device assembly are often used with low conductivity.
In this case, magnetic cores are installed on pads. Expansion resistors are often used. Modulators are standardly used to adjust the rated voltage. Some modifications use trigger blocks. For normal operation of the system, linear tetrodes are also indispensable. It is better to buy clamps for the device separately. Making them yourself is very difficult.

Use of PP22 transformers
Chargers (pulse) with these transformers are quite common. In order to assemble the modification yourself, you will need to find a high-quality oscillator. Also, the transformer will only work with a 3 micron magnetic core. In this case, expansion type resistors are most suitable. However, it is important to install the regulator first. For this purpose, you need to use a switched modulator, which is installed on the lining.
Next, it is important to deal with the semiconductor transistor. In order to avoid short circuits, many experts recommend using stabilizers. There are many single-pole modifications on the market. In this case, the rated voltage will be around 5 V. The operating current is approximately 4 A.

Charging equipment with transformer PP30
In order to assemble chargers (pulse) with the indicated transformers, you will need a powerful magnetic circuit. In this case, it is more expedient to use the oscillator at 2 microns. The negative resistance parameter in the circuit must be higher than 3 ohms. A magnetic core is installed next to the transformer. To connect the modulator you will need two contacts. It is also important to note that it is more advisable to use rotary type regulators.
Many experts recommend installing resistors on the plate. All this will significantly reduce the incidence of short circuits. To stabilize the voltage, filters are used as standard. Trigger blocks with these zooms are most often used of the tuning type. However, nowadays they are difficult to find. Most often, it is operational analogues that come across. They can withstand a nominal voltage in the circuit of 15 V.
Application of isolation transformers
Isolation transformers are very rare. Their main problem lies in the low current conductivity. It is also important to note that they are only capable of working with code resistors, which are expensive in the store. However, the models have advantages. First of all, this concerns the increased rated voltage in the circuit. Thus, charging a car battery will not take much time.
It should also be noted that these transformers are compact and will not take up much space in the car. In this case, thyristors are used only of the wave type. They are most often installed on covers. An insulator is used to solder the modulator. Many experts strongly recommend using semiconductor type transistors. In the store they are presented with different conductivities. As a result, the negative resistance parameter in the circuit should not exceed 8 ohms. Clamps are used to connect the device to car batteries.
Model with transformer KU2
Transformers of this series are large in size and can only work with 4 micron magnetic cores. All this suggests that triggers will be required for normal operation of the device. Using these devices you can stabilize the output voltage. You will also need to install two filters near the transformers. Some experts strongly recommend using zener diodes. However, these devices can only operate under moderate network congestion.
In this case, resistors can be safely used of the expansion type. Switched modulators are used to regulate the output voltage. The regulators should be installed directly through the throttle. If you believe the reviews of experts, then for safe use the transformer should be placed on a lining. In this case, two insulators will be required. Transistors are most often used of the semiconductor type.
Charging equipment with transformer KU5
Chargers (pulse) with the specified transformers are not in great demand. This is primarily caused by low output voltage. So it takes a lot of time. However, if you use a powerful oscillator, the situation can be improved a little. Also, many experts recommend installing expansion resistors.
In this case, the modulator is suitable only for the switched type. Some models have single-pole zener diodes. However, in this situation, the transformer may not be able to withstand the excessive load. The trigger is often used as a tuning type. To combat short-wave interference, you cannot do without filters. Clamps are used to connect the device to the car battery.
Twin throttle model
Chargers (pulse) with dual chokes allow the use of more than two modulators. Thus, digital voltage regulators can be installed. In this case, transformers are most often selected of the step-down type. The oscillators themselves are used at 3 microns. Many experts recommend installing resistors of the expansion type. In turn, code analogues will not last long. Thyristor blocks are used of both wave and operational types.

Summarizing
Considering all of the above, it should be noted that three-phase modifications are considered the most popular. In order to assemble them, you need to know how to use a blowtorch. Parts for the device must be purchased in specialized stores. You should also remember safety precautions when connecting the device to the network.
A fairly simple diagram of a laboratory power supply or charger, for example, for a battery. It is implemented quite simply, as can be seen from the diagram. A unique feature of the circuit is the fact that it is possible to adjust not only the voltage, but also the current, which even many commercial chargers do not have.
The circuit is built on 4 transistors, the main role is played by the power transistor V4 (see diagram), in this case the 2N3055 is taken, which can easily be replaced with the domestic analogue of the KT803. In general, the output power of the device and the possible maximum current will ultimately depend on this transistor, so if you need higher currents, just replace V4 with a more powerful transistor. It is clear that the power transistor must be installed on the heat sink.

Another feature of such a charger is its cost-effectiveness; all the elements will cost you 100-200 rubles. When using the 2N3055 transistor shown in the diagram or its domestic analogue KT803, the current can be accelerated to 6 A. Although the transistor itself, according to its characteristics, can handle 15 A, we do not recommend loading it to such an extent. Limiting resistor R2 with a nominal value of 1 Ohm is taken with a power of at least 5 W, for the remaining resistors 0.25 W is enough.

So far we have considered only the part of the circuit responsible for regulating voltage and current. However, it is clear that the device must be powered with something, especially with a constant voltage, so a power source is needed capable of delivering sufficient output power, with a constant voltage of up to 16 V, and a current of up to 10 A. In principle, for power supply from a 220V, 50 Hz network it was It would be enough to wind up a step-down transformer and put a bridge at its output. However, even a superficial calculation shows that a transformer is needed with a power of up to 200 W.

The core for it can be obtained from old tube TVs, but not everyone has this opportunity, and if you buy it, it will be quite expensive. Plus, using such a circuit will greatly increase the dimensions of the device itself. Therefore, to reduce the dimensions of the transformer, we will use the presented circuit of a switching power supply increasing the frequency to 50 kHz, which ultimately leads to a reduction in the dimensions of the output transformer.

The only thing is that the transformer was taken from a computer power supply designed for bipolar voltage; we understand that one polarity is enough. The ratings and types of elements are indicated in the diagram.

The circuit has short circuit protection; when it is triggered, the LED lights up, which is also very useful when working with a source. When winding an output transformer, the primary winding consists of 37 turns with a wire with a cross-section of at least 0.5 mm?, the secondary winding consists of 6 turns with a cross-section of at least 2.5 mm?, which can be wound with three cores with a wire of 0.8 mm?. The core can be taken from any computer power supply. The diodes of the rectifier bridge at the output must be high-frequency, we recommend taking KD213.

To adjust the limiting current (protection operation), it is enough to change the value of resistor R10; the lower its value, the greater the protection operation current will be and vice versa. All transistors involved in the circuit must be installed on separate heat sinks or isolated from each other.

After the first rectifier bridge, filter capacitors should be rated from 100 to 470 µF with permissible voltage values up to 400 V.